Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >Super practical advanced Linux commands that programmers must understand!
Super practical advanced Linux commands that programmers must understand!
- Linux中文社区forward
- 2023-08-02 15:47:531337browse
Preface
I have been struggling in the pit of operation and maintenance for several years. I still remember that when I first started, I only knew Use some simple commands, and when writing scripts, you also want to be as simple as possible, so sometimes the scripts written are long and smelly.

Like some advanced commands, such as Xargs command, pipeline command, automatic response command, etc. If I had known that, I might have written a concise and efficient script.
No matter for any reason, I want to explain the usage of some advanced commands used in Linux to benefit others and myself. If I don’t remember it in the future, I can also look back at it.
##1. Practical xargs command
For example, we want to find files ending with .conf in a certain path and classify these files. The common approach is to first find the files ending with .conf and then output them to In a file, then cat the file, and use the file file classification command to classify the output files.
This ordinary method is indeed a little troublesome, so this is when the xargs command comes in handy.
Example 1: Find the files ending with .conf in the / directory and classify the files
Command:
find / -name *.conf -type f \ -print | xargs file
The output results are as follows Display:
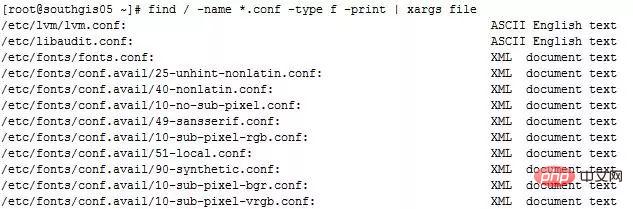
xargs Not only can you add file classification commands after it, you can also add many other commands, for example, to be honest tar command, you can use the find command with the tar command to find the special file in the specified path using the find command, and then use the tar command to directly package the found file. The command is as follows:
find / -name *.conf -type f \ -print | xargs tar cjf test.tar.gz
二、命令或脚本后台运行
有时候我们进行一些操作的时候,不希望我们的操作在终端会话断了之后就跟着断了,特别是一些数据库导入导出操作,如果涉及到大数据量的操作,我们不可能保证我们的网络在我们的操作期间不出问题,所以后台运行脚本或者命令对我们来说是一大保障。
比如说我们想把数据库的导出操作后台运行,并且将命令的操作输出记录到文件,那么我们可以这么做:(反斜杠代表换行,可以忽略)
nohup mysqldump -uroot -pxxxxx \ —all-databases > \ ./alldatabases.sql &(xxxxx是密码)
当然如果你不想密码明文,你还可以这么做:
nohup mysqldump -uroot -pxxxxx \ —all-databases \ > ./alldatabases.sql (后面不加&符号)
执行了上述命令后,会提示叫你输入密码,输入密码后,该命令还在前台运行,但是我们的目的是后天运行该命令,这个时候你可以按下Ctrl+Z,然后在输入bg就可以达到第一个命令的效果,让该命令后台运行,同时也可以让密码隐蔽输入。
命令后台执行的结果会在命令执行的当前目录下留下一个nohup.out文件,查看这个文件就知道命令有没有执行报错等信息。
三、找出当前系统内存使用量较高的进程
在很多运维的时候,我们发现内存耗用较为严重,那么怎么样才能找出内存消耗的进程排序呢?
命令:
ps -aux | sort -rnk 4 | head -20
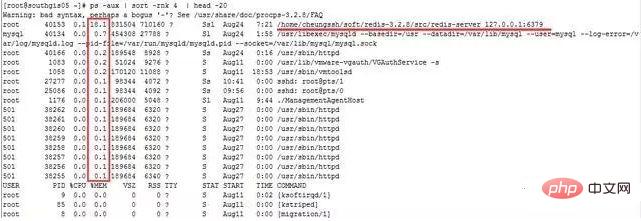
输出的第4列就是内存的耗用百分比。最后一列就是相对应的进程。
四、找出当前系统CPU使用量较高的进程
在很多运维的时候,我们发现CPU耗用较为严重,那么怎么样才能找出CPU消耗的进程排序呢?
命令:
ps -aux | sort -rnk 3 | head -20
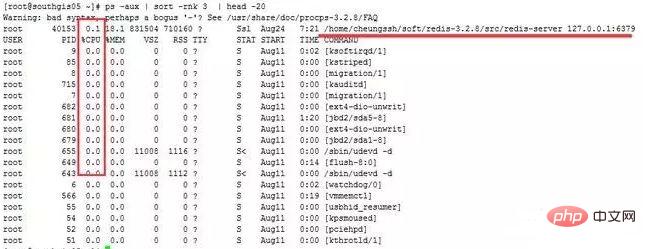
输出的第3列为CPU的耗用百分比,最后一列就是对应的进程。
牛逼啊!接私活必备的 N 个开源项目!赶快收藏
我想大家应该也发现了,sort 命令后的3、4其实就是代表着第3列进行排序、第4列进行排序。
五、同时查看多个日志或数据文件
在日常工作中,我们查看日志文件的方式可能是使用tail命令在一个个的终端查看日志文件,一个终端就看一个日志文件。包括我在内也是,但是有时候也会觉得这种方式略显麻烦,其实有个工具叫做multitail可以在同一个终端同时查看多个日志文件。
首先安装multitail:
wget ftp://ftp.is.co.za/mirror/ftp.rpmforge.net/redhat/el6/en/x86_64/dag/RPMS/multitail-5.2.9-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm yum -y localinstall multitail-5.2.9-1.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm
multitail工具支持文本的高亮显示,内容过滤以及更多你可能需要的功能。
如下就来一个有用的例子:
此时我们既想查看secure的日志指定过滤关键字输出,又想查看实时的网络ping情况:
命令如下:
multitail -e "Accepted" \/var/log/secure -l "ping baidu.com"
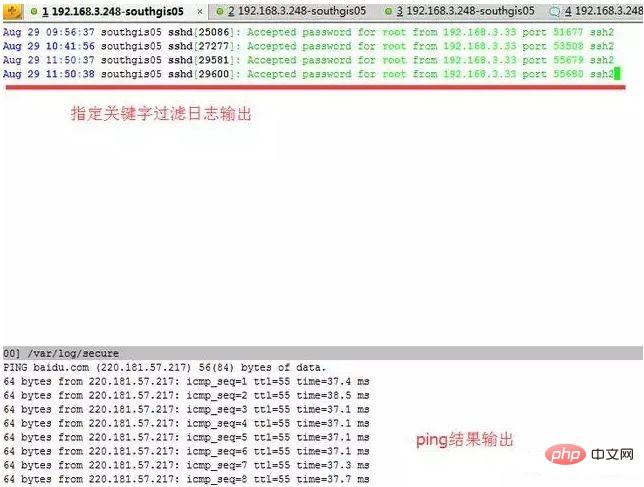
不是很方便?如果平时我们想查看两个日志之间的关联性,可以观察日志输出是否有触发等。如果分开两个终端可能来回进行切换有点浪费时间,这个multitail工具查看未尝不是一个好方法。
##6. Continue pinging and record the results to the log
At this time, if you ping a few packets and throw out the results, people will refute you. It was just a problem during that period. Now that the business is back to normal, the network must be normal. You're probably going to be pissed off at this point.
你要是再拿出zabbix等网络监控的数据,这个时候就不太妥当了,zabbix的采集数据间隔你不可能设置成1秒钟1次吧?小编就遇到过这样的问题,结果我通过以下的命令进行了ping监控采集。 然后再有人让我背锅的时候,我把出问题时间段的ping数据库截取出来,大家公开谈,结果那次被我叼杠回去了,以后他们都不敢轻易甩锅了,这个感觉好啊。 命令: 输出的结果会记录到/tmp/jiguang.log 中,每秒钟新增一条ping记录,如下: 七、查看tcp连接状态 指定查看80端口的tcp连接状态,有利于分析连接是否释放,或者攻击时进行状态分析。另外,搜索公众号Java架构师技术后台回复“面试题”,获取一份惊喜礼包。 命令: 八、查找80端口请求数最高的前20个IP 有时候业务的请求量突然上去了,那么这个时候我们可以查看下请求来源IP情况,如果是集中在少数IP上的,那么可能是存在攻击行为,我们使用防火墙就可以进行封禁。命令如下: #Nine , ssh implements port forwarding Instance background: Our company has a bastion machine, and any operation needs to be performed on the bastion machine. Some developers need to access the head panel of ElasticSearch to view the cluster status, but we don’t want to Map the 9200 port of ElasticSearch and still want to access it through the bastion machine. Therefore, the request to the bastion machine (192.168.1.15) is forwarded to 9200 of the server ElasticSearch (192.168.1.19). Example: Forward the 9200 port access sent to the local machine (192.168.1.15) to the 9200 port of 192.168.1.19 记住:前提是先进行秘钥传输。 命令执行完后,访问192.168.1.15:9200端口则真实是访问192.168.1.19:9200端口。ping api.jpush.cn | awk '{ print $0 " " strftime(“%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S”,systime()) }' >> /tmp/jiguang.log &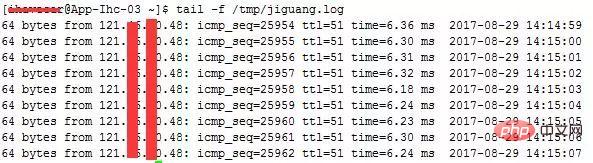
netstat -nat |awk \'{print $6}' |sort|\uniq -c|sort -rn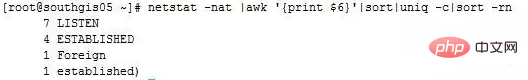
netstat -anlp|grep 80|grep tcp|awk '{print $5}' \|awk -F: '{print $1}'|sort|uniq -c|sort -nr|head -n20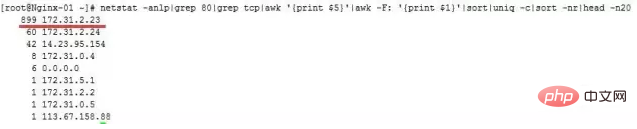
ssh -p 22 -C -f -N -g -L \9200:192.168.1.19:9200 \ihavecar@192.168.1.19
The above is the detailed content of Super practical advanced Linux commands that programmers must understand!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

