Home >Backend Development >C++ >Use C language to explain deleting elements in the queue
Use C language to explain deleting elements in the queue
- 王林forward
- 2023-08-28 09:45:151111browse
A data structure is a collection of data organized in a structured manner. It is divided into two types as mentioned below -
Linear Data Structure - Data is organized in a linear manner. For example, arrays, structures, stacks, queues, and linked lists.
Nonlinear Data Structure - Data is organized in a hierarchical manner. For example, trees, graphs, sets, tables.
Queue
It is a linear data structure, insertion is done on the backend, and deletion is done on the frontend.
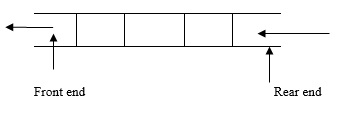
The order of the queue is FIFO – first in, first out
Operation
- Insert – Insert elements into the queue.
- Delete – Remove an element from the queue.
Conditions
Queue overflow − Attempt to insert an element into a full queue.
Queue is in streaming state − An attempt is made to remove an element from an empty queue.
Algorithm
Given below is the algorithm for inserting ( ) -
- Check for queue overflow.
if (r==n)
printf ("Queue overflow")- Otherwise, insert an element into the queue.
q[r] = item r++gives the HTML code of a deletion algorithm:
Given below is an algorithm for deletion ( ) −
- Check for queue under flow.
if (f==r)
printf ("Queue under flow")- Otherwise, remove an element from the queue.
item = q[f] f++
The following is the algorithm of display ( ) -
- Check whether the queue is empty. ul>
if (f==r)
printf("Queue is empty")- Otherwise, print all elements from 'f' to 'r'.
for(i=f; i<r; i++)
printf ("%d", q[i]);Program
The following is the C program for removing elements from the queue −
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 50
void insert();
int array[MAX];
int rear = - 1;
int front = - 1;
main(){
int add_item;
int choice;
while (1){
printf("1.Insert element to queue </p><p>");
printf("2.Delete an element from queue</p><p>");
printf("3.Display elements of queue </p><p>");
printf("4.Quit </p><p>");
printf("Enter your choice : ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch (choice){
case 1:
insert();
break;
case 2:
delete();
case 3:
display();
break;
case 4:
exit(1);
default:
printf("Wrong choice </p><p>");
}
}
}
void insert(){
int add_item;
if (rear == MAX - 1)
printf("Queue Overflow </p><p>");
else{
if (front == - 1)
/*If queue is initially empty */
front = 0;
printf("Inset the element in queue : ");
scanf("%d", &add_item);
rear = rear + 1;
array[rear] = add_item;
}
}
void display(){
int i;
if (front == - 1)
printf("Queue is empty </p><p>");
else{
printf("Queue is : </p><p>");
for (i = front; i <= rear; i++)
printf("%d ", array[i]);
printf("</p><p>");
}
}
void delete(){
if (front == - 1 || front > rear){
printf("Queue Underflow </p><p>");
return ;
}
else{
printf("Element deleted from queue is : %d</p><p>",array[front]);
front = front + 1;
}
}Output
When executing the above program, the following results will be produced -
1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 12 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 23 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 1 Inset the element in queue: 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 2 Element deleted from queue is: 12 Queue is: 23 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 2 Element deleted from queue is: 23 Queue is: 34 1.Insert element to queue 2.Delete an element from queue 3.Display elements of queue 4.Quit Enter your choice: 4
The above is the detailed content of Use C language to explain deleting elements in the queue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- C++ compilation error: A header file is referenced multiple times, how to solve it?
- C++ compilation error: wrong function parameters, how to fix it?
- C++ error: The constructor must be declared in the public area, how to deal with it?
- Process management and thread synchronization in C++
- How to deal with data splitting problems in C++ development

