 Java
Java javaTutorial
javaTutorial A powerful tool to improve the efficiency of Java function development: microservice architecture
A powerful tool to improve the efficiency of Java function development: microservice architecture
A powerful tool to improve the efficiency of Java function development: microservice architecture
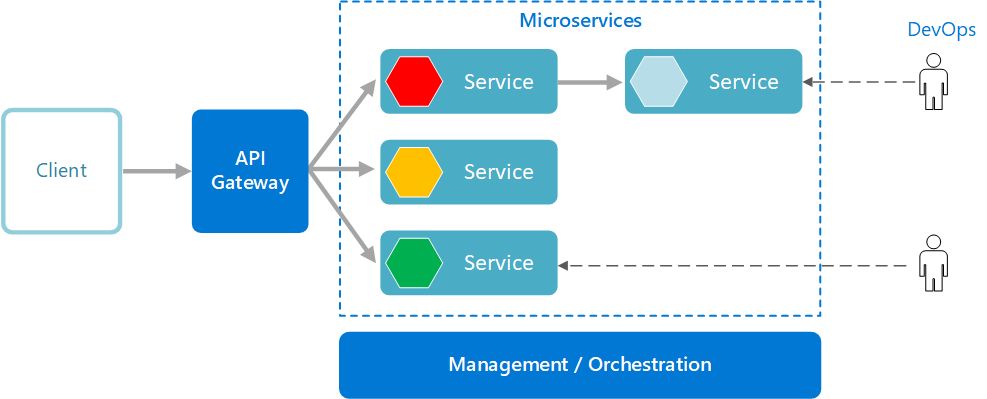
With the continuous development of software development, developers are increasingly pursuing the improvement of development efficiency. In order to quickly iterate and deploy new features, using microservice architecture has become the choice of many enterprises. Microservices architecture is a method of splitting software applications into a set of small, loosely coupled services, each running in its own process and can be independently deployed, managed, and scaled.
In Java development, using a microservice architecture can bring many advantages, including:
- Independent development and deployment: Each microservice represents a small business function that can It is developed and maintained by an independent development team. This independence speeds development and allows for rapid deployment of new features or bug fixes without requiring the entire application to be redeployed.
- Loose coupling and scalability: Microservices communicate through APIs and have no direct dependencies on each other. This means microservices can be scaled and updated independently without affecting other parts of the overall application. In addition, the microservice architecture also supports horizontal expansion, which can dynamically increase or decrease microservice instances according to demand.
- Technology Diversity: Microservices architecture supports the use of different technology stacks to build each microservice, which means that the most suitable technology can be selected based on the needs of each service. For example, one microservice can be written in Java and another microservice in Node.js. This can maximize the technical capabilities of the development team and draw on the latest technology trends.
The following is a simple example showing how to build a basic microservice application using Java and Spring Boot. Suppose we have two microservices: user service and order service.
First, we create a Java project named "UserService". In the project, we create a UserController, which is responsible for handling user-related requests.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/")
public User createUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return userService.createUser(user);
}
// 其他方法省略...
}In the above code, we use Spring Boot annotations to create a RESTful API to handle user-related requests. UserService is a service developed by the development team and is responsible for specific business logic.
Next, we create a Java project named "OrderService". In the project, we create an OrderController to handle order-related requests.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/orders")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Order getOrderById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return orderService.getOrderById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/")
public Order createOrder(@RequestBody Order order) {
return orderService.createOrder(order);
}
// 其他方法省略...
}In the above code, we use the same method to create a RESTful API that handles order-related requests. OrderService is also a service developed by the development team.
Finally, we need to deploy these two microservices to different servers so that they can run and scale independently.
This is just a simple example, actual microservice applications may involve more services and dependencies. However, regardless of the size of the application, using a microservices architecture can improve the efficiency and flexibility of Java development.
To sum up, the microservice architecture is a powerful tool that can improve the efficiency of Java function development. By splitting applications into a set of small, loosely coupled services, each developed, deployed, and scaled independently, developers can iterate on new features more quickly and achieve greater scalability and flexibility. Of course, the microservice architecture is not a panacea, and different factors need to be weighed in actual applications to choose the most suitable architecture.
The above is the detailed content of A powerful tool to improve the efficiency of Java function development: microservice architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 应用实例:使用go-micro 构建微服务推荐系统Jun 18, 2023 pm 12:43 PM
应用实例:使用go-micro 构建微服务推荐系统Jun 18, 2023 pm 12:43 PM随着互联网应用的普及,微服务架构已成为目前比较流行的一种架构方式。其中,微服务架构的关键就是将应用拆分为不同的服务,通过RPC方式进行通信,实现松散耦合的服务架构。在本文中,我们将结合实际案例,介绍如何使用go-micro构建一款微服务推荐系统。一、什么是微服务推荐系统微服务推荐系统是一种基于微服务架构的推荐系统,它将推荐系统中的不同模块(如特征工程、分类
 使用go-zero实现微服务的动态路由Jun 22, 2023 am 10:33 AM
使用go-zero实现微服务的动态路由Jun 22, 2023 am 10:33 AM随着云计算和容器化技术的普及,微服务架构已成为现代化软件开发中的主流方案。而动态路由技术则是微服务架构中必不可少的一环。本文将介绍如何使用go-zero框架实现微服务的动态路由。一、什么是动态路由在微服务架构中,服务的数量和种类可能非常多,如何管理和发现这些服务是一项非常棘手的任务。传统的静态路由并不适用于微服务架构,因为服务数量以及运行时的状态都是动态变化
 go-zero与Docker的完美结合:高效构建容器化的微服务架构Jun 22, 2023 am 09:08 AM
go-zero与Docker的完美结合:高效构建容器化的微服务架构Jun 22, 2023 am 09:08 AM随着互联网的快速发展,微服务架构渐渐成为了业界的热门话题,而Docker作为容器化的利器,更是被广泛应用于微服务架构中的部署和运维。而今天我要介绍的是另一款非常优秀的微服务框架——go-zero,以及它与Docker的完美结合。一、什么是go-zerogo-zero是一款由饿了么点评公司开源的,基于Go语言构建的微服务框架。它的特点是高性能、易于使用和功能全
 自动扩展的go-zero微服务架构Jun 22, 2023 am 11:14 AM
自动扩展的go-zero微服务架构Jun 22, 2023 am 11:14 AM近年来,随着云计算和微服务架构的普及,越来越多的企业和开发者开始使用微服务架构来搭建自己的应用。然而,微服务架构也存在着一些问题,比如服务的扩展、管理、监控等方面。为了解决这些问题,很多开发者开始使用go-zero微服务框架。go-zero是一款基于Go语言开发的微服务框架,它提供了一系列的组件和工具,帮助开发者快速构建、管理和扩展自己的微服务。其中最重要的
 Python 对微服务架构有效吗?May 18, 2023 pm 09:28 PM
Python 对微服务架构有效吗?May 18, 2023 pm 09:28 PM在选择适合微服务架构的编程语言时,Python是其中一种选择。它具有活跃的社区、更好的原型设计以及在开发人员中受欢迎等好处。它有一些限制,因此可以使用其他语言来避免它们。快速开发架构风格回顾与统计两种主要的开发架构风格是单体架构和微服务架构。Monolithic具有一体化的原则,并作为一个整体结构发挥作用,最适合小型开发项目或初创企业。当一个平台增长并且业务需要复杂的应用程序时,将其拆分为微服务架构是合理的。一些语言和框架更适合构建微服务架构。Java、Javascript和Python被列为微
 有哪些适合于Go语言开发的微服务框架?Jun 03, 2023 am 08:41 AM
有哪些适合于Go语言开发的微服务框架?Jun 03, 2023 am 08:41 AM随着微服务架构的兴起,越来越多的开发者开始探索如何将应用程序拆分成小而独立的服务,并将它们组合成一个更大的应用。Go语言因其高效、简洁和并发性能出色的特点,成为了其中一个热门的用于微服务开发的语言。而本文将介绍一些适合于Go语言开发的微服务框架。GinGin是一款快速、灵活和轻量级的Web框架,具有丰富的功能和优雅的API。它通过HTTP路由机制和中间件来帮
 PHP中的KubernetesMay 26, 2023 pm 10:10 PM
PHP中的KubernetesMay 26, 2023 pm 10:10 PMKubernetes是近年来非常火热的容器编排和管理工具,PHP作为一种非常流行的Web开发语言,也需要适应这个趋势,通过Kubernetes来管理自己的应用。在本文中,我们将探讨如何在PHP应用中使用Kubernetes。一、Kubernetes概述Kubernetes是由Google公司开发的一个容器编排和管理工具,用于管理容器化应用。Kubernete
 如何使用Go构建微服务架构的应用Jun 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
如何使用Go构建微服务架构的应用Jun 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM随着软件开发的不断发展,微服务架构已经逐渐成为了一种非常流行的架构模式。而在微服务架构中,Go语言作为一种高性能的编程语言也逐渐受到了越来越多的关注。那么,如何使用Go构建微服务架构的应用呢?下面将通过几个步骤来详细介绍。1.选择合适的Go框架选择合适的Go框架非常重要,它能够让我们更快地构建出一些基础服务,比如HTTP服务、日志服务、数据库服务等等。当前,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.




