
Using an SSD drive leaves you with the constant worry of losing your data and being unable to recover it. However, Windows allows you to achieve optimal performance by executing TRIM commands that write only necessary data without having to manage old data blocks.
To do this, you need to make sure your SSD supports TRIM and enable it in your operating system.
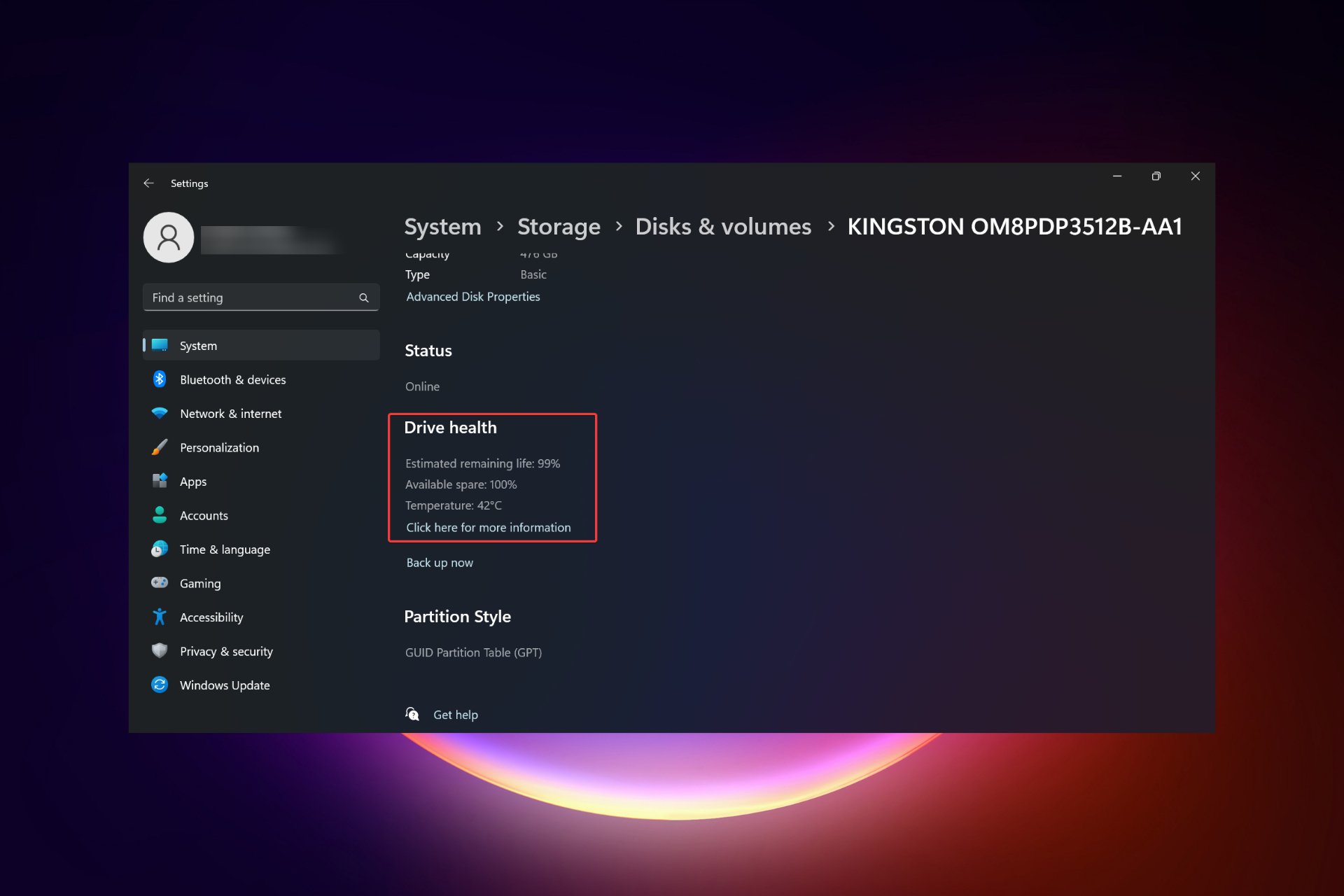
How to check if TRIM is enabled?
In most cases, the TRIM feature is enabled by default in modern SSDs. But to make sure this is checked out, you can run the command with administrative rights.
Just open an elevated command prompt, run the fsutil Behavioral Query DisableDeleteNotify command and your SSD will be listed. 0 means enabled, 1 means disabled.
How to turn on TRIM in Windows 11?
By using the Command Prompt
- key, type cmd and click Run as administrator. Windows
- Type the following command and click: Enter
<strong>fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify 0</strong>
- Restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
How to disable TRIM in Windows 11?
While enabling TRIM can extend the life of your SSD, sometimes older hardware tends to experience slower boot times due to this feature.
In this case it is best to disable TRIM. Just reverse engineer the above steps and replace the value data with 1.
How do I improve my SSD performance in Windows 11?
- Run Disk Cleanup Often – If your SSD is slow, this tool can help you remove unnecessary files from your PC and free up space for great performance.
- Check the disk for errors – You must check your hard drive for errors using a utility such as CHKDSK, which scans the drive for bad sectors and repairs them if necessary.
- Disable Hibernation – Hibernation is a power saving feature, but it is not compatible with most SSDs. Since it can slow them down significantly, it's best to turn hibernation off.
- Optimization Software – With the right SSD optimization tool, you can ensure that your disk drive is always performing at its best.
Solid-state drives are extremely fast, but they are not immune to the same problems as hard drives. Unfortunately, they have a limited number of reads and writes before they wear out. In fact, if not properly maintained, their performance degradation will be more severe over time.
Luckily, you can squeeze more life out of them by optimizing them using the tips above. As a rule of thumb, it’s always a good idea to enable TRIM as it’s an essential feature to ensure your SSD runs at optimal speed and life expectancy.
After all, you want your SSD to last as long as possible before being forced to upgrade. Hopefully these pointers help get TRIM working on your drive.
The above is the detailed content of How to enable and disable TRIM on Windows 11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 在 Windows 11上检查 SSD 运行状况的 4 种方法Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:49 PM
在 Windows 11上检查 SSD 运行状况的 4 种方法Sep 27, 2023 pm 09:49 PM由于其快速的读取、写入和访问速度,SSD正在迅速取代HDD,但即使它们更可靠,您仍然需要在Windows11中检查SSD的运行状况。我可以检查固态硬盘的运行状况吗?当然,您可以,而且应该这样做,因为它们的读/写周期有限。SLCNAND闪存SSD是目前最流行的,可以处理大约50,000到100,000个写入周期。尽管如此,在本文中,您将学习如何在Windows11上检查SSD的运行状况并延长其生命周期。如何检查Windows11上的SSD运行状况?首先,以下是识别即将发生故障的SSD的方法:您开始
 修复:任务栏溢出在 Windows 11 上不起作用Jul 18, 2023 am 09:41 AM
修复:任务栏溢出在 Windows 11 上不起作用Jul 18, 2023 am 09:41 AM当Windows11任务栏溢出功能停止工作时,用户将丢失重要的自定义选项。这是因为该功能允许您将尽可能多的应用程序添加到任务栏并轻松启动它们。虽然这个问题可能令人沮丧,但并不是最难解决的。在本综合指南中,我们准备了万无一失的方法,以使任务栏溢出功能再次正常工作。为什么任务栏溢出在Windows11上不起作用?正如用户报告的那样,有几个因素可能导致任务栏溢出在Windows11上不起作用。以下是一些值得注意的原因:过时的PC:过时的操作系统是此问题的主要原因。如果您使用高于Windows11预览体
 Windows11中如何检查 SSD 运行状况?Win11上检查 SSD 运行状况的方法Feb 14, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Windows11中如何检查 SSD 运行状况?Win11上检查 SSD 运行状况的方法Feb 14, 2024 pm 08:21 PMWindows11中如何检查SSD运行状况?对于其快速的读取、写入和访问速度,SSD正在迅速取代HDD,但即使它们更可靠,您仍然需要在Windows11中检查SSD的运行状况。怎么去操作呢?本篇教程小编就来为大家分享一下方法吧。方法一:使用WMIC1、使用按键组合Win+R,键入wmic,然后按或单击“确定”。Enter2、现在,键入或粘贴以下命令以检查SSD运行状况:diskdrivegetstatus如果您收到“状态:正常”消息,则您的SSD驱动器运行正
 如何在iOS 17上启用和使用屏幕距离Jun 29, 2023 pm 01:37 PM
如何在iOS 17上启用和使用屏幕距离Jun 29, 2023 pm 01:37 PM在其年度开发者大会上,苹果推出了下一代操作系统来为其设备套件提供支持。像往常一样,iOS17是所有主要变化的核心,具有实时语音邮件、消息转录、实时贴纸、待机模式、全屏实时活动、交互式小部件等功能。在这些新增功能中脱颖而出的功能之一是“屏幕距离”。这是一项以健康为中心的功能,专注于防止iPhone屏幕上的眼睛疲劳和近视。在这篇文章中,我们将解释什么是屏幕距离以及如何在iOS17中启用它。什么是iOS17上的屏幕距离?作为iOS17推出的新健康功能的一部分,Apple提供了屏幕距离功能,以帮助用户预
 金士顿 NV3 M.2 SSD 国行开售:可选 512G-2TB、读速 5000 MB/s,319 元起Aug 12, 2024 pm 01:36 PM
金士顿 NV3 M.2 SSD 国行开售:可选 512G-2TB、读速 5000 MB/s,319 元起Aug 12, 2024 pm 01:36 PM本站8月12日消息,金士顿NV3M.2SSD目前已在京东现货开售,该SSD可选512GB(500GB)/1TB/2TB版本(4TB版本未上架),其主打读取速度5000MB/s,本站整理价格信息如下:512GB:319元1TB:449元2TB:929元金士顿NV3采用单面M.22280尺寸,适合笔记本电脑,搭载PCIe4.0x4控制器,本站附读写速度如下:512GB:5000/3000MB/s1TB:6000/4000MB/s2TB:6000/5000MB/s金士顿将为NV3固态硬盘提供3年有限保
 纯白便携 ITX 机箱 九州风神 CH160 试装体验Apr 23, 2024 am 08:19 AM
纯白便携 ITX 机箱 九州风神 CH160 试装体验Apr 23, 2024 am 08:19 AM在之前的九州风神"风暴海景房"一文中,我们介绍了以九州风神全新冰暴360水冷散热器、CH780机箱,以及PX1200G电源"三件套"为基础,打造的游戏玩家平台。那么今天,我们将以新款ITX机箱——CH160,全新阿萨辛4S散热器,以及DQ750M-V3LWH电源,为大家带来一套纯白ITX个性组合。九州风神纯白ITX机电散套装这两年,喜欢小机箱的玩家,普通DIY用户越来越多。不少网友通过后台留言,新媒体平台私信我们,希望我们能推荐一些"好用不贵,安装简易"的ITX产品。那今天我们所选择的这三款产品
 英睿达 T705 PRO M.2 PCIe 5.0 固态硬盘国行上架:顺序读取至高 14500 MB/s,1899 元起Mar 16, 2024 pm 04:22 PM
英睿达 T705 PRO M.2 PCIe 5.0 固态硬盘国行上架:顺序读取至高 14500 MB/s,1899 元起Mar 16, 2024 pm 04:22 PM本站3月15日消息,英睿达今天在京东上架了T705PROM.2NVMePCIe5.0固态硬盘国行版本,可选1TB/2TB/4TB,本站整理具体售价信息如下:1TB款:1899元2TB款:3499元4TB款:4999元参数方面,T705PROM.2NVMePCIe5.0SSD使用镁光232层TLCNAND技术,支持MicrosoftDirectStorage、多层数据完整性算法、TRIM、断电数据保护、自适应热保护、动态写入加速、APST、SMART、TCG、独立NAND、ECC等功能,具体硬盘参
 SK海力士存储产品全线提价,涨幅高达20%May 06, 2024 pm 12:34 PM
SK海力士存储产品全线提价,涨幅高达20%May 06, 2024 pm 12:34 PM5月6日消息,据供应链最新爆料,SK海力士计划对其LPDDR5、LPDDR4、NAND以及DDR5等存储产品进行价格上调,预计涨幅将达到15%-20%。自去年第四季度起,海力士的DRAM产品价格已呈现连续递升的趋势,截至目前,其累计涨幅已达到惊人的60%-100%。然而,据市场观察,下半年的价格上涨速度可能会有所放缓。同时,三星电子也受益于存储产品的价格上涨。截至2024年第一季度的财报显示,一季度其存储业务的营收高达6.606亿韩元。据三星电子的财报披露,一季度其存储业务的营收高达17.49亿

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment








