 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Study: Artificial intelligence shortens stroke treatment time and reduces mortality by 60%
Study: Artificial intelligence shortens stroke treatment time and reduces mortality by 60%Study: Artificial intelligence shortens stroke treatment time and reduces mortality by 60%
News on September 22: For stroke patients, timely endovascular thrombectomy surgery is crucial to improving the patient’s prognosis. The time it takes for a patient to arrive at the hospital and undergo endovascular thrombectomy surgery has become an important indicator for a hospital to achieve stroke center certification
The application of artificial intelligence in diagnosing various medical conditions using CT images has been extensively explored. Therefore, automated methods based on artificial intelligence can be utilized to screen CT angiograms in patients with possible AIS, thereby shortening the time between evaluation and internal vessel thrombectomy
In this study, researchers used a randomized assignment ladder-like clinical trial to determine the effectiveness of an automated artificial intelligence-based system in detecting LVO in patients with possible AIS and improving hospital arrival and endovascular thrombectomy. Efficiency of time between start of assessment and workflow. Implementing random assignment analyzes at the individual patient level may cause problems while retaining the robustness of the randomized assessment.

Picture source note: The picture is generated by AI, and the picture is authorized by the service provider Midjourney
The trial was conducted at four comprehensive stroke centers in the Houston area from January 2021 to the end of February 2022. The phased rollout at the hospital level comes after receiving clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use of the AI platform in clinical care and receiving significant financial support to implement the software.
Participants in the trial included patients who presented to the emergency departments of these four comprehensive stroke centers with symptoms of AIS and LVO and underwent CT angiography. All patients included in the study were those with AIS associated with LVO of the middle cerebral artery, internal carotid artery, anterior cerebral artery, posterior cerebral artery, basilar artery, or intracranial vertebral artery
Since these patients had already decided to undergo internal vessel thrombectomy in the hospital, the time between the initial CT scan and internal vessel thrombectomy was significantly different in the inpatient cases and were therefore excluded from the analysis. For patients referred from other medical centers, the decision has been made for endovascular thrombectomy and they will proceed directly to the procedure without further imaging, which will change the workflow time
The intervention includes activation of artificial intelligence-based LVO detection from CT angiography, which is integrated with a secure messaging system. The system was activated in a randomized fashion at four comprehensive stroke centers. The activated system alerts radiologists and clinicians via mobile phone within minutes of completion of CT imaging of a possible LVO.
Research results
Key research findings include the impact of an automated artificial intelligence-based LVO detection system on door-to-abdomen time, which was determined using a linear regression model. Secondary outcomes included the time between arrival at the hospital and intravenous tissue kinase activator injection, the time between starting a CT scan and starting endovascular thrombectomy, and length of hospital stay.
By implementing an automated artificial intelligence-based LVO detection system, combined with a safety application that uses mobile phones for communication, inpatient AIS workflow time has been significantly improved. During the trial, a total of about 250 patients attended the emergency departments of the four hospitals, and door-to-abdominal time was reduced by 11 minutes through the use of the AI-based automated system. Additionally, mortality was reduced by 60%, along with a reduction in the time between the initial CT scan and initiation of endovascular thrombectomy
in conclusion
By using an automated AI-based system to detect LVO in patients with possible AIS, combined with a secure communication application, we successfully reduced the workflow within the hospital and significantly reduced the number of endovascular thrombectomies performed clinically Treatment time
[Source: Webmaster’s Home]
The above is the detailed content of Study: Artificial intelligence shortens stroke treatment time and reduces mortality by 60%. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Cooking Up Innovation: How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Food ServiceApr 12, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Cooking Up Innovation: How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Food ServiceApr 12, 2025 pm 12:09 PMAI Augmenting Food Preparation While still in nascent use, AI systems are being increasingly used in food preparation. AI-driven robots are used in kitchens to automate food preparation tasks, such as flipping burgers, making pizzas, or assembling sa
 Comprehensive Guide on Python Namespaces & Variable ScopesApr 12, 2025 pm 12:00 PM
Comprehensive Guide on Python Namespaces & Variable ScopesApr 12, 2025 pm 12:00 PMIntroduction Understanding the namespaces, scopes, and behavior of variables in Python functions is crucial for writing efficiently and avoiding runtime errors or exceptions. In this article, we’ll delve into various asp
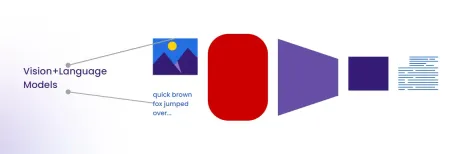 A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AM
A Comprehensive Guide to Vision Language Models (VLMs)Apr 12, 2025 am 11:58 AMIntroduction Imagine walking through an art gallery, surrounded by vivid paintings and sculptures. Now, what if you could ask each piece a question and get a meaningful answer? You might ask, “What story are you telling?
 MediaTek Boosts Premium Lineup With Kompanio Ultra And Dimensity 9400Apr 12, 2025 am 11:52 AM
MediaTek Boosts Premium Lineup With Kompanio Ultra And Dimensity 9400Apr 12, 2025 am 11:52 AMContinuing the product cadence, this month MediaTek has made a series of announcements, including the new Kompanio Ultra and Dimensity 9400 . These products fill in the more traditional parts of MediaTek’s business, which include chips for smartphone
 This Week In AI: Walmart Sets Fashion Trends Before They Ever HappenApr 12, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This Week In AI: Walmart Sets Fashion Trends Before They Ever HappenApr 12, 2025 am 11:51 AM#1 Google launched Agent2Agent The Story: It’s Monday morning. As an AI-powered recruiter you work smarter, not harder. You log into your company’s dashboard on your phone. It tells you three critical roles have been sourced, vetted, and scheduled fo
 Generative AI Meets PsychobabbleApr 12, 2025 am 11:50 AM
Generative AI Meets PsychobabbleApr 12, 2025 am 11:50 AMI would guess that you must be. We all seem to know that psychobabble consists of assorted chatter that mixes various psychological terminology and often ends up being either incomprehensible or completely nonsensical. All you need to do to spew fo
 The Prototype: Scientists Turn Paper Into PlasticApr 12, 2025 am 11:49 AM
The Prototype: Scientists Turn Paper Into PlasticApr 12, 2025 am 11:49 AMOnly 9.5% of plastics manufactured in 2022 were made from recycled materials, according to a new study published this week. Meanwhile, plastic continues to pile up in landfills–and ecosystems–around the world. But help is on the way. A team of engin
 The Rise Of The AI Analyst: Why This Could Be The Most Important Job In The AI RevolutionApr 12, 2025 am 11:41 AM
The Rise Of The AI Analyst: Why This Could Be The Most Important Job In The AI RevolutionApr 12, 2025 am 11:41 AMMy recent conversation with Andy MacMillan, CEO of leading enterprise analytics platform Alteryx, highlighted this critical yet underappreciated role in the AI revolution. As MacMillan explains, the gap between raw business data and AI-ready informat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function




