
How to solve the thread priority problem in Java
In Java multi-threaded programming, we can adjust the execution order of threads by setting the priority of the thread. Thread priority is an integer ranging from 1 to 10, where 1 is the lowest priority and 10 is the highest priority. The priority of a thread can be used to express the relative importance of a thread relative to other threads when competing for CPU resources.
However, in actual applications, we rarely rely directly on thread priorities to control the execution order of threads, because thread priorities may behave differently in different operating systems and JVM implementations. In order to avoid the uncertainty caused by thread priority issues, we should use other methods to control the execution order of threads.
The following are some commonly used methods to solve thread priority issues in Java:
- Use the Thread.sleep() method: By making high-priority threads sleep for a period of time, let Low priority threads have a chance to execute. For example, we can add a Thread.sleep() statement to the task of a high-priority thread.
Thread highPriorityThread = new Thread(() -> {
// 高优先级线程的任务
Thread.sleep(1000);
});
Thread lowPriorityThread = new Thread(() -> {
// 低优先级线程的任务
});
highPriorityThread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
lowPriorityThread.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
highPriorityThread.start();
lowPriorityThread.start();- Use the wait() and notify() methods of the Object class: By using the wait() and notify() methods of the object, we can control the execution order of the threads. A high-priority thread can enter a waiting state while a low-priority thread is running, and then wake up the high-priority thread after the low-priority thread completes. For example:
Object lock = new Object();
Thread highPriorityThread = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
// 高优先级线程的任务
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Thread lowPriorityThread = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
// 低优先级线程的任务
lock.notify();
}
});
highPriorityThread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
lowPriorityThread.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
highPriorityThread.start();
lowPriorityThread.start();- Use the thread's join() method: By using the thread's join() method, we can wait for other threads to complete their execution before continuing. The high-priority thread can wait when the low-priority thread calls the join() method until the low-priority thread completes execution before continuing. For example:
Thread highPriorityThread = new Thread(() -> {
// 高优先级线程的任务
});
Thread lowPriorityThread = new Thread(() -> {
// 低优先级线程的任务
});
highPriorityThread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
lowPriorityThread.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
lowPriorityThread.start();
lowPriorityThread.join();
highPriorityThread.start();In summary, although we can use thread priority to control the execution order of threads, in practical applications, we should avoid relying directly on thread priority. By using other methods such as Thread.sleep(), the wait() and notify() methods of the Object class, and the thread's join() method, we can better control the execution order of threads and avoid inconsistencies caused by thread priority issues. Certainty.
The above is the detailed content of How to solve thread priority issues in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 修复:Sysprep 无法验证 Windows 11 安装May 19, 2023 am 10:15 AM
修复:Sysprep 无法验证 Windows 11 安装May 19, 2023 am 10:15 AMSysprep问题可能出现在Windows11、10和8平台上。出现该问题时,Sysprep命令不会按预期运行和验证安装。如果您需要修复Sysprep问题,请查看下面的Windows11/10解决方案。Sysprep错误是如何在Windows中出现的?Sysprep无法验证您的Windows安装错误自Windows8以来一直存在。该问题通常是由于用户安装的UWP应用程序而出现的。许多用户已确认他们通过卸载从MSStore安装的某些UWP应用程序解决了此问题。如果缺少应该与Windows一起预安装
 重置管理员权限: 如何重新获得管理员权限?Apr 23, 2023 pm 10:10 PM
重置管理员权限: 如何重新获得管理员权限?Apr 23, 2023 pm 10:10 PM您将找到多个用户报告,确认NETHELPMSG2221错误代码。当您的帐户不再是管理员时,就会显示此信息。根据用户的说法,他们的帐户自动被撤销了管理员权限。如果您也遇到此问题,我们建议您应用指南中的解决方案并修复NETHELPMSG2221错误。您可以通过多种方式将管理员权限恢复到您的帐户。让我们直接进入它们。什么是NETHELPMSG2221错误?当您不是PC的管理员时,无法使用提升的程序。因此,例如,你将无法在电脑上运行命令提示符、WindowsPowerShell或任
 如何解决Windows更新错误代码0x8024800c?Apr 21, 2023 am 09:55 AM
如何解决Windows更新错误代码0x8024800c?Apr 21, 2023 am 09:55 AM什么原因导致WindowsUpdate错误0x8024800c?导致WindowsUpdate错误的原因0x8024800c尚不完全清楚。但是,此问题可能与其他更新错误具有类似的原因。以下是一些潜在的0x8024800c错误原因:损坏的系统文件–某些系统文件需要修复。不同步的软件分发缓存–软件分发数据存储不同步,这意味着此错误是超时问题(它有一个WU_E_DS_LOCKTIMEOUTEXPIRED结果字符串)。损坏的WindowsUpdate组件-错误0x8024800c是由错误的Win
 如何解决您的 Office 许可证有问题May 20, 2023 pm 02:08 PM
如何解决您的 Office 许可证有问题May 20, 2023 pm 02:08 PMMSOffice产品是任何Windows系统上用于创建Word、Excel表格等文档的应用程序的绝佳选择。但是您需要从Microsoft购买Office产品的有效许可证,并且必须激活它才能使其有效工作.最近,许多Windows用户报告说,每当他们启动任何Office产品(如Word、Excel等)时,他们都会收到一条警告消息,上面写着“您的Office许可证存在问题,并要求用户获取正版Office许可证”。一些用户不假思索,就去微软购买了Office产品的许可证
 WWAHost.exe 进程高磁盘、CPU 或内存使用修复Apr 14, 2023 pm 04:43 PM
WWAHost.exe 进程高磁盘、CPU 或内存使用修复Apr 14, 2023 pm 04:43 PM许多用户在系统变慢时报告任务管理器中存在WWAHost.exe进程。WWAHost.exe进程会占用大量系统资源,例如内存、CPU或磁盘,进而降低PC的速度。因此,每当您发现您的系统与以前相比变得缓慢时,请打开任务管理器,您会在那里找到这个WWAHost.exe进程。通常,已观察到启动任何应用程序(如Mail应用程序)会启动WWAHost.exe进程,或者它可能会自行开始执行,而无需在您的WindowsPC上进行任何外部输入。此进程是安全有效的Microsoft程序,是Wi
 如何在iPhone上修复iTunes错误1667Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:58 PM
如何在iPhone上修复iTunes错误1667Apr 17, 2023 pm 09:58 PM大多数人作为备份实践将他们的文件从iPhone传输到PC/Mac,以防由于某些明显的原因而丢失。为此,他们必须通过避雷线将iPhone连接到PC/Mac。许多iPhone用户在尝试将iPhone连接到计算机以在它们之间同步文件时遇到错误1667。此错误背后有相当潜在的原因,可能是计算机或iPhone中的内部故障,闪电电缆损坏或损坏,用于同步文件的过时的iTunes应用程序,防病毒软件产生问题,不更新计算机的操作系统等。在这篇文章中,我们将向您解释如何使用以下给定的解决方案轻松有效地解决此错误。初
 Excel中如何根据数据大小自动调整行和列May 20, 2023 pm 07:56 PM
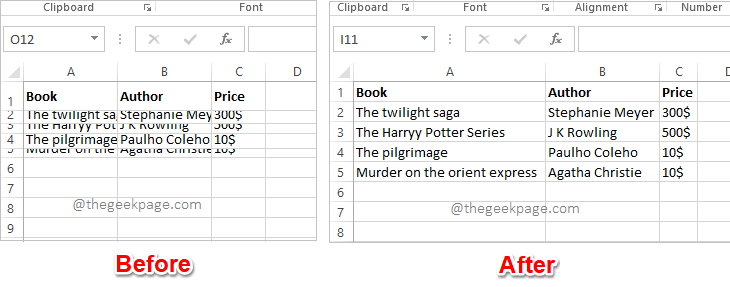
Excel中如何根据数据大小自动调整行和列May 20, 2023 pm 07:56 PM你有一个紧迫的截止日期,你即将提交你的工作,那时你注意到你的Excel工作表不整洁。行和列的高度和宽度不同,大部分数据是重叠的,无法完美查看数据。根据内容手动调整行和列的高度和宽度确实会花费大量时间,当然不建议这样做。顺便说一句,当你可以通过一些简单的点击或按键来自动化整个事情时,你为什么还要考虑手动做呢?在本文中,我们详细解释了如何通过以下3种不同的解决方案轻松地在Excel工作表中自动调整行高或列宽。从现在开始,您可以选择自己喜欢的解决方案并成为Excel任务的高手!解决方案1:通过
![修复:Windows 11 不关闭显示 [6 个简单的解决方案]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/887/227/168171288789845.jpg) 修复:Windows 11 不关闭显示 [6 个简单的解决方案]Apr 17, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
修复:Windows 11 不关闭显示 [6 个简单的解决方案]Apr 17, 2023 pm 02:28 PMWindows11可以选择在一段时间不活动后关闭显示器。当用户离开计算机并且不手动使其进入睡眠状态时,此功能可以节省电量。用户报告了即使在设置的持续时间之后他们的显示器也没有关闭的问题。幸运的是,有一些简单的解决方案可以解决这个问题。如果您的Windows11显示屏在设置时间后未关闭,则可能是由于应用程序或外部设备有问题。继续阅读本文以找到解决方案。如何调整睡眠和屏幕设置?单击开始并转到设置(或按Windows+I)。在系统下转到电源和电池。在屏幕和睡眠下,调整您希望显示器进入睡眠或关闭的时


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






