Operating system interview high-frequency test points
- 嵌入式Linux充电站forward
- 2023-07-31 16:23:071268browse
1. The difference between process and thread
Process is resource allocation The smallest unit, thread is the basic unit of CPU scheduling. The process has an independent address space, and the thread does not have an independent address space, but it has an independent stack and local variables. In multi-process and multi-thread, multi-process is more robust than multi-thread. Since the process has an independent address space, when a process ends abnormally, it will not affect other processes; threads do not have an independent address space, and when a thread ends abnormally, it may affect other threads. The cost of creating a process is greater than that of creating a thread; the cost of process context switching is greater than the cost of thread context switching.
2. What are the methods of inter-process communication?
Pipeline: (1) Unnamed pipe: used for inter-process communication with affinity, in the form of byte stream. (2) Famous pipes: It breaks the boundaries of romantic relationships and enables two unrelated processes to communicate through pipes in the form of byte streams. Message Queue: Data is transmitted in blocks, but copying data from user space to kernel space is expensive. Shared memory: There is a problem of resource competition Signal: Asynchronous communication Semaphore: Synchronous mutual exclusion socket communication: Implement communication between two computers .
3. Process scheduling algorithm
First come, first served scheduling algorithm ; Execution of one process according to the order of joining the queue Shortest job priority scheduling algorithm; Prioritize the process with the shortest running time High response ratio priority scheduling algorithm; when scheduling the process, first calculate the response ratio priority, and then select the process with the highest response ratio priority to run Time slice rotation scheduling algorithm; The time that each process can run is the same, and the processes run in turn according to the time slice Highest priority scheduling algorithm; Select the process with the highest priority Multi-level feedback queue scheduling algorithm; Set up a multi-level queue, and the queue priority will be from High to bottom, time slice from small to large
4. What is an orphan process
(1) The parent process first At the end of the child process, the child process becomes an orphan process.
(2) Linux system regulations: All orphan processes become child processes of a special process (process 1, which is the init process).
5. What are the multi-thread synchronization mechanisms?
Mutex Read-write lock Condition variable Semaphore Spin lock
#6. Brief description of process memory partition
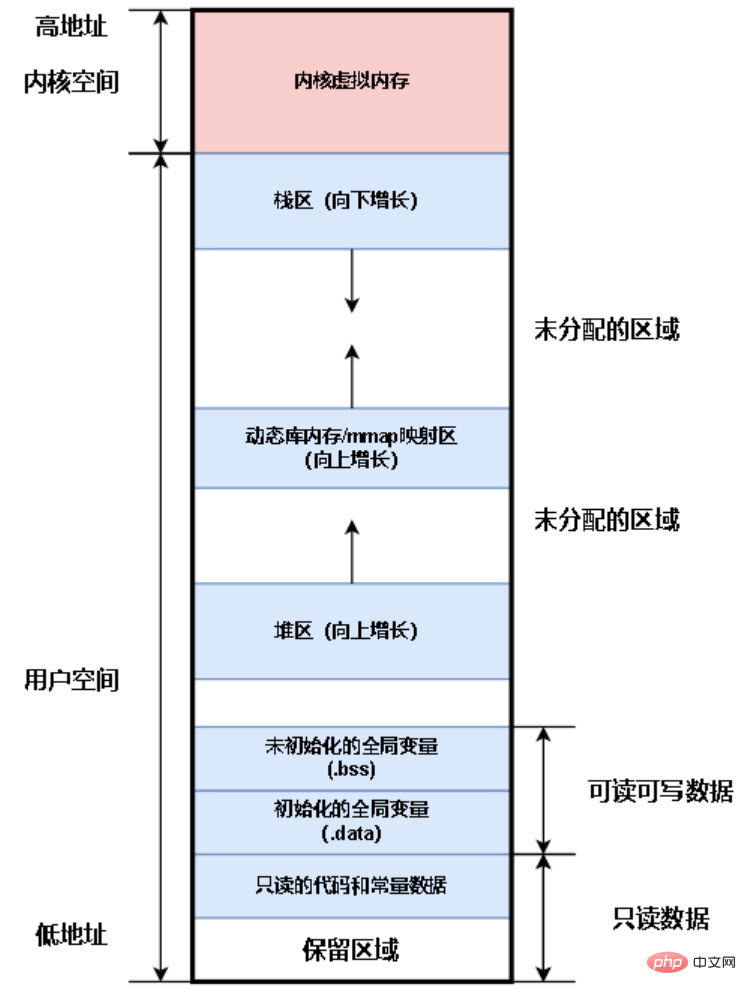
Kernel space: stores operating system code and data Stack area: stores local variables, function parameter values, etc. This area is controlled by the operating system Dynamic library/shared memory mapping area: The dynamic library that the executable program depends on is loaded in this area; the shared memory mapped by mmap is also in this area Heap area: A memory area provided for programmers to operate by themselves. Malloc/free and new/delete operate on this memory Readable and writable data area:
(1) .bss section: stores uninitialized global variables and static variables that are initialized to 0.
(2).data section: stores global variables, static variables, and const constants that are not initialized to 0.
Read-only data area: stores binary code, some const modified variables, string constants, etc.
7. Memory fragmentation
#How to generate memory fragmentation
Programmer In the program, malloc is used to dynamically apply for memory from the heap space of the virtual memory, and free is used to release the memory. If the program has a large number of malloc/free operations and runs for a long time, the heap space of the virtual memory can easily cause memory fragmentation
-
What is memory fragmentation
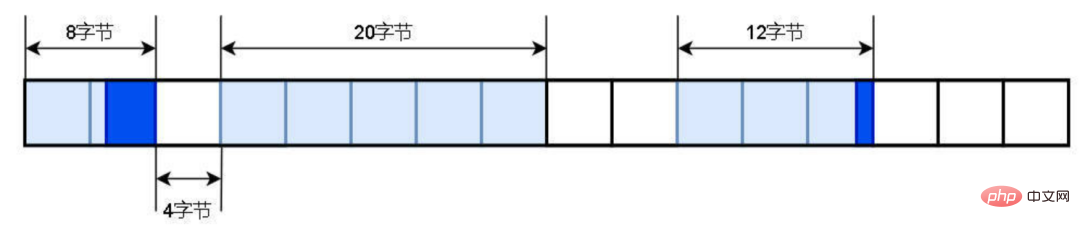
Memory fragmentation means that there is a lot of discrete free memory left in the heap space, but it cannot satisfy malloc's allocation request. Memory fragmentation is divided into external fragmentation and internal fragmentation. The following figure describes the memory allocation of part of the heap space. The heap space is divided into many allocation blocks in units of 4 bytes. The white blocks represent free memory, and the light blue and dark blue blocks represent allocated memory. Assume that the smallest unit of memory allocation is an allocation block (4 bytes).
External fragmentation: Since there is no free memory (white block) with a continuous allocation block size of 4 in the heap space, but there are many discrete ones less than 4 allocation block size of free memory. So when malloc(16) applies for 16 bytes, the allocation will fail. The reason is that there is no free memory for 4 consecutive allocation blocks, but there is free memory for less than 4 allocation blocks. These memories are called external fragments Internal fragmentation: Since the minimum unit of allocated memory is an allocation block (4 bytes), when malloc(5) applies for 5 bytes, the heap space is allocated two free blocks A total of 8 bytes, but the program only needs 5 bytes, and the remaining 3 bytes (dark blue) are not used. These 3 bytes of memory are called internal fragmentation
8. What is the difference between heap and stack?
Different allocation methods
Stack: automatically allocated by the system
Heap: Manual application by the programmer
The application size is different
Stack: The memory size of the stack area is fixed, as long as If the requested memory is less than the remaining memory in the stack area, the allocation can be successful, otherwise the stack will overflow.
Heap: The memory size of the heap area is determined by the computer’s virtual memory,
9. The difference between mutex locks and semaphores
(1) Semaphores are used for thread synchronization, and mutex locks are used for thread mutual exclusion.
(2) The semaphore can be a non-negative integer, which can realize multi-thread synchronization of multiple similar resources; the mutex can only be 0/1, which can only be used for mutually exclusive access to one resource.
(3) The semaphore can be released by one thread and obtained by another thread; the locking and unlocking of the mutex must be used by the same thread respectively, and attention must be paid to the use of multiple mutexes by multiple threads Unify the order, otherwise deadlock may occur.
10. The difference between synchronization and asynchronousness
Synchronization: A calls B, it must Wait for B to finish processing and return before A can continue to execute Asynchronous: A calls B without waiting for B to finish processing. A can continue to execute. After B finishes processing, it notifies A through callback etc.
11. Deadlock
What is deadlock Lock? What causes deadlock?
(1) Deadlock refers to a deadlock (waiting for each other) caused by multiple processes competing for resources. Without external force, these processes will not be able to move forward.
(2) Reason: ① Insufficient system resources. ② Improper allocation of resources. ③The order of process advancement is inappropriate.
What are the four necessary conditions for deadlock?
(1)Mutual exclusion condition: A resource can only be used by one process at a time, and other processes can only wait.
(2)Request and retention conditions: The process has obtained at least one resource, but has made a new resource request, and the resource has been occupied by other processes. At this time, the process is Blocking, but still holding on to the acquired resources.
(3)Nondeprivation condition: The resources obtained by the process cannot be deprived by other processes and can only be released by itself.
(4)Loop waiting condition: Several processes form a relationship of cyclic waiting for resources end to end.
Note: The above four conditions are indispensable.
How to deal with deadlock?
(1) Prevent deadlock: By setting some restrictions, destroy the necessary conditions for deadlock.
(2) Avoid deadlock: During the resource allocation process, use some method to prevent the system from entering an unsafe state, thereby avoiding deadlock.
(3) Detect and remove deadlock: Allow deadlock to occur, but after passing the system detection, take some measures to clear the deadlock.
How to prevent deadlock?
(1)Destroy the "request and hold conditions":
①Static allocation, that is, each process applies for all the resources it needs when it starts executing:
②Dynamic allocation, that is, each process does not occupy the system when it applies for the resources it needs resource.
(2)Destroy the "inalienable condition": During a process's blocking and waiting period, the resources it occupies are implicitly released and then used by other processes, while the blocked and waiting resources can only be obtained All resources required to restart.
(3)Destroy the "cyclic waiting condition": Adopt the orderly allocation of resources, number all resources, use relatively large numbers for scarce resources, and a process can only obtain a smaller number. Only resources with larger numbers can apply for resources with larger numbers
The above is the detailed content of Operating system interview high-frequency test points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

