Home >Backend Development >C++ >Node product of singly linked list
Node product of singly linked list
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-08-28 09:13:08699browse
Given n nodes, the task is to print the product of all nodes in a singly linked list. The program must traverse all nodes of the one-way linked list starting from the initial node until NULL is not found.
Example
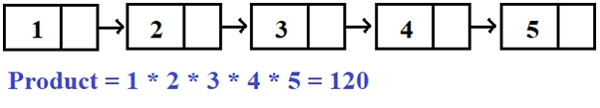
Input -: 1 2 3 4 5 Output -: 120
In the above example, starting from the first node and traversing all the nodes, i.e. 1, 2 3, 4, 5, 6, their product is 1*2* 3*4*5*6 = 120
The method used below is as follows
- Get a temporary pointer, such as temp## of the node type #Set this temporary pointer to the first node pointed by the head pointer
- When temp is not NULL, move temp to temp ->next.
- Set Product=product*(temp->data)
H2>Start
Step 1 -> create structure of a node and temp, next and head as pointer to a structure node
struct node
int data
struct node *next, *head, *temp
End
Step 2 -> declare function to insert a node in a list
void insert(int val)
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node))
newnode->data = val
IF head= NULL
set head = newnode
set head->next = NULL
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp->next!=NULL
Set temp=temp->next
End
Set newnode->next=NULL
Set temp->next=newnode
End
Step 3 -> Declare a function to display list
void display()
IF head=NULL
Print no node
End
Else
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Print temp->data
Set temp=temp->next
End
End
Step 4 -> declare a function to find alternate nodes
void product_nodes()
declare int product=1
Set temp=head
Loop While temp!=NULL
Set product=product * (temp->data)
Set temp=temp->next
End
Print product
Step 5 -> in main()
Create nodes using struct node* head = NULL;
Call function insert(10) to insert a node
Call display() to display the list
Call product_nodes() to find alternate nodes product
Stop
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node{
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head,*temp;
//function for inserting nodes into a list
void insert(int val){
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(head == NULL){
head = newnode;
temp = head;
} else {
temp->next=newnode;
temp=temp->next;
}
}
//function for displaying a list
void display(){
if(head==NULL)
printf("no node ");
else{
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL){
printf("%d ",temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
}
}
//function for finding product
void product_nodes(){
int product=1;
temp=head;
while(temp!=NULL){
product=product * (temp->data);
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("</p><p>product of nodes is : %d" ,product);
}
int main(){
//creating list
struct node* head = NULL;
//inserting elements into a list
insert(1);
insert(2);
insert(3);
insert(4);
insert(5);
insert(6);
//displaying the list
printf("linked list is : ");
display();
//calling function for finding prodouct
Product_nodes();
return 0;
}
Outputlinked list is : 1 2 3 4 5 6
product of nodes is : 720
The above is the detailed content of Node product of singly linked list. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:tutorialspoint.com. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete
Previous article:Floating-point arithmetic and associativity in C, C++, and JavaNext article:Floating-point arithmetic and associativity in C, C++, and Java
Related articles
See more- PHP method to calculate the sum and product of values in an array (with functions)
- Detailed explanation of Python data structure singly linked list with examples
- How to find and delete nodes in python singly linked list?
- The number of leaf nodes of a complete binary tree
- How to delete the current node in javascript

