 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance How to solve the problem of insufficient disk space in Linux system
How to solve the problem of insufficient disk space in Linux systemHow to deal with the problem of insufficient disk space usage in Linux systems
Introduction:
In the process of using the Linux operating system, sometimes you will encounter the problem of insufficient disk space
. When the disk space is insufficient, the system will have many problems, such as being unable to install new software, unable to store large files, etc. This article will introduce several effective methods to help us deal with the problem of insufficient disk space in Linux systems.
1. Check the disk space usage
First of all, we need to understand the current disk space usage of each directory so that we can perform targeted optimization. You can use the following command to check the disk space usage:
df -h
This command will list the space usage of all partitions on the system and the mount point of each partition. By observing the directory corresponding to the mount point, you can determine which directory takes up a lot of disk space.
2. Clean up temporary files
In Linux systems, there are many temporary files that take up a lot of disk space. We can free up disk space by cleaning these temporary files regularly. The following are the directories where some common temporary files are located:
/tmp: This directory is the default directory for storing temporary files. You can use the following command to clean up the temporary files in this directory:
rm -rf /tmp/*
/var/tmp: This directory is also the directory where temporary files are stored. Use the following command to clean it:
rm -rf /var/tmp/*
3. Clean up log files
In Linux In the system, log files also occupy a large amount of disk space. We can free up disk space by cleaning unnecessary log files. The following are the directories where some common log files are located:
/var/log: System log files are stored in this directory. Use the following command to clean up unnecessary log files:
rm -rf /var/log/ *
4. Compressed files
If we have some large files that are not used frequently and urgently need to free up disk space, we can consider compressing these files to save disk space. In Linux systems, you can use tools such as gzip, bzip2 or zip to compress and decompress files.
5. Delete unnecessary software and files
Sometimes we will install some unnecessary software in the system, or save some unused files. These will take up disk space. Therefore, unnecessary software and files can be deleted by using the following command:
sudo apt-get remove software package name
rm -rf file path
6. Clean the Recycle Bin
When we When you delete a file in the graphical interface, it will be put into the Recycle Bin and the disk space will not be released immediately. Therefore, we can manually empty the Recycle Bin to make space. The following is the command to empty the Recycle Bin:
rm -rf ~/.local/share/Trash/*
7. Adjust the log rotation policy
In the Linux system, the system will automatically rotate the logs , retain log files for a certain period of time. We can adjust the log rotation policy as needed to prevent log files from taking up too much disk space. You can edit the "/etc/logrotate.conf" file to configure log rotation.
8. Expand the disk space
If none of the above methods can meet your needs, then you need to consider expanding the disk space. We can expand disk space by adding a new hard drive, extending an existing hard drive partition, or adjusting the file system size.
Conclusion:
Insufficient disk space usage is a common problem in Linux systems, and it will affect the normal operation of the system. Through the methods introduced in this article, we can quickly and effectively deal with this problem. In daily use, we should also develop a good habit of regularly cleaning temporary files and log files to maintain sufficient disk space.
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the problem of insufficient disk space in Linux system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
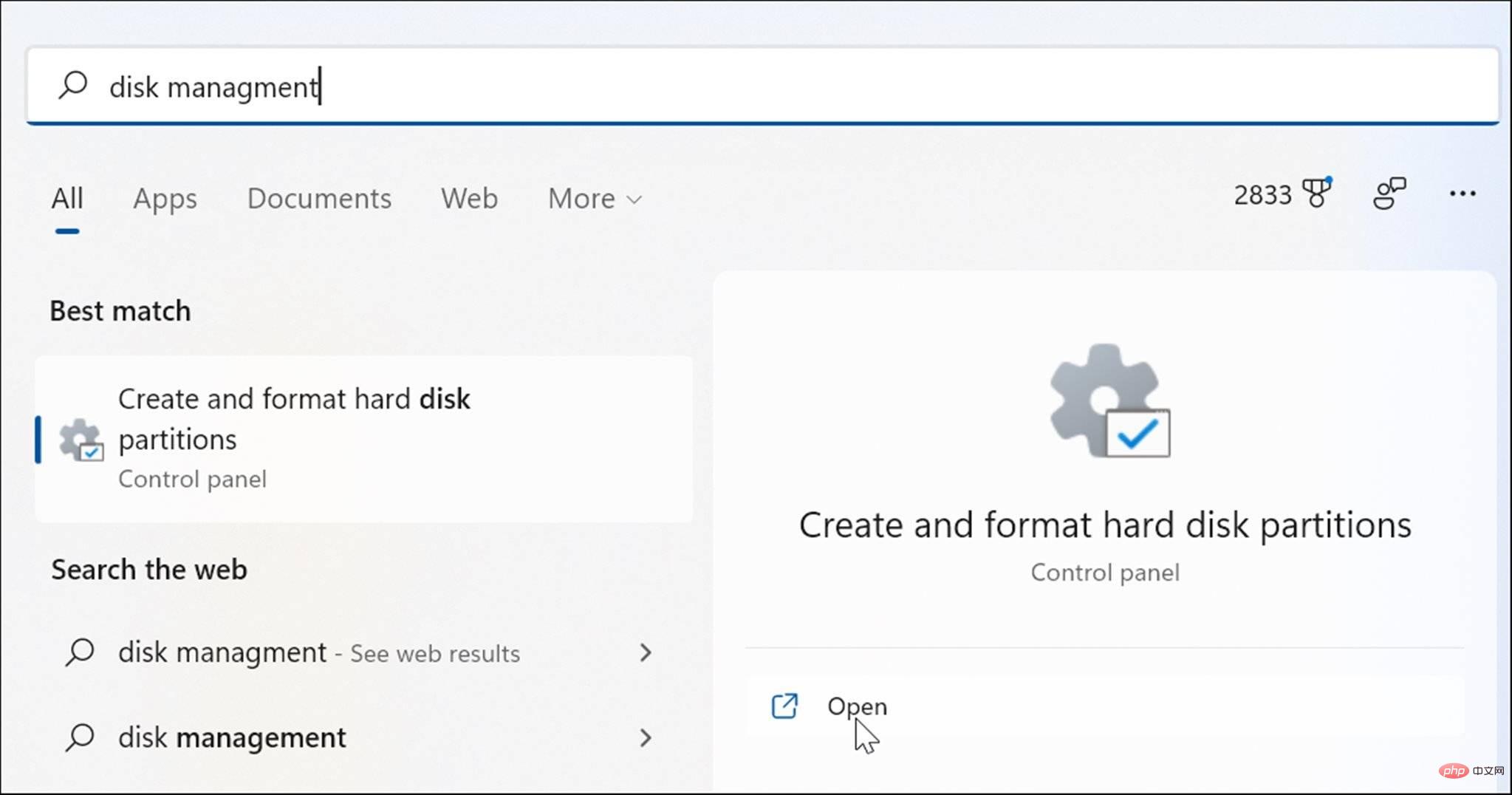 在 Windows 11 上打开磁盘管理的 6 种方法May 02, 2023 pm 04:25 PM
在 Windows 11 上打开磁盘管理的 6 种方法May 02, 2023 pm 04:25 PM需要在Windows11上快速分区新驱动器或更改驱动器号?您需要使用磁盘管理。这是在Windows11PC上启动它的方法。如果要在Windows11上创建和调整分区大小、初始化硬盘驱动器、更改驱动器号等,则需要使用磁盘管理工具。您可以通过多种方式使用此工具,也可以打开它。如果您想加快工作流程,可以通过以下六种不同方式在Windows11中打开磁盘管理。1.搜索磁盘管理为了避免点击菜单,您可以搜索磁盘管理并直接打开它。要使用开始菜单中的搜索栏打开磁盘管理,请使用以下步骤:单击开始
![磁盘管理中未显示系统保留分区 [快速恢复]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/168376632735495.jpg) 磁盘管理中未显示系统保留分区 [快速恢复]May 11, 2023 am 08:52 AM
磁盘管理中未显示系统保留分区 [快速恢复]May 11, 2023 am 08:52 AM系统保留分区是否未显示在Windows10/11设备的磁盘管理中?系统保留分区或SRP是硬盘驱动器上的一个小分区,用于存储Windows启动信息。如果文件以某种方式被删除,则可能会出现操作系统启动问题。通常,如果分区大小小于600MB,则会出现此问题。系统保留分区在磁盘管理中可用,因为Windows没有为其分配驱动器号。因此,与其他驱动器不同,它不会在文件资源管理器中可见。如果从磁盘管理中删除系统保留分区,事情可能会变得很严重。如果发生这种情况,用户可能无法将Windows更新到
 win7磁盘管理在哪里Feb 29, 2024 pm 02:22 PM
win7磁盘管理在哪里Feb 29, 2024 pm 02:22 PM想必很多的用户都发现自己的内存有点多,快要满了,就想要了解一下磁盘管理在哪里进行,那就一起来看看win7系统中的磁盘管理在哪里吧。win7磁盘管理在哪里1、点击windoes按钮,找到“控制面板”然后点击。2、下一步将是寻找并单击“管理工具”这一选项。3、在这里,需要双击并启用“计算机管理”功能,这将会展示出一个全面的管理窗口。4、接下来,请点开位于该窗口左侧所列的“存储”类别项目。5、然后进一步单击“磁盘管理”,这样就能顺利地进行后续操作了。
 修复:新 SSD 未在 Windows 11、10 中显示Apr 14, 2023 pm 02:52 PM
修复:新 SSD 未在 Windows 11、10 中显示Apr 14, 2023 pm 02:52 PMSSD 彻底改变了技术世界。这些数据存储解决方案凭借其超快和无与伦比的读/写速度,让每个用户都渴望在其中安装系统操作系统。但是,如果您的新 SSD 没有出现在您的 Windows 设备上怎么办?这是插入系统的全新 SSD 可能面临的一个典型问题。不用担心。我们刚刚得到了正确的解决方案,您所要做的就是按照这些步骤操作,SSD 将立即回到您的文件资源管理器。解决方法——1. 检查SSD的连接。如果您使用的是 USB 集线器,请将 SSD 直接连接到您的系统。查看 SSD 的连接器是否有任何物理缺陷。
 win7如何磁盘分区Jan 08, 2024 pm 07:02 PM
win7如何磁盘分区Jan 08, 2024 pm 07:02 PMwin7系统是一款非常经典的电脑系统。最近很多的win7系统小伙伴们都在问win7如何磁盘分区?今天小编就为大家带来了win7系统磁盘分区教程让我们一起来看一下吧。win7如何磁盘分区的详细教程:图文详细教程:1、右键点击“计算机”,选择“管理”。2、在页面中找到存储,点开。3、在存储下的“磁盘管理”,双击打开。4、目前的分区状况。5、选择磁盘大的空间选择压缩卷。6、在压缩的对话框中,在“输入压缩空间量”上面输入压缩的大小,然后再点击“压缩”即可完成操作。7、如果需要将压缩卷合并到其他的磁盘的话
 windows10磁盘管理在哪位置介绍Jul 10, 2023 pm 06:37 PM
windows10磁盘管理在哪位置介绍Jul 10, 2023 pm 06:37 PMwindows10磁盘管理在哪呢,许多用户在使用win10的时候一定会碰到硬盘分配的难题,那么如何操作找到磁盘管理器呢,最先必须进到计算机管理界面,随后找到磁盘管理,这儿就可找到许多磁盘管理的相关内容,下面就告知用户们关于windows10磁盘管理在哪位置介绍的内容,用户们可以学习参照。windows10磁盘管理在哪1.最先进到win10系统桌面,鼠标右键此电脑图标,在发生的界面中挑选“管理”选项,进到下一步。(还可以按住WIN+X,随后挑选【计算机管理】进到)2.在开启的计算机管理界面中,点击
 教你如何清理c盘无用文件以优化win11Jan 10, 2024 am 12:00 AM
教你如何清理c盘无用文件以优化win11Jan 10, 2024 am 12:00 AM有些朋友在使用win11系统时,发现自己的c盘内存不足了,但是又不知道怎么清理其中的无用文件,其实系统自带了磁盘清理功能,我们可以直接使用它进行清理,下面就一起来看一下吧。win11怎么清理c盘无用文件1、首先在桌面上找到“此电脑”,双击打开它。2、接着右键选择c盘,点击最下方的“属性”3、在属性界面中选择“磁盘清理”如图所示。4、在其中勾选不需要的文件,然后点击下方“确定”5、最后在弹出提示窗口选择“删除文件”就可以了。
 win11怎么打开磁盘管理Jul 05, 2023 am 08:53 AM
win11怎么打开磁盘管理Jul 05, 2023 am 08:53 AMwin11怎么打开磁盘管理?近期有用户反映自己电脑上的本地磁盘找不到,那么对于这一情况应该如何打开磁盘显示呢?本期教程小编就来和大家讲讲Win11系统磁盘显示打开方法,有需要的朋友们一起来学习下吧。 Win11系统磁盘显示打开步骤 1、首先,鼠标右键桌面的开始菜单,打开运行窗口。 2、然后,输入gpedit.msc命令后点击确定按钮。 3、接着,在用户配置下找到管理模板菜单,点击打开Windows组件栏目。 4、随后,在文件资源管理器右侧双击打开隐藏我的电脑中的指定驱动选项。 5


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.





