 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Application of VMS: Improving multi-brand equipment management efficiency
Application of VMS: Improving multi-brand equipment management efficiency
In the current environment, integrators and installers are looking for cost-saving solutions while upgrading older safety projects. To increase efficiency, many people prefer to use video management software to handle multiple brands of video equipment, including IP cameras and NVRs, rather than being limited to just one brand. This approach provides greater flexibility to optimize spend while increasing profits. This article will explore how to enhance multi-brand device management with a video management system (VMS), discover effective strategies to optimize surveillance operations, leverage scalable solutions, and take full advantage of the power of user-friendly interfaces to take your security infrastructure to the next level. the height of. We'll learn how to realize the full potential of a VMS, ensure compatibility, explore third-party integrations, and adopt cost-effective practices, all designed to increase the effectiveness and flexibility of your video surveillance system
 How to use video management system (VMS) to enhance multi-brand device management?
How to use video management system (VMS) to enhance multi-brand device management?
What is a video management system (VMS) and its role in video surveillance?
A video management system (VMS) is a software platform used to manage and control video surveillance systems, which serves as a central hub to handle, Record and monitor video streams from a variety of cameras and devices. VMS plays a key role in simplifying and enhancing video surveillance operations, providing users with a unified and intuitive interface to effectively manage their security infrastructure. Key features include:
- Camera control and configuration: VMS allows users to configure and control connected cameras, including adjusting camera settings, managing PTZ (pan tilt zoom) functions and setting up video analytics.
- Video Recording and Storage: VMS facilitates continuous or event-triggered video recording from multiple cameras. It efficiently manages video storage, ensuring data is retained according to user-defined settings.
- Real-time monitoring and video playback: Users can view live video sources from all connected cameras in real time. VMS also enables seamless video playback and retrieval of recorded footage for investigative purposes.
- Event Management and Alerting: VMS supports event-based triggers and alerts, allowing users to receive notifications of specific events, such as motion detection, tampering, or unauthorized access.
- User Access Control: VMS implements role-based access control, enabling administrators to define user permissions and restrict access to video streams and system settings.
- Video analytics integration: Many VMS platforms offer integration with video analytics software, supporting advanced features such as people counting, facial recognition, object tracking, and more.
- Centralized Management: VMS provides a centralized interface for managing and monitoring video equipment in different locations, ideal for multi-site or enterprise-level installations.
- Integration with third-party devices: VMS typically supports integration with a variety of third-party devices, including cameras, access control systems, and other security devices from different manufacturers.
- Scalability and Flexibility: VMS systems are designed to be scalable and can be easily expanded as the monitoring infrastructure grows. It is flexible and can be adapted to a variety of camera types and technologies.
- Data Security and Privacy: VMS ensures the security of video data through encryption, user authentication and secure access protocols to prevent unauthorized access and data leakage.
What video devices are included in multi-brand device management?
By integrating and managing a video management system (VMS), multi-brand device management of various video devices from different manufacturers can be achieved. Common video equipment includes:
- IP Camera: Different brands of Internet Protocol (IP) cameras with various features and functions.
- Network Video Recorder (NVR): A recording device that stores video footage from an IP camera.
- Digital Video Recorder (DVR): An analog or digital recording device that is compatible with analog cameras.
- Video encoder/decoder: A device that converts analog video signals to digital signals, or converts digital video signals to analog video signals.
- Thermal camera: Specialized camera that can detect heat signals and work in low light conditions.
- Pan-Tilt (PTZ) Camera: A camera with remote control capabilities that can be used to adjust pan, tilt, and zoom functions.
- Dome Camera: A camera enclosed in a dome-shaped housing for covert surveillance.
- Bullet Camera: A camera designed in a cylindrical or bullet shape, suitable for outdoor use.
- Box Camera: A traditional camera with interchangeable lenses that allows for customizable viewing angles.
- Fisheye Camera: A camera with a wide-angle lens that allows Provides a 360-degree view.
- Doorbell Camera: A camera integrated into the doorbell system for video door surveillance.
- License Plate Recognition (LPR) Camera: Cameras equipped with software for capturing and identifying license plates.
- Thermal Cameras: Cameras that detect thermal signatures for surveillance in challenging environments.
- 360 Degree Camera: A camera capable of capturing a complete 360 degree view.
- Hidden Camera: A hidden camera designed for covert surveillance.
Things to consider when choosing a video management system (VMS)
When choosing a video that is compatible with various device brands When managing your VMS, there are several key factors to consider to ensure seamless integration and efficient management of your monitoring infrastructure. Here are the important factors to consider:
- Equipment Compatibility: It is critical to verify that the video management system (VMS) you choose is compatible with various camera types, makes and models. This includes support for IP and analog cameras. Thoroughly check for compatibility with well-known camera manufacturers and any specialized cameras required for your specific use case. VMS with broad device compatibility ensures a seamless integration process and maximizes monitoring system flexibility.
- Scalability: When selecting a video management system (VMS), it is critical to evaluate its scalability to meet the future expansion needs of the surveillance system. The ideal VMS should be able to easily accommodate more cameras and devices as the organization's needs and infrastructure grow. This ensures a future-proof solution that can adapt to changing security needs without compromising performance.
- Third-Party Integration: Look for a video management system (VMS) that can seamlessly integrate with third-party devices and systems, including access control, intrusion detection, and video analytics. This feature significantly enhances the overall functionality and efficiency of the entire security ecosystem. By integrating various tools, VMS enhances the effectiveness of existing security measures by optimizing data sharing, automating responses, and enabling monitoring infrastructure to work in harmony.
- User-Friendly Interface: An intuitive user interface is crucial for smooth operation and efficient management of a video management system (VMS). A VMS should have a simple layout, easy navigation, and powerful search and playback capabilities. The user-friendly interface simplifies tasks, reduces training time, and gives users quick and easy access to critical video data, enhancing overall user experience and productivity.
- Video quality and bandwidth management: Ensure that the video management system (VMS) can handle high-resolution video streams without impacting network bandwidth. Look for essential features like adaptive streaming and video compression that intelligently optimize bandwidth usage. By integrating these features, VMS can maintain excellent video quality while effectively managing network resources to ensure a seamless and optimized video surveillance experience.
- Storage and Retention Options: Evaluate the storage capabilities of the video management system (VMS) and the availability of various video data retention options. Look for features like flexible storage allocation, automatic data archiving, and compatibility with external storage devices. These capabilities enable VMS to effectively manage video data storage, optimize space utilization, and ensure seamless access to historical footage when needed, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of the surveillance system.
- Remote Access and Mobile Support: The Verified Video Management System (VMS) provides easy remote access to live and recorded video streams, allowing users to access from a variety of devices, including smartphones and tablets computer. This essential feature ensures seamless monitoring and surveillance anytime, anywhere, allowing users to stay connected to their security systems anytime, anywhere, enhancing situational awareness and response capabilities.
- Security and Encryption: When dealing with sensitive video data, it is crucial to prioritize security. Ensure video management systems (VMS) employ strong encryption protocols, user authentication mechanisms, and role-based access controls to prevent unauthorized access. These stringent security measures enhance VMS, protecting valuable video footage from potential threats and unauthorized users, ensuring data privacy and maintaining the integrity of the surveillance system.
- Reliability and Redundancy: When selecting a video management system (VMS), prioritize solutions that offer reliability and redundancy features, such as failover servers and backup options. These basic features ensure uninterrupted video surveillance, even in the event of hardware failure. By integrating redundancy, VMS ensures continuous operations, enhances system resiliency and minimizes potential outages, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and performance of the monitoring infrastructure.
- Vendor Support and Updates: When considering a video management system (VMS), evaluate the vendor's reputation and reliability. Choose a trusted provider that offers consistent software updates, reliable technical support, and ongoing product development. This commitment to vendor support ensures your VMS remains up-to-date with features, improvements, and security patches, as well as guaranteeing access to help when needed, ultimately helping to provide a smoother, more effective video surveillance experience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: When selecting a video management system (VMS), carefully evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, maintenance, and hardware requirements. This review ensures that the selected VMS is aligned with the organization's budget constraints and long-term goals. By prioritizing cost-effectiveness, you can optimize your investment and obtain a VMS solution that delivers strong performance and value without straining financial resources.
- User Training and Support: Verify that the VMS vendor provides comprehensive training and valuable resources to help users become proficient in utilizing the system's features and functionality. Obtaining proper training and ongoing support ensures users are able to maximize the capabilities of VMS, enhance their expertise in the operating system, and optimize overall video surveillance operations.
Ensure smooth control of video equipment and improve overall surveillance performance through seamless integration, scalability and user-friendly interface. The power of third-party integration opens up a world of potential to leverage a variety of devices and technologies to enhance the security ecosystem. In addition, through careful consideration of device compatibility, security measures and cost-effectiveness, the potential of VMS can be maximized while achieving goals within budget constraints
The above is the detailed content of Application of VMS: Improving multi-brand equipment management efficiency. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PMVibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AMFebruary 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
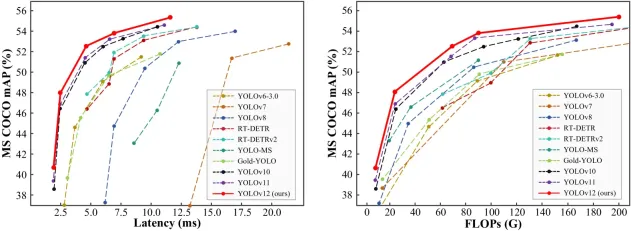 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AMYOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 How to Use DALL-E 3: Tips, Examples, and FeaturesMar 09, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to Use DALL-E 3: Tips, Examples, and FeaturesMar 09, 2025 pm 01:00 PMDALL-E 3: A Generative AI Image Creation Tool Generative AI is revolutionizing content creation, and DALL-E 3, OpenAI's latest image generation model, is at the forefront. Released in October 2023, it builds upon its predecessors, DALL-E and DALL-E 2
 Elon Musk & Sam Altman Clash over $500 Billion Stargate ProjectMar 08, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Elon Musk & Sam Altman Clash over $500 Billion Stargate ProjectMar 08, 2025 am 11:15 AMThe $500 billion Stargate AI project, backed by tech giants like OpenAI, SoftBank, Oracle, and Nvidia, and supported by the U.S. government, aims to solidify American AI leadership. This ambitious undertaking promises a future shaped by AI advanceme
 Google's GenCast: Weather Forecasting With GenCast Mini DemoMar 16, 2025 pm 01:46 PM
Google's GenCast: Weather Forecasting With GenCast Mini DemoMar 16, 2025 pm 01:46 PMGoogle DeepMind's GenCast: A Revolutionary AI for Weather Forecasting Weather forecasting has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving from rudimentary observations to sophisticated AI-powered predictions. Google DeepMind's GenCast, a groundbreak
 Sora vs Veo 2: Which One Creates More Realistic Videos?Mar 10, 2025 pm 12:22 PM
Sora vs Veo 2: Which One Creates More Realistic Videos?Mar 10, 2025 pm 12:22 PMGoogle's Veo 2 and OpenAI's Sora: Which AI video generator reigns supreme? Both platforms generate impressive AI videos, but their strengths lie in different areas. This comparison, using various prompts, reveals which tool best suits your needs. T
 Which AI is better than ChatGPT?Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
Which AI is better than ChatGPT?Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PMThe article discusses AI models surpassing ChatGPT, like LaMDA, LLaMA, and Grok, highlighting their advantages in accuracy, understanding, and industry impact.(159 characters)


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






