Home >Common Problem >What is the principle of Java's reflection mechanism?
What is the principle of Java's reflection mechanism?
- 百草Original
- 2023-06-21 10:53:033244browse
The principle of Java reflection mechanism is that when a bytecode file is loaded into memory, the jvm will dissect the bytecode and create a Class object of the object. The jvm will store all the bytecode file information. To the Class object, as long as the Class object is obtained, the object can be used to set the properties or methods of the object, etc. The reflection mechanism is the function of knowing all the attributes and methods of any class in the running state. For any object, it can call any of its attributes and methods, dynamically obtain information, and dynamically call object methods.

Operating system for this tutorial: Windows 10 system, Java 19.0.1 version, Dell G3 computer.
1. Reflection
1.1 Overview of reflection
Reflection mechanism: in the running state, for any class , can know all the properties and methods of this class; for any object, can call any of its properties and methods; this function of dynamically obtaining information and dynamically calling object methods is called the reflection mechanism of the java language
He works like this: when a bytecode file is loaded into memory, jvm will dissect the bytecode, and then create a Class object of the object. The jvm will store all the information of the bytecode file. Stored in the Class object, as long as we obtain the Class object, we can use the object to set the properties of the object or call the object's methods and other operations.
反射可以动态获取类的信息,进一步实现需要的功能 例如: Spring框架通过XML文件描述类的基本信息,使用反射机制动态装配对象
Why is reflection needed?
Objects in Java programs can appear in two types at runtime, namely compile-time type and run-time type. For example, Person p = new Student();, this line of code will generate a p variable, the compile-time type of the variable is Person, and the run-time type is Student.
Sometimes, the program receives an object passed in from the outside during runtime. The compile-time type of the object is Object, but the program needs to call the run-time type method of the object. This requires that the program needs to discover the real information of objects and classes at runtime. There are two ways to solve this problem:
The first way is to assume that the specific information of the type is fully known at compile time and runtime. Information, in this case, you can first use the instanceof operator to make a judgment, and then use forced type conversion to convert it into a variable of its runtime type.
The second method is that it is impossible to predict which classes the object and class may belong to at compile time. The program only relies on runtime information to discover the real information of the object and class, which requires reflection.
Specifically, through the reflection mechanism, we can achieve the following operations:
When the program is running, you can obtain the Class object of any class through reflection, and view the Class object of this class through this object. Information;
When the program is running, you can create an instance of any class through reflection and access the members of the instance;
When the program is running, you can generate a dynamic proxy class of a class through the reflection mechanism Or a dynamic proxy object.
1.2 Three ways to obtain Class class objects
There are three ways to obtain Class class objects:
Class name.class attribute
Object name.getClass() method
Class.forName (full class name) method
These three methods are called when the program is not in use, and the program running stage corresponds to the get class method. The relationship diagram is as follows:
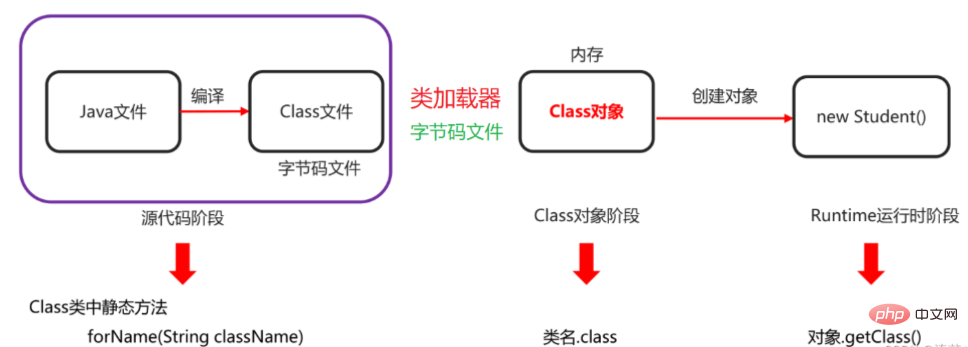
##1.2.1 Code example
class ReflectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 1.Class类中的静态方法forName("全类名")
//全类名:包名 - 类名
Class clazz1 = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
System.out.println(clazz1);
// 2.通过class属性来获取
Class clazz2 = Student.class;
System.out.println(clazz2);
// 3.利用对象的getClass方法来获取class对象
// getClass方法是定义在Object类中.
Student s = new Student();
Class clazz3 = s.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz3);
System.out.println(clazz1 == clazz2);
System.out.println(clazz2 == clazz3);
}
}The running results are as follows:
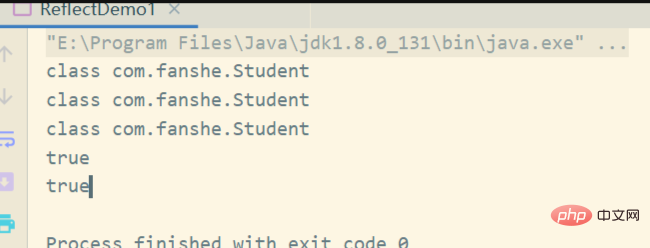
1.3 Reflection to obtain the constructor and apply it
1.3.1 Class class method to obtain the constructor object
Method introduction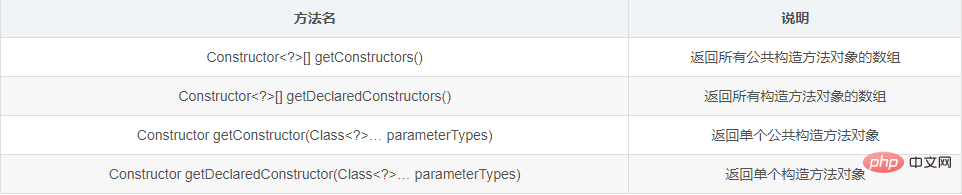
1.3.2 Code example
package com.fanshe;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
// 私有的有参构造方法
private Student(String name) {
System.out.println("name的值为:" + name);
System.out.println("private...Student的有参构造方法");
}
// 公共的无参构造方法
public Student() {
System.out.println("public...Student的无参构造方法");
}
// 公共的有参构造方法
public Student(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("name的值为:" + name + "age的值为:" + age);
System.out.println("public...Student的有参构造方法");
}
}
class ReflectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
System.out.println("获取所有公共构造方法对象的数组===========");
method1();
System.out.println("获取单个构造方法对象===========");
method2();
System.out.println("获取所有构造方法对象的数组===========");
method3();
System.out.println("获取单个构造方法对象===========");
method4();
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes):
// 返回单个构造方法对象
//1.获取Class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
System.out.println("String+int的构造");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
System.out.println(constructor);
System.out.println("String的构造");
constructor=clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes):
// 返回单个公共构造方法对象
//1.获取Class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//小括号中,一定要跟构造方法的形参保持一致.
Constructor constructor1 = clazz.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor1);
Constructor constructor2 = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
System.out.println(constructor2);
//因为Student类中,没有只有一个int的构造,所以这里会报错.
// Constructor constructor3 = clazz.getConstructor(int.class);
// System.out.println(constructor3);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors():
// 返回所有构造方法对象的数组
//1.获取Class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Constructor<?>[] getConstructors():
// 返回所有公共构造方法对象的数组
//1.获取Class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
}
}The running results are as follows:
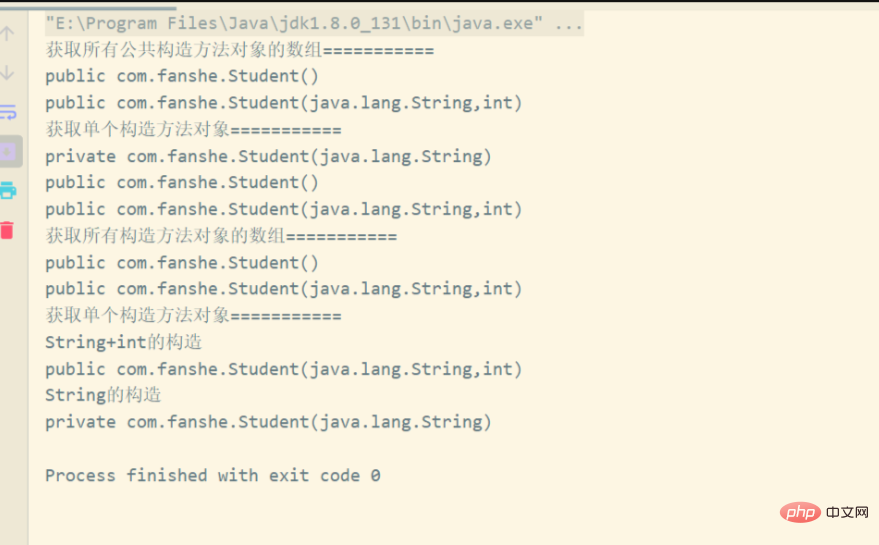
1.3.3 Methods used by the Constructor class to create objects
Method introduction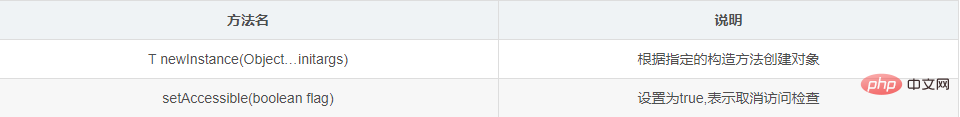
1.3.4 Code examples
Note: Members modified by private cannot be used directly. If you use reflection to obtain and use them forcibly, you need to temporarily cancel the access checkpackage com.fanshe;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
// 私有的有参构造方法
private Student(String name) {
System.out.println("name的值为:" + name);
System.out.println("private...Student的有参构造方法");
}
// 公共的无参构造方法
public Student() {
System.out.println("public...Student的无参构造方法");
}
// 公共的有参构造方法
public Student(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("name的值为:" + name + "age的值为:" + age);
System.out.println("public...Student的有参构造方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
// T newInstance(Object... initargs):根据指定的构造方法创建对象
class ReflectDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
method1();
method2();
method3();
method4();
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//获取一个私有的构造方法并创建对象
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取一个私有化的构造方法.
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
//被private修饰的成员,不能直接使用的
//如果用反射强行获取并使用,需要临时取消访问检查
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//3.直接创建对象
Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance("zhangsan");
System.out.println(student);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//简写格式
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.在Class类中,有一个newInstance方法,可以利用空参直接创建一个对象
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();//这个方法现在已经过时了,了解一下
System.out.println(student);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取构造方法对象
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
//3.利用空参来创建Student的对象
Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(student);
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取构造方法对象
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
//3.利用newInstance创建Student的对象
Student student = (Student) constructor.newInstance("杨天真", 22);
System.out.println(student);
}
}The running results are as follows:

1.3.5 Summary
Get the class objectThree ways: Class.forName("Full class name") , class name.class, object name.getClass()Get the constructor object insidegetConstructor (Class<?>... parameterTypes) getDeclaredConstructor (Class<?>... parameterTypes)If it is public, create the object directly
newInstance(Object... initargs)If it is non-public , you need to temporarily cancel the check and then create the object
setAccessible(boolean) 暴力反射
1.4 反射获取成员变量并使用
1.4.1 Class类获取成员变量对象的方法
方法分类
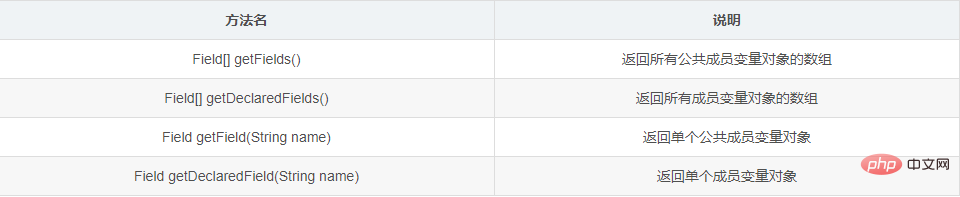
1.4.2 示例代码
package com.fanshe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public String gender;
private int money = 300;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
class ReflectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
method1();
method2();
method3();
method4();
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Field getDeclaredField(String name):返回单个成员变量对象
System.out.println("返回单个成员变量对象==================");
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取money成员变量
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("money");
//3.打印一下
System.out.println(field);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Field getField(String name):返回单个公共成员变量对象
System.out.println("返回单个公共成员变量对象==================");
//想要获取的成员变量必须是真实存在的
//且必须是public修饰的.
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取name这个成员变量
Field field = clazz.getField("name");
//3.打印一下
System.out.println(field);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Field[] getDeclaredFields():返回所有成员变量对象的数组
System.out.println("返回所有成员变量对象的数组==================");
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取所有的Field对象
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
//3.遍历
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Field[] getFields():返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组
System.out.println("返回所有公共成员变量对象的数组==================");
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取Field对象.
Field[] fields = clazz.getFields();
//3.遍历
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
}运行结果如下:
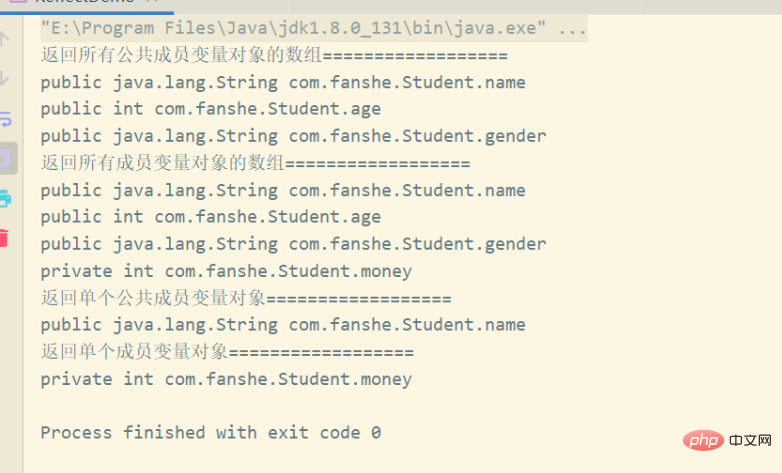
1.4.3 Field类用于给成员变量赋值的方法
方法介绍
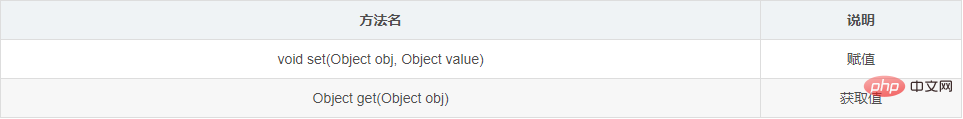
1.4.4 示例代码
package com.fanshe;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public String gender;
private int money = 300;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
class ReflectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
// Object get(Object obj) 返回由该 Field表示的字段在指定对象上的值。
method1();
method2();
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取成员变量Field的对象
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("money");
//3.取消一下访问检查
field.setAccessible(true);
//4.调用get方法来获取值
//4.1创建一个对象
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();
//4.2获取指定对象的money的值
Object o = field.get(student);
//5.打印一下
System.out.println(o);
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// void set(Object obj, Object value):给obj对象的成员变量赋值为value
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取name这个Field对象
Field fieldname = clazz.getField("name");
Field fieldage = clazz.getField("age");
//3.利用set方法进行赋值.
//3.1先创建一个Student对象
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();
//3.2有了对象才可以给指定对象进行赋值
fieldname.set(student,"杨天真");
fieldage.set(student,12);
System.out.println(student);
}
}运行结果如下:

1.5 反射获取成员方法并使用
1.5.1 Class类获取成员方法对象的方法
方法分类
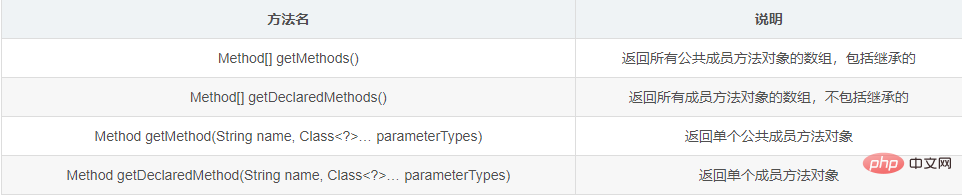
1.5.2 示例代码
package com.fanshe;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Student {
//私有的,无参无返回值
private void show() {
System.out.println("私有的show方法,无参无返回值");
}
//公共的,无参无返回值
public void function1() {
System.out.println("function1方法,无参无返回值");
}
//公共的,有参无返回值
public void function2(String name) {
System.out.println("function2方法,有参无返回值,参数为" + name);
}
//公共的,无参有返回值
public String function3() {
System.out.println("function3方法,无参有返回值");
return "aaa";
}
//公共的,有参有返回值
public String function4(String name) {
System.out.println("function4方法,有参有返回值,参数为" + name);
return "bbb";
}
}
class ReflectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
method1();
method2();
method3();
method4();
method5();
}
private static void method5() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes):
// 返回单个成员方法对象
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取一个成员方法show
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");
//3.打印一下
System.out.println(method);
}
private static void method4() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取一个有形参的方法function2
Method method = clazz.getMethod("function2", String.class);
//3.打印一下
System.out.println(method);
}
private static void method3() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) :
// 返回单个公共成员方法对象
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取成员方法function1
Method method1 = clazz.getMethod("function1");
//3.打印一下
System.out.println(method1);
}
private static void method2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Method[] getDeclaredMethods():
// 返回所有成员方法对象的数组,不包括继承的
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取Method对象
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
//3.遍历一下数组
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
private static void method1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Method[] getMethods():返回所有公共成员方法对象的数组,包括继承的
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取成员方法对象
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
//3.遍历
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
}运行结果为 :

1.5.3 Method类用于执行方法的方法
方法介绍

参数说明:
参数一: 用obj对象调用该方法
参数二: 调用方法的传递的参数(如果没有就不写)
返回值: 方法的返回值(如果没有就不写)
1.5.4 示例代码
package com.fanshe;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Student {
//私有的,无参无返回值
private void show() {
System.out.println("私有的show方法,无参无返回值");
}
//公共的,无参无返回值
public void function1() {
System.out.println("function1方法,无参无返回值");
}
//公共的,有参无返回值
public void function2(String name) {
System.out.println("function2方法,有参无返回值,参数为" + name);
}
//公共的,无参有返回值
public String function3() {
System.out.println("function3方法,无参有返回值");
return "aaa";
}
//公共的,有参有返回值
public String function4(String name) {
System.out.println("function4方法,有参有返回值,参数为" + name);
return "bbb";
}
}
class ReflectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException, InvocationTargetException {
// Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args):运行方法
// 参数一:用obj对象调用该方法
// 参数二:调用方法的传递的参数(如果没有就不写)
// 返回值:方法的返回值(如果没有就不写)
//1.获取class对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.fanshe.Student");
//2.获取里面的Method对象 function4
Method method = clazz.getMethod("function4", String.class);
//3.运行function4方法就可以了
//3.1创建一个Student对象,当做方法的调用者
Student student = (Student) clazz.newInstance();
//3.2运行方法
Object result = method.invoke(student, "杨天真");
//4.打印一下返回值
System.out.println(result);
}
}运行结果为:

2.反射的应用
Java的反射机制在实际项目中应用广泛,常见的应用场景有:
使用JDBC时,如果要创建数据库的连接,则需要先通过反射机制加载数据库的驱动程序 ;
多数框架都支持注解/XML配置,从配置中解析出来的类是字符串,需要利用反射机制实例化;
面向切面编程(AOP)的实现方案,是在程序运行时创建目标对象的代理类,这必须由反射机制来实现。
The above is the detailed content of What is the principle of Java's reflection mechanism?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

