
Wireshark is a free and open source, cross-platform, GUI-based network packet analyzer available for Linux, Windows, MacOS, Solaris, and more. It captures network packets in real-time and presents them in human-readable format. It enables us to monitor network packets at a microscopic level. It also has a command line program called tshark which performs the same functions as Wireshark, but through the terminal rather than through the GUI.
Wireshark can be used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and for educational purposes. Wireshark uses a library called pcap to capture network packets.
Features of Wireshark
- Supports inspection of hundreds of protocols
- Ability to capture packets in real time and save them for later offline analysis
- Some Filters for analyzing data
- Captured data can be compressed and decompressed dynamically
- Supports multiple data analysis file formats, and output can also be saved in XML, CSV, plain text format
- Can capture data from multiple interfaces such as Ethernet, WiFi, Bluetooth, USB, Frame Relay, Token Ring, etc.
Prerequisites
- Pre-installed Ubuntu 22.04
- Local user with sudo privileges
- Internet connection
Wireshark installation steps
Install from Ubuntu repository
Wireshark The package is available in the default Ubuntu repository and can be simply installed using the following command. But you may not be able to get the latest version of wireshark.
$ sudo apt update$ sudo apt install wireshark
 Apt-Command-Install-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Apt-Command-Install-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Select "Yes" to allow non-superusers to use Wireshark to capture packets:
 Allow-Non-SuperUsers-To-Capture-Packets-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Allow-Non-SuperUsers-To-Capture-Packets-Wireshark-Ubuntu
After successful installation, access the Wireshare UI. Search for "Wireshark" in "Activities" and click on its icon.
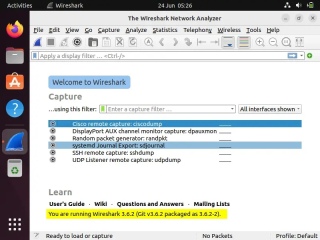 Wireshark-UI-Ubuntu-Linux-Desktop
Wireshark-UI-Ubuntu-Linux-Desktop
The above confirms that your Wireshark installation has been completed successfully.
Install the latest version
If you want to install the latest version of Wireshark, we must enable the official Wireshark repository using the following apt command:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:wireshark-dev/stable$ sudo apt update
Now, To install the latest version of Wireshark, run:
$ sudo apt install wireshark -y
After installing Wireshark, verify its version:
$ wireshark --version
 Wireshark-Version-Check-Ubuntu-Linux
Wireshark-Version-Check-Ubuntu-Linux
To allow normal users to use Wireshark to consume and capture packets, run the following command:
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure wireshark-common
Select "Yes" and press Enter.
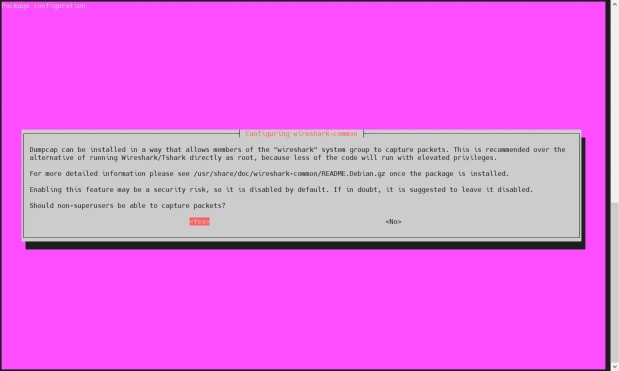 Allow-Regular-User-Use-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Allow-Regular-User-Use-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Use the usermod command to add local users to wireshark Group:
$ sudo usermod -aG wireshark $USER$ newgrp wireshark
For the above changes to take effect, please restart the system.
$ sudo reboot
Use Wireshark to capture packets
Start Wireshark and search for "wireshark" from "Activities"->.
 Access-Wireshark-Ubuntu-Desktop
Access-Wireshark-Ubuntu-Desktop
Access-Wireshark-Ubuntu-Desktop
Click the Wireshark icon,
 Choose-Interface-Wireshark-UI-Ubuntu
Choose-Interface-Wireshark-UI-Ubuntu
All these are the interfaces through which we can capture network packets. Depending on the interface on your system, this page may look different.
We choose "enp0s3" to capture the network traffic of this interface. After selecting the interface, we can start populating network packets for all the devices on our network (see screenshot below)
 Capturing-Packets-WireShark-UI-Ubuntu
Capturing-Packets-WireShark-UI-Ubuntu
The first time we see this page, we may be overwhelmed by the data displayed in this screen and may think of how to organize this data, but don’t worry, one of the best features of Wireshark is its filter.
We can sort/filter data based on IP address, port number, we can also use source and destination filters, packet size, etc. We can also combine 2 or more filters together to create More comprehensive search. We can write a filter in the "Apply a Display Filter" tab or select one of the already created rules. If you want to select a pre-built filter, click the "Flag" icon and select the "Apply Display Filter" tab.
 IP-Based-Filtering-WireShark-UI-Ubuntu
IP-Based-Filtering-WireShark-UI-Ubuntu
We can also filter data based on color code, by default, light purple is TCP Traffic, light blue is UDP traffic, and black identifies packets with errors. To see the meaning of these codes, click "View" -> "Coloring Rules", we can also change these codes.
 Coloring-Rules-WireShark-Ubuntu
Coloring-Rules-WireShark-Ubuntu
Once we get the desired results, we can click on any captured packet to get information about that packet for more details, which will display all the data about that network packet.
To stop capturing packets, click the red stop button and save the captured packets to a file.
 Save-Captured-Packets-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Save-Captured-Packets-Wireshark-Ubuntu
Summary
Wireshark is a very powerful tool that takes some time to Get used to it and master it, this article will help you get started.
The above is the detailed content of How to install and use Wireshark in Ubuntu 22.04. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 NGINX vs. Apache: A Look at Their ArchitecturesApr 28, 2025 am 12:13 AM
NGINX vs. Apache: A Look at Their ArchitecturesApr 28, 2025 am 12:13 AMThe main architecture difference between NGINX and Apache is that NGINX adopts event-driven, asynchronous non-blocking model, while Apache uses process or thread model. 1) NGINX efficiently handles high-concurrent connections through event loops and I/O multiplexing mechanisms, suitable for static content and reverse proxy. 2) Apache adopts a multi-process or multi-threaded model, which is highly stable but has high resource consumption, and is suitable for scenarios where rich module expansion is required.
 NGINX vs. Apache: Examining the Pros and ConsApr 27, 2025 am 12:05 AM
NGINX vs. Apache: Examining the Pros and ConsApr 27, 2025 am 12:05 AMNGINX is suitable for handling high concurrent and static content, while Apache is suitable for complex configurations and dynamic content. 1. NGINX efficiently handles concurrent connections, suitable for high-traffic scenarios, but requires additional configuration when processing dynamic content. 2. Apache provides rich modules and flexible configurations, which are suitable for complex needs, but have poor high concurrency performance.
 NGINX and Apache: Understanding the Key DifferencesApr 26, 2025 am 12:01 AM
NGINX and Apache: Understanding the Key DifferencesApr 26, 2025 am 12:01 AMNGINX and Apache each have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice should be based on specific needs. 1.NGINX is suitable for high concurrency scenarios because of its asynchronous non-blocking architecture. 2. Apache is suitable for low-concurrency scenarios that require complex configurations, because of its modular design.
 NGINX Unit: Key Features and CapabilitiesApr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
NGINX Unit: Key Features and CapabilitiesApr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AMNGINXUnit is an open source application server that supports multiple programming languages and provides functions such as dynamic configuration, zero downtime updates and built-in load balancing. 1. Dynamic configuration: You can modify the configuration without restarting. 2. Multilingual support: compatible with Python, Go, Java, PHP, etc. 3. Zero downtime update: Supports application updates that do not interrupt services. 4. Built-in load balancing: Requests can be distributed to multiple application instances.
 NGINX Unit vs. Other Application ServersApr 24, 2025 am 12:14 AM
NGINX Unit vs. Other Application ServersApr 24, 2025 am 12:14 AMNGINXUnit is better than ApacheTomcat, Gunicorn and Node.js built-in HTTP servers, suitable for multilingual projects and dynamic configuration requirements. 1) Supports multiple programming languages, 2) Provides dynamic configuration reloading, 3) Built-in load balancing function, suitable for projects that require high scalability and reliability.
 NGINX Unit: The Architecture and How It WorksApr 23, 2025 am 12:18 AM
NGINX Unit: The Architecture and How It WorksApr 23, 2025 am 12:18 AMNGINXUnit improves application performance and manageability with its modular architecture and dynamic reconfiguration capabilities. 1) Modular design includes master processes, routers and application processes, supporting efficient management and expansion. 2) Dynamic reconfiguration allows seamless update of configuration at runtime, suitable for CI/CD environments. 3) Multilingual support is implemented through dynamic loading of language runtime, improving development flexibility. 4) High performance is achieved through event-driven models and asynchronous I/O, and remains efficient even under high concurrency. 5) Security is improved by isolating application processes and reducing the mutual influence between applications.
 Using NGINX Unit: Deploying and Managing ApplicationsApr 22, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Using NGINX Unit: Deploying and Managing ApplicationsApr 22, 2025 am 12:06 AMNGINXUnit can be used to deploy and manage applications in multiple languages. 1) Install NGINXUnit. 2) Configure it to run different types of applications such as Python and PHP. 3) Use its dynamic configuration function for application management. Through these steps, you can efficiently deploy and manage applications and improve project efficiency.
 NGINX vs. Apache: A Comparative Analysis of Web ServersApr 21, 2025 am 12:08 AM
NGINX vs. Apache: A Comparative Analysis of Web ServersApr 21, 2025 am 12:08 AMNGINX is more suitable for handling high concurrent connections, while Apache is more suitable for scenarios where complex configurations and module extensions are required. 1.NGINX is known for its high performance and low resource consumption, and is suitable for high concurrency. 2.Apache is known for its stability and rich module extensions, which are suitable for complex configuration needs.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version







