Distribution is a computing and data processing method that distributes computing tasks or data to multiple computers or nodes for processing, which can provide high performance, high availability and elastic computing and data processing capabilities. To meet the application requirements of different scales and complexity, the design and implementation of distributed systems also face some challenges, such as data consistency, performance optimization, fault handling and debugging, etc. Programmers need to have solid distributed system knowledge and skills to Design and build reliable and efficient distributed systems.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, DELL G3 computer.
Distribution is a method of computing and data processing that distributes computing tasks or data to multiple computers or nodes for processing. A distributed system consists of multiple independent computers or nodes, which can be physical machines located in different geographical locations, or they can be virtual machines or containers.
In a distributed system, each node can perform tasks independently without relying on the status or resources of other nodes. Nodes communicate and coordinate through the network to complete the functions of the entire system. Distributed systems usually have the characteristics of high availability, fault tolerance and scalability, and can handle large-scale computing and data processing tasks.
The design and implementation of distributed systems need to consider the following aspects:
Communication: Nodes communicate through the network to transmit data and messages. Communication can use different protocols and communication methods, such as TCP/IP, HTTP, message queue, etc. Communication reliability, latency, and throughput are important factors to consider when designing distributed systems.
Data consistency: In a distributed system, data is usually stored on different nodes. In order to ensure data consistency, appropriate data replication and synchronization mechanisms need to be adopted. Common data consistency models include strong consistency, weak consistency and eventual consistency. Choosing a suitable data consistency model can be based on specific application scenarios and requirements.
Fault tolerance: Nodes in a distributed system may fail or the network may be disconnected. In order to improve the fault tolerance of the system, an appropriate fault tolerance mechanism needs to be adopted. For example, redundant nodes can be used to back up data or tasks. When the primary node fails, the backup node can take over the work to ensure the normal operation of the system.
Load balancing: Distributed systems usually face a large number of requests and tasks. In order to balance the load of each node, a load balancing strategy needs to be adopted. Load balancing can allocate requests and tasks to different nodes based on the node's performance and load conditions to improve system performance and throughput.
Scalability: Distributed systems can be expanded horizontally or vertically according to needs. Horizontal expansion increases the system's processing capabilities by adding more nodes, while vertical expansion increases the system's processing capabilities by improving the performance of a single node. Choosing the appropriate scaling method can make decisions based on system bottlenecks and resource constraints.
Security: Data and communication in distributed systems may face various security threats, such as data leakage, hijacking, and malicious attacks. In order to protect the security of the system, appropriate security mechanisms need to be adopted, such as identity authentication, data encryption and access control.
Distributed systems are widely used in various fields, such as cloud computing, big data processing, distributed storage and distributed databases, etc. It can provide high performance, high availability and elastic computing and data processing capabilities to meet application requirements of different scales and complexity. However, the design and implementation of distributed systems also face some challenges, such as data consistency, performance optimization, fault handling and debugging. Therefore, programmers need to have solid distributed systems knowledge and skills to design and build reliable and efficient distributed systems.
The above is the detailed content of What is distributed. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 PHP实现开源SeaweedFS分布式文件系统Jun 18, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
PHP实现开源SeaweedFS分布式文件系统Jun 18, 2023 pm 03:56 PM在分布式系统的架构中,文件管理和存储是非常重要的一部分。然而,传统的文件系统在应对大规模的文件存储和管理时遇到了一些问题。为了解决这些问题,SeaweedFS分布式文件系统被开发出来。在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用PHP来实现开源SeaweedFS分布式文件系统。什么是SeaweedFS?SeaweedFS是一个开源的分布式文件系统,它用于解决大规模文件存储和
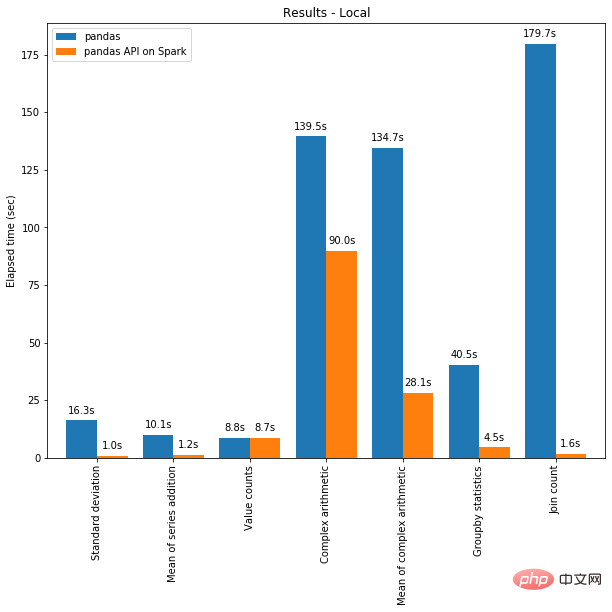 Pandas 与 PySpark 强强联手,功能与速度齐飞!May 01, 2023 pm 09:19 PM
Pandas 与 PySpark 强强联手,功能与速度齐飞!May 01, 2023 pm 09:19 PM使用Python做数据处理的数据科学家或数据从业者,对数据科学包pandas并不陌生,也不乏像云朵君一样的pandas重度使用者,项目开始写的第一行代码,大多是importpandasaspd。pandas做数据处理可以说是yyds!而他的缺点也是非常明显,pandas只能单机处理,它不能随数据量线性伸缩。例如,如果pandas试图读取的数据集大于一台机器的可用内存,则会因内存不足而失败。另外pandas在处理大型数据方面非常慢,虽然有像Dask或Vaex等其他库来优化提升数
 PHP中的分布式数据中心May 23, 2023 pm 11:40 PM
PHP中的分布式数据中心May 23, 2023 pm 11:40 PM随着互联网的快速发展,网站的访问量也在不断增长。为了满足这一需求,我们需要构建高可用性的系统。分布式数据中心就是这样一个系统,它将各个数据中心的负载分散到不同的服务器上,增加系统的稳定性和可扩展性。在PHP开发中,我们也可以通过一些技术实现分布式数据中心。分布式缓存分布式缓存是互联网分布式应用中最常用的技术之一。它将数据缓存在多个节点上,提高数据的访问速度和
 使用Redis实现分布式计数器May 11, 2023 am 08:06 AM
使用Redis实现分布式计数器May 11, 2023 am 08:06 AM什么是分布式计数器?在分布式系统中,多个节点之间需要对共同的状态进行更新和读取,而计数器是其中一种应用最广泛的状态之一。通俗地讲,计数器就是一个变量,每次被访问时其值就会加1或减1,用于跟踪某个系统进展的指标。而分布式计数器则指的是在分布式环境下对计数器进行操作和管理。为什么要使用Redis实现分布式计数器?随着分布式计算的普及,分布式系统中的许多细节问题也
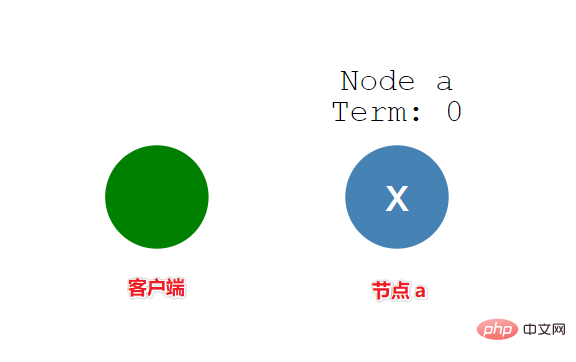 分布式系统必须知道的一个共识算法:RaftApr 07, 2023 pm 05:54 PM
分布式系统必须知道的一个共识算法:RaftApr 07, 2023 pm 05:54 PM一、Raft 概述Raft 算法是分布式系统开发首选的共识算法。比如现在流行 Etcd、Consul。如果掌握了这个算法,就可以较容易地处理绝大部分场景的容错和一致性需求。比如分布式配置系统、分布式 NoSQL 存储等等,轻松突破系统的单机限制。Raft 算法是通过一切以领导者为准的方式,实现一系列值的共识和各节点日志的一致。二、Raft 角色2.1 角色跟随者(Follower):普通群众,默默接收和来自领导者的消息,当领导者心跳信息超时的
 Redis实现分布式配置管理的方法与应用实例May 11, 2023 pm 04:22 PM
Redis实现分布式配置管理的方法与应用实例May 11, 2023 pm 04:22 PMRedis实现分布式配置管理的方法与应用实例随着业务的发展,配置管理对于一个系统而言变得越来越重要。一些通用的应用配置(如数据库连接信息,缓存配置等),以及一些需要动态控制的开关配置,都需要进行统一管理和更新。在传统架构中,通常是通过在每台服务器上通过单独的配置文件进行管理,但这种方式会导致配置文件的管理和同步变得十分复杂。因此,在分布式架构下,采用一个可靠
 Redis实现分布式对象存储的方法与应用实例May 10, 2023 pm 08:48 PM
Redis实现分布式对象存储的方法与应用实例May 10, 2023 pm 08:48 PMRedis实现分布式对象存储的方法与应用实例随着互联网的快速发展和数据量的快速增长,传统的单机存储已经无法满足业务的需求,因此分布式存储成为了当前业界的热门话题。Redis是一个高性能的键值对数据库,它不仅支持丰富的数据结构,而且支持分布式存储,因此具有极高的应用价值。本文将介绍Redis实现分布式对象存储的方法,并结合应用实例进行说明。一、Redis实现分
 PHP与数据库分布式的集成May 15, 2023 pm 09:40 PM
PHP与数据库分布式的集成May 15, 2023 pm 09:40 PM随着互联网技术的发展,对于一个网络应用而言,对数据库的操作非常频繁。特别是对于动态网站,甚至有可能出现每秒数百次的数据库请求,当数据库处理能力不能满足需求时,我们可以考虑使用数据库分布式。而分布式数据库的实现离不开与编程语言的集成。PHP作为一门非常流行的编程语言,具有较好的适用性和灵活性,这篇文章将着重介绍PHP与数据库分布式集成的实践。分布式的概念分布式

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software






