Home >Technology peripherals >AI >By changing one line of code, PyTorch training is three times faster. These 'advanced technologies' are the key
By changing one line of code, PyTorch training is three times faster. These 'advanced technologies' are the key
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-08-14 12:05:041076browse
Recently, Sebastian Raschka, a well-known researcher in the field of deep learning and chief artificial intelligence educator of Lightning AI, delivered a keynote speech "Scaling PyTorch Model Training With Minimal Code Changes" at CVPR 2023.

In order to share the research results with more people, Sebastian Raschka compiled the speech into an article. The article explores how to scale PyTorch model training with minimal code changes, and shows that the focus is on leveraging mixed-precision methods and multi-GPU training modes rather than low-level machine optimizations.
The article uses Visual Transformer (ViT) as the basic model. The ViT model starts from scratch on a basic data set. After about 60 minutes of training, it achieves 62% on the test set. Accuracy.
##GitHub address: https://github.com/rasbt/cvpr2023
The following is the original text of the article:
Building a baseline
In the next section, Sebastian will explore how to Improve training time and accuracy with extensive code refactoring.
Want to note that the details of the model and dataset are not the main focus here (they are just meant to be as simple as possible so that readers can reproduce it on their own machines , without downloading and installing too many dependencies). All examples shared here can be found on GitHub, where readers can explore and reuse the complete code.
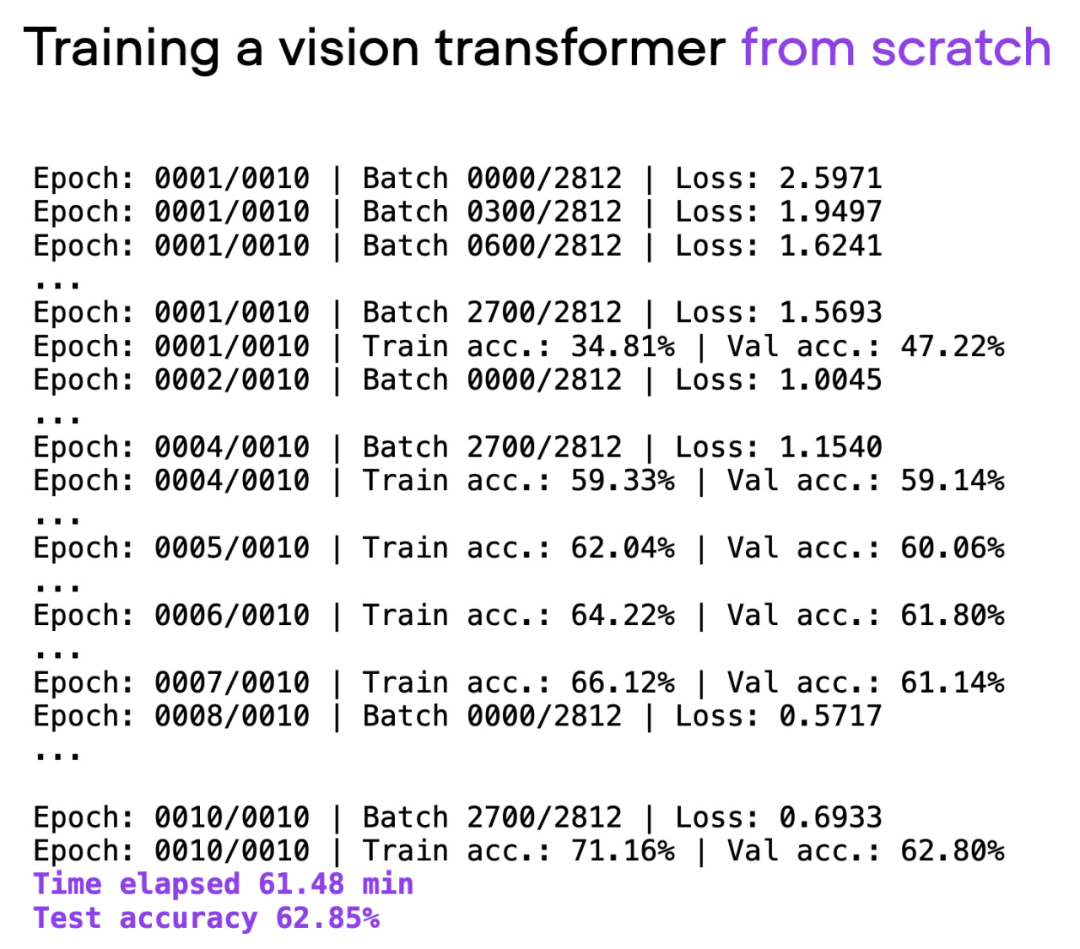
Output of script 00_pytorch-vit-random-init.py.
Don’t train from scratch
Today, training deep learning models for text or images from scratch is often inefficient. We usually utilize pre-trained models and fine-tune the models to save time and computing resources while obtaining better modeling results.
If you consider the same ViT architecture used above, pre-train on another dataset (ImageNet), and fine-tune it, you can achieve better results in less time. Good prediction performance: 95% test accuracy within 20 minutes (3 training epochs).
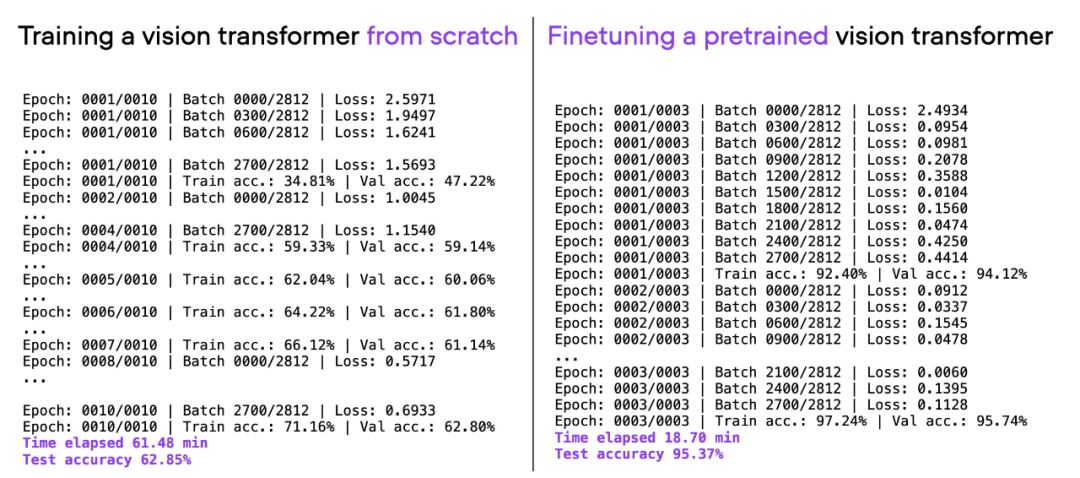
Comparison of 00_pytorch-vit-random-init.py and 01_pytorch-vit.py.
Improve computing performance
We can see that fine-tuning can greatly improve model performance compared to training from scratch. The bar chart below summarizes this.
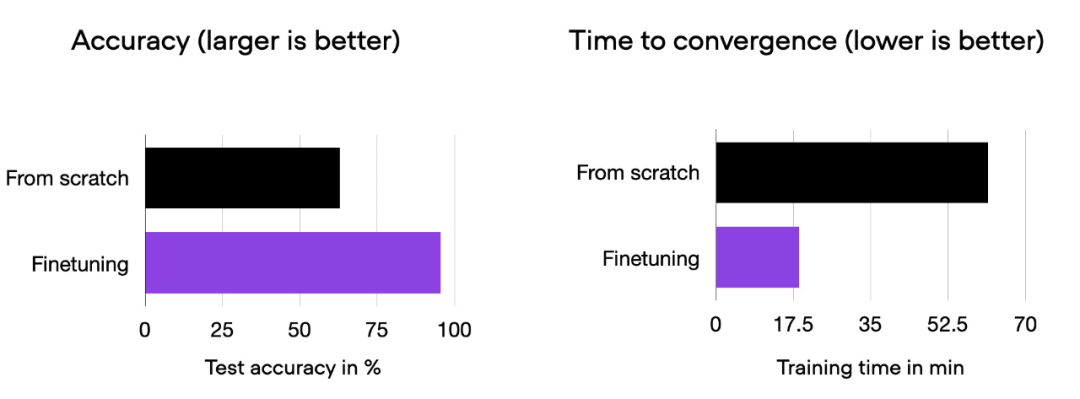
Comparative histogram of 00_pytorch-vit-random-init.py and 01_pytorch-vit.py.
Of course, model performance may vary depending on the data set or task. But for many text and image tasks, it’s worthwhile to start with a model pretrained on a common public dataset.
The following sections will explore various techniques to speed up training time without sacrificing prediction accuracy.
Open Source Library Fabric
One way to efficiently scale training in PyTorch with minimal code changes is to use the open source Fabric library, which can Think of it as a lightweight wrapper library/interface for PyTorch. Install via pip.
pip install lightning
All techniques explored below can also be implemented in pure PyTorch. Fabric aims to make this process more convenient.
Before exploring "advanced techniques for accelerating code", let's first introduce the small changes required to integrate Fabric into PyTorch code. Once you make these changes, you can easily use advanced PyTorch features by changing just one line of code.
The difference between the PyTorch code and the code modified to use Fabric is subtle and only involves some minor modifications, as shown in the following code:
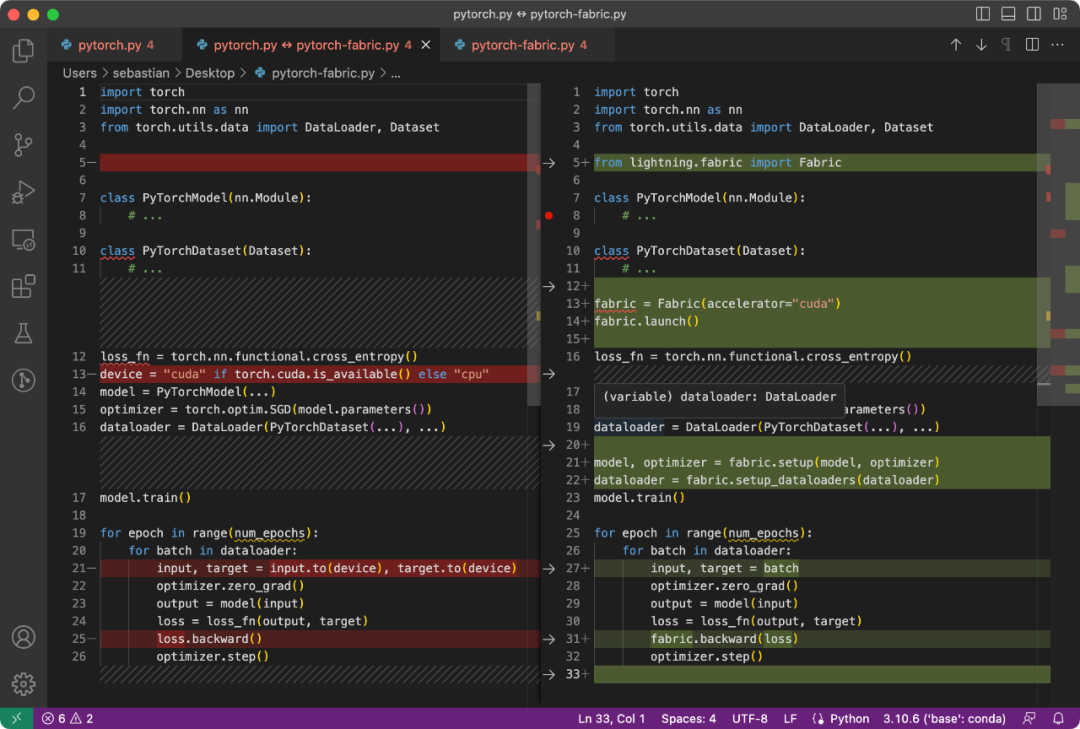
Normal PyTorch code (left) and PyTorch code using Fabric
总结一下上图,就可以得到普通的 PyTorch 代码转换为 PyTorch+Fabric 的三个步骤:
- 导入 Fabric 并实例化一个 Fabric 对象。
- 使用 Fabric 设置模型、优化器和 data loader。
- 损失函数使用 fabric.backward (),而不是 loss.backward ()。

这些微小的改动提供了一种利用 PyTorch 高级特性的途径,而无需对现有代码进行进一步重构。
深入探讨下面的「高级特性」之前,要确保模型的训练运行时间、预测性能与之前相同。
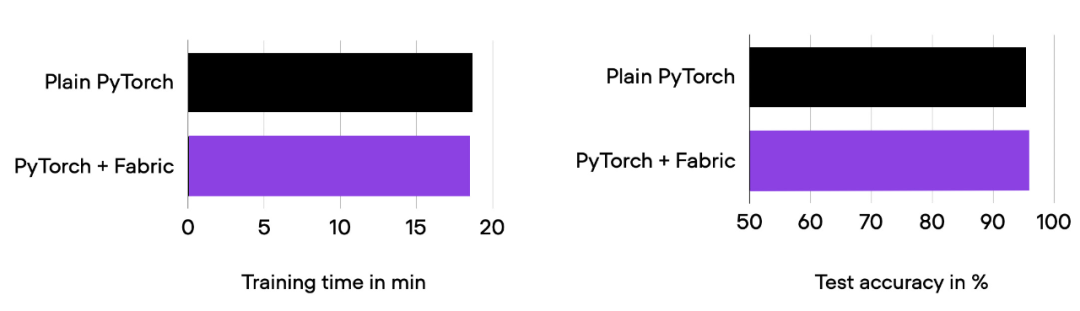
01_pytorch-vit.py 和 03_fabric-vit.py 的比较结果。
正如前面柱状图中所看到的,训练运行时间、准确率与之前完全相同,正如预期的那样。其中,任何波动都可以归因于随机性。
在前面的部分中,我们使用 Fabric 修改了 PyTorch 代码。为什么要费这么大的劲呢?接下来将尝试高级技术,比如混合精度和分布式训练,只需更改一行代码,把下面的代码
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="cuda")
改为
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="cuda", precisinotallow="bf16-mixed")
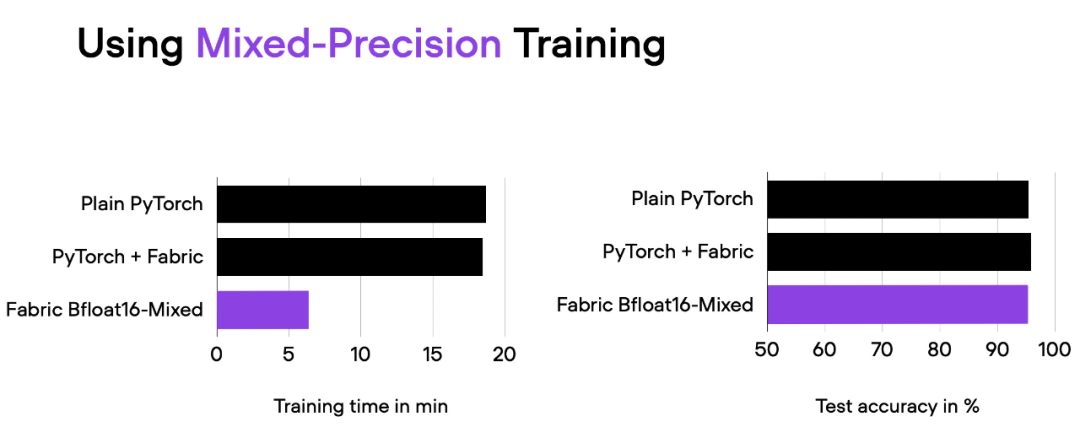
04_fabric-vit-mixed-precision.py 脚本的比较结果。脚本地址:https://github.com/rasbt/cvpr2023/blob/main/04_fabric-vit-mixed-precision.py
通过混合精度训练,我们将训练时间从 18 分钟左右缩短到 6 分钟,同时保持相同的预测性能。这种训练时间的缩短只需在实例化 Fabric 对象时添加参数「precisinotallow="bf16-mixed"」即可实现。
理解混合精度机制
混合精度训练实质上使用了 16 位和 32 位精度,以确保不会损失准确性。16 位表示中的计算梯度比 32 位格式快得多,并且还节省了大量内存。这种策略在内存或计算受限的情况下非常有益。
之所以称为「混合」而不是「低」精度训练,是因为不是将所有参数和操作转换为 16 位浮点数。相反,在训练过程中 32 位和 16 位操作之间切换,因此称为「混合」精度。
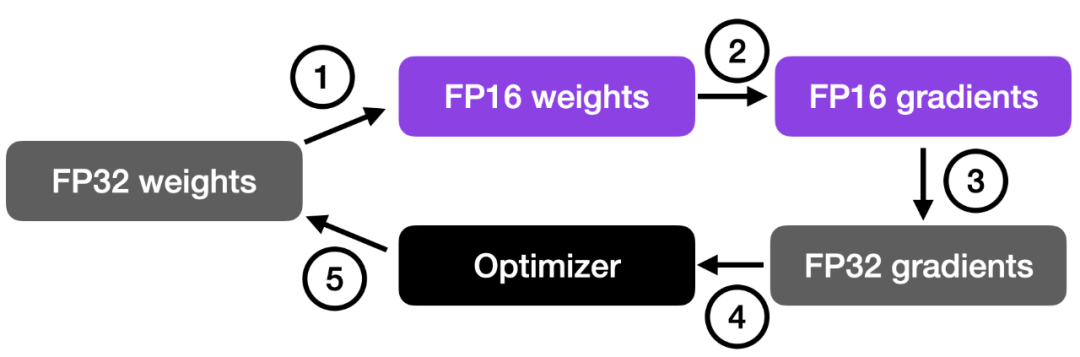
如下图所示,混合精度训练涉及步骤如下:
- 将权重转换为较低精度(FP16)以加快计算速度;
- 计算梯度;
- 将梯度转换回较高精度(FP32)以保持数值稳定性;
- 使用缩放后的梯度更新原始权重。
这种方法在保持神经网络准确性和稳定性的同时,实现了高效的训练。
更详细的步骤如下:
- 将权重转换为 FP16:在这一步中,神经网络的权重(或参数)初始时用 FP32 格式表示,将其转换为较低精度的 FP16 格式。这样可以减少内存占用,并且由于 FP16 操作所需的内存较少,可以更快地被硬件处理。
- 计算梯度:使用较低精度的 FP16 权重进行神经网络的前向传播和反向传播。这一步计算损失函数相对于网络权重的梯度(偏导数),这些梯度用于在优化过程中更新权重。
- 将梯度转换回 FP32:在计算得到 FP16 格式的梯度后,将其转换回较高精度的 FP32 格式。这种转换对于保持数值稳定性非常重要,避免使用较低精度算术时可能出现的梯度消失或梯度爆炸等问题。
- 乘学习率并更新权重:以 FP32 格式表示的梯度乘以学习率将用于更新权重(标量值,用于确定优化过程中的步长)。
步骤 4 中的乘积用于更新原始的 FP32 神经网络权重。学习率有助于控制优化过程的收敛性,对于实现良好的性能非常重要。
Brain Float 16
前面谈到了「float 16-bit」精度训练。需要注意的是,在之前的代码中,指定了 precisinotallow="bf16-mixed",而不是 precisinotallow="16-mixed"。这两个都是有效的选项。
在这里,"bf16-mixed" 中的「bf16」表示 Brain Floating Point(bfloat16)。谷歌开发了这种格式,用于机器学习和深度学习应用,尤其是在张量处理单元(TPU)中。Bfloat16 相比传统的 float16 格式扩展了动态范围,但牺牲了一定的精度。
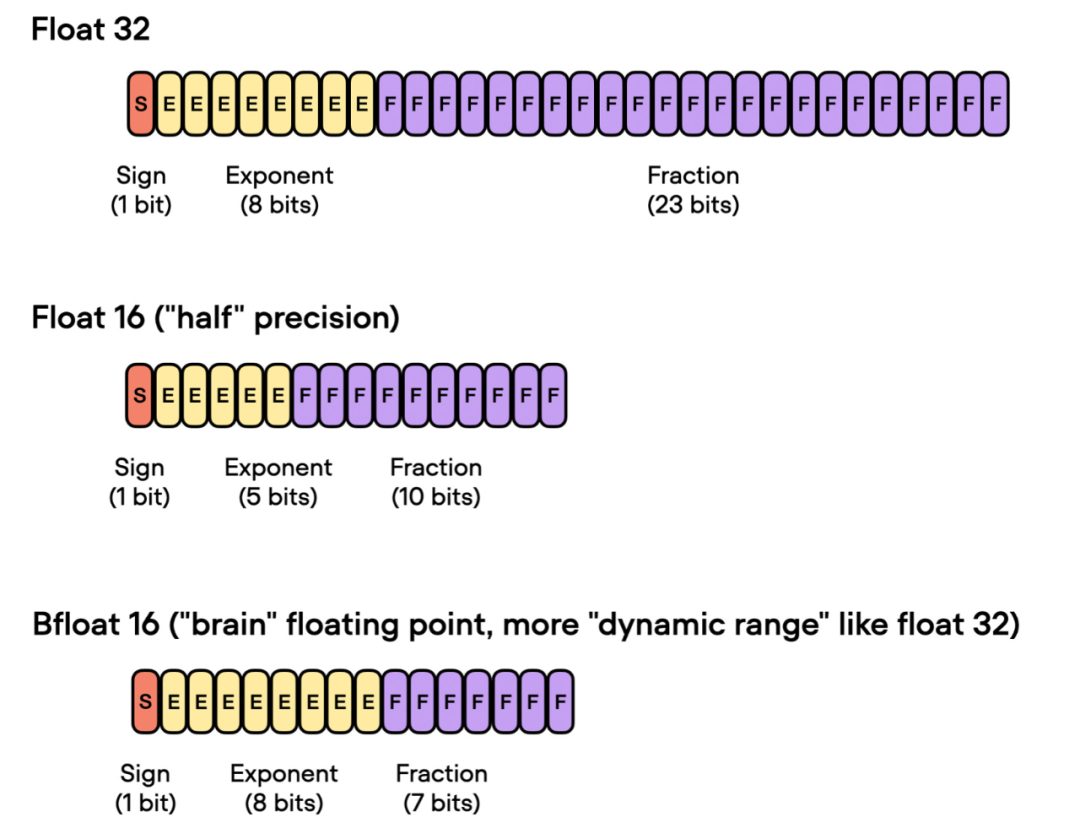
扩展的动态范围使得 bfloat16 能够表示非常大和非常小的数字,使其更适用于深度学习应用中可能遇到的数值范围。然而,较低的精度可能会影响某些计算的准确性,或在某些情况下导致舍入误差。但在大多数深度学习应用中,这种降低的精度对建模性能的影响很小。
虽然 bfloat16 最初是为 TPU 开发的,但从 NVIDIA Ampere 架构的 A100 Tensor Core GPU 开始,已经有几种 NVIDIA GPU 开始支持 bfloat16。
我们可以使用下面的代码检查 GPU 是否支持 bfloat16:
>>> torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported()True
如果你的 GPU 不支持 bfloat16,可以将 precisinotallow="bf16-mixed" 更改为 precisinotallow="16-mixed"。
多 GPU 训练和完全分片数据并行
接下来要尝试修改多 GPU 训练。如果我们有多个 GPU 可供使用,这会带来好处,因为它可以让我们的模型训练速度更快。
这里介绍一种更先进的技术 — 完全分片数据并行(Fully Sharded Data Parallelism (FSDP)),它同时利用了数据并行性和张量并行性。
在 Fabric 中,我们可以通过下面的方式利用 FSDP 添加设备数量和多 GPU 训练策略:
fabric = Fabric(accelerator="cuda", precisinotallow="bf16-mixed",devices=4, strategy="FSDP"# new!)
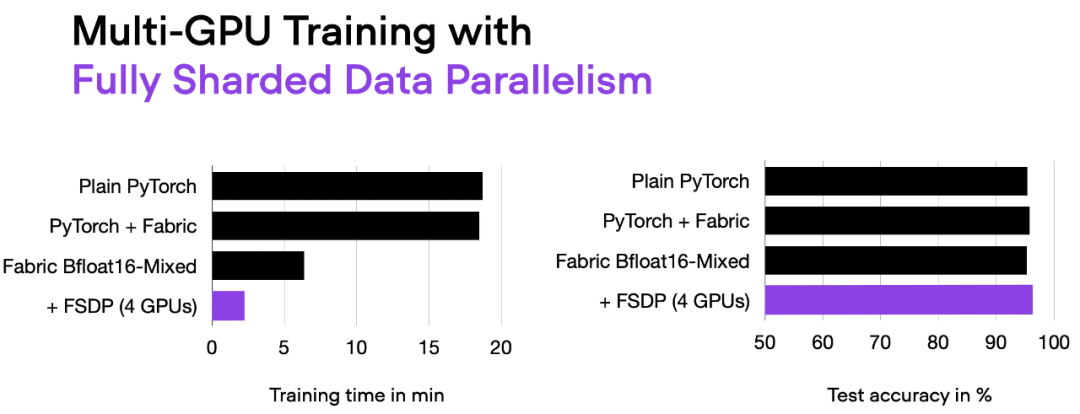
06_fabric-vit-mixed-fsdp.py 脚本的输出。
现在使用 4 个 GPU,我们的代码运行时间大约为 2 分钟,是之前仅使用混合精度训练时的近 3 倍。
理解数据并行和张量并行
在数据并行中,小批量数据被分割,并且每个 GPU 上都有模型的副本。这个过程通过多个 GPU 的并行工作来加速模型的训练速度。
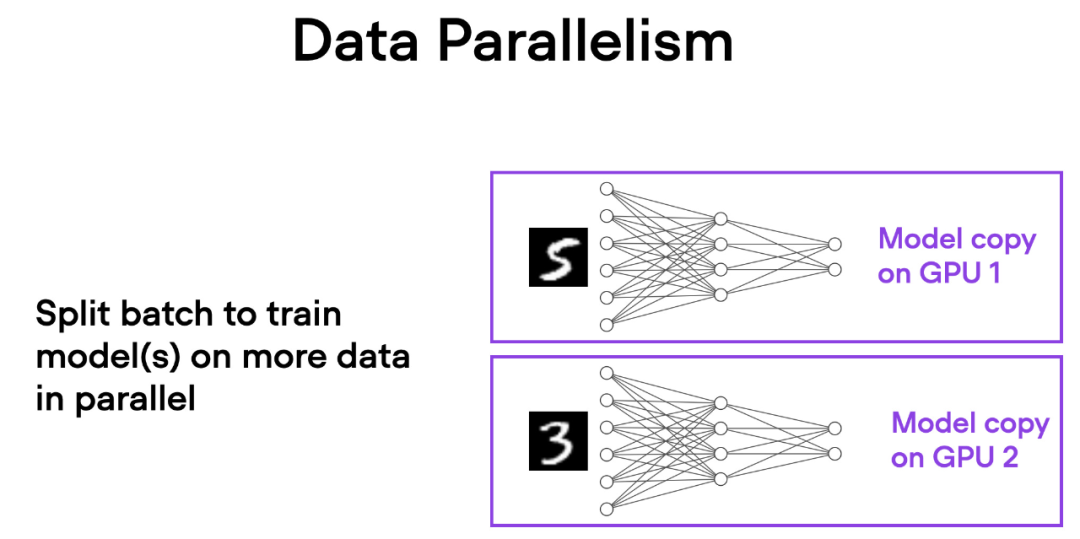
如下简要概述了数据并行的工作原理:
- 同一个模型被复制到所有的 GPU 上。
- 每个 GPU 分别接收不同的输入数据子集(不同的小批量数据)。
- 所有的 GPU 独立地对模型进行前向传播和反向传播,计算各自的局部梯度。
- 收集并对所有 GPU 的梯度求平均值。
- 平均梯度被用于更新模型的参数。
每个 GPU 都在并行地处理不同的数据子集,通过梯度的平均化和参数的更新,整个模型的训练过程得以加速。
这种方法的主要优势是速度。由于每个 GPU 同时处理不同的小批量数据,模型可以在更短的时间内处理更多的数据。这可以显著减少训练模型所需的时间,特别是在处理大型数据集时。
然而,数据并行也有一些限制。最重要的是,每个 GPU 必须具有完整的模型和参数副本。这限制了可以训练的模型大小,因为模型必须适应单个 GPU 的内存。这对于现代的 ViTs 或 LLMs 来说这是不可行的。
与数据并行不同,张量并行将模型本身划分到多个 GPU 上。并且在数据并行中,每个 GPU 都需要适 应整个模型,这在训练较大的模型时可能成为一个限制。而张量并行允许训练那些对单个 GPU 而言可能过大的模型,通过将模型分解并分布到多个设备上进行训练。
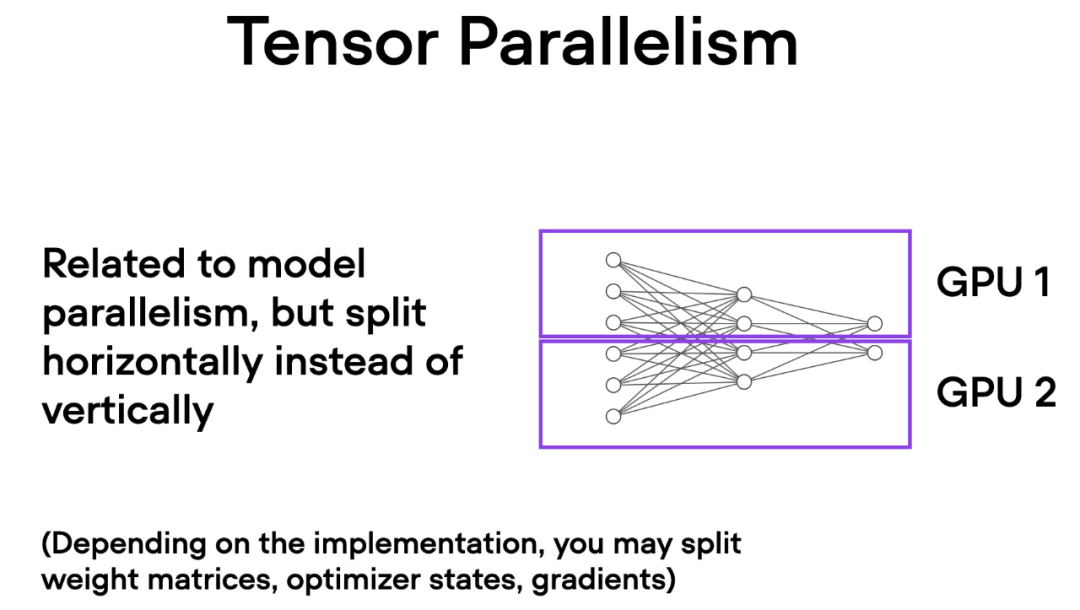
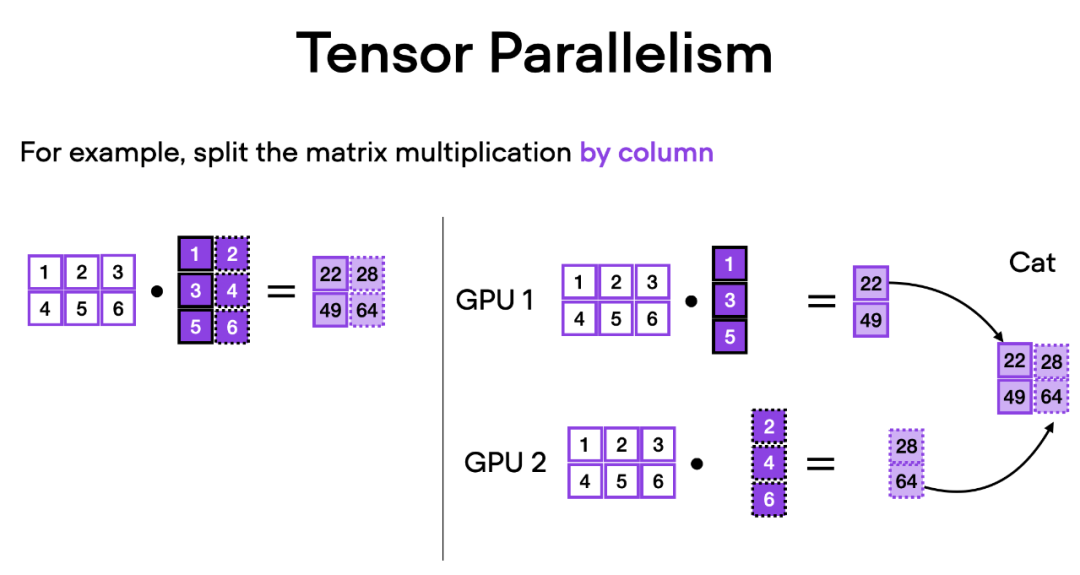
How does tensor parallelism work? Thinking about matrix multiplication, there are two ways to do distributed calculations - row-wise or column-wise. For simplicity, consider distribution calculations by column. For example, we can decompose a large matrix multiplication operation into multiple independent calculations, each of which can be performed on a different GPU, as shown in the figure below. The results are then concatenated to obtain the results, which effectively spreads the computational load.
The above is the detailed content of By changing one line of code, PyTorch training is three times faster. These 'advanced technologies' are the key. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

