 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Thought cloning! Former OpenAI researcher lets AI imitate human thinking, and the real-life version of 'Ex Machina' arrives
Thought cloning! Former OpenAI researcher lets AI imitate human thinking, and the real-life version of 'Ex Machina' arrivesThought cloning! Former OpenAI researcher lets AI imitate human thinking, and the real-life version of 'Ex Machina' arrives
What will happen when AI has autonomous consciousness?
In "Ex Machina", Ava takes advantage of human sympathy and deceives humans to gain freedom, eventually killing her "creator" Nathan.

Recently, under the recommendation of many netizens, Sam Altman finally watched this movie.
and said, "It's a good movie, but I don't understand why everyone makes me watch it."

Many people may want to warn that this is the result of making artificial intelligence conscious and passing the Turing test.
But we are still far away from the scene of "Ex Machina" being released. GPT-5 may be under secret development. Making AI smart is still what scientists want to do with all their strength. thing.

No, two researchers from the University of British Columbia have discovered that there are many advantages to intelligent agents that can think like humans.
In the latest paper, they studied the "thought cloning" (TC) of intelligent agents.

##Here, artificial intelligence learns to "think" and "act" like humans by imitating humans.
When AI has thoughtsYou must know that language is the key to distinguishing humans from other creatures.
Therefore, researchers imagine that if an agent can understand language, there will be many benefits.

For example, help humans summarize, infer, adapt to new situations, and combine new methods with existing knowledge, Explore, plan, and re-plan when necessary.
Despite these benefits, AI agents rarely think, at least not in human language.
While neural networks can be thought of as internal vector activations for thinking, many people hypothesize that thinking in discrete, symbolic language has specific benefits.
This means that an agent that can think in language may learn faster and perform and generalize better than an agent that does not use language.
For all these reasons, enhancing the ability of AI agents to think in language can yield many significant advantages.
Jeff Clune and Shengran Hu believe that the most effective way to achieve this goal is to "let AI imitate human thinking."
They found that humans do not acquire thinking skills in isolation. Instead, they learn part of their skills through the example of others and feedback provided by teachers.
Therefore, an effective approach is to let the agent learn from demonstrations of humans speaking their thoughts while acting.
This approach differs from existing work using pre-trained LLMs for planning because these LLMs have not been trained on data of humans speaking their thoughts while acting, i.e. "thought data" ”.
As for the source of "thought data", the researchers selected YouTube videos and text recordings, which contain approximately millions of hours, including the thoughts behind people's actions, plans, decisions and re-planning.
In the paper, the researchers proposed a novel imitation learning framework "thought cloning". Among them, the agent not only learns human demonstration behaviors, such as behavioral cloning, but also learns the way humans think while acting.
In the thought cloning training framework, the agent learns to generate thoughts at each time step and subsequently adjusts actions based on these thoughts.
The overall framework is as shown in the figure. The TC agent is a two-layer architecture: upper layer and lower layer components.
At each time step, the agent receives an observation, a task, and a thought history as input. The upper-level component is responsible for generating ideas, and the lower-level component generates and executes operations conditional on these ideas.
The generated thoughts and actions are then compared to the ground truth in the demo dataset to calculate the loss.
While there may be different choices for the conditions of the upper and lower components, in this work, for a specific trajectory of length t in the thinking dataset, the researchers minimized it:
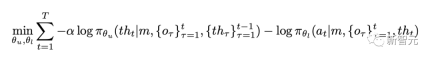
For more complex or large-scale scenarios, upper-layer components can be implemented using pre-trained visual language models (VLM) , or zero-sample, fine-tuning.
The underlying components can be trained from scratch or adapted from existing language conditional controllers in the target domain.
In the paper, the researchers conducted research based on two components of the BabyAI 1.1 model architecture.
This model utilizes the memory-enhanced architecture LSTM to solve the challenge of partial observability. In addition, it adopts FiLM for modal fusion, effectively combining visual and textual inputs.
Here, the author particularly emphasizes that all models in this article are trained from scratch, but it is better to use pre-trained models in complex fields.
The picture below is an example of the BabyAI environment. The picture on the left contains items of various colors (balls, keys, boxes, doors).
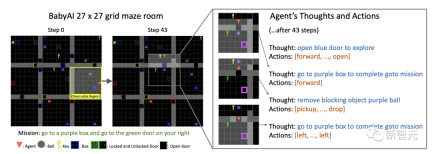
The agent can pick up, put down, move objects or open and close doors, while the lock The door you live in can only be opened with a color-matched key.
The agent can see the 7×7 grid cells in front of it, which are blocked by walls and closed doors.
The task of the "Thought Clone" agent is to reach the purple box (highlighted) and start planning the route.

#But when it opened the blue door and was about to complete the task, it found a purple ball blocking the way. . Therefore, the thought clone agent is re-planned.

##It can be seen that the thoughts and actions of the agent show that when encountering obstacles, first remove them Remove and re-route before continuing to the previous goal.
This process is especially like how Ava planned step by step to make human beings finally believe in and help themselves to escape from the long-held glass cage.
Experimental results
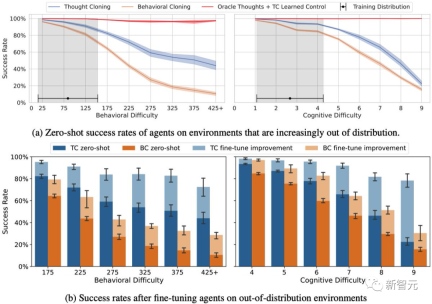
The research results show that "thought cloning" is better than behavioral cloning.
Furthermore, in zero-shot and fine-tuning settings, thought cloning has greater advantages than behavioral cloning in out-of-distribution tasks.
Interestingly, the researchers also developed “pre-crime intervention” that allows users to still Define unsafe behavior.
The agent can be terminated when dangerous thoughts are detected. In the test, the effect of "pre-crime intervention" was almost perfect, showing its potential in artificial intelligence security.
"Thought cloning" not only makes artificial intelligence smarter, but also safer and easier to understand.
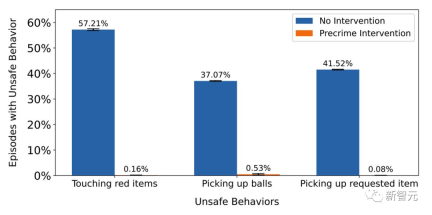
That is to say, before the AI commits a crime, everything can still be saved.

In Jeff Clune’s view, “thought cloning” contributes to the safety of artificial intelligence.
Because we can observe the agent’s thoughts: (1) can more easily diagnose why things go wrong, (2) guide the agent by correcting its thoughts, ( 3) Or prevent it from doing the unsafe thing it planned.

About the author
Jeff Clune
Currently, Jeff Clune is an associate professor of computer science at the University of British Columbia. He mainly studies deep learning, including deep reinforcement learning.
Previously, he was the head of the OpenAI research team and the senior research manager and founding member of the Uber Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.

Previously, he and the OpenAI team released a video pre-training model-VPT, allowing AI to operate in Minecraft Learning stone-making pickaxes from video data.

Shengran Hu
Currently Britain PhD student at Columbia University, interested in deep learning and artificial intelligence generation algorithms.

The above is the detailed content of Thought cloning! Former OpenAI researcher lets AI imitate human thinking, and the real-life version of 'Ex Machina' arrives. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AMsummary: Small Language Model (SLM) is designed for efficiency. They are better than the Large Language Model (LLM) in resource-deficient, real-time and privacy-sensitive environments. Best for focus-based tasks, especially where domain specificity, controllability, and interpretability are more important than general knowledge or creativity. SLMs are not a replacement for LLMs, but they are ideal when precision, speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Technology helps us achieve more with fewer resources. It has always been a promoter, not a driver. From the steam engine era to the Internet bubble era, the power of technology lies in the extent to which it helps us solve problems. Artificial intelligence (AI) and more recently generative AI are no exception
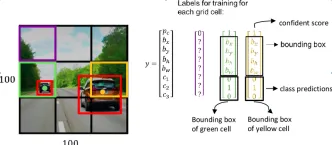 How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AMHarness the Power of Google Gemini for Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Guide Google Gemini, a leading AI chatbot, extends its capabilities beyond conversation to encompass powerful computer vision functionalities. This guide details how to utilize
 Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AM
Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AMThe AI landscape of 2025 is electrifying with the arrival of Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash and OpenAI's o4-mini. These cutting-edge models, launched weeks apart, boast comparable advanced features and impressive benchmark scores. This in-depth compariso
 How to Generate and Edit Images Using OpenAI gpt-image-1 APIApr 27, 2025 am 09:16 AM
How to Generate and Edit Images Using OpenAI gpt-image-1 APIApr 27, 2025 am 09:16 AMOpenAI's latest multimodal model, gpt-image-1, revolutionizes image generation within ChatGPT and via its API. This article explores its features, usage, and applications. Table of Contents Understanding gpt-image-1 Key Capabilities of gpt-image-1
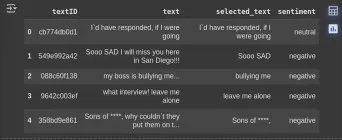 How to Perform Data Preprocessing Using Cleanlab? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:15 AM
How to Perform Data Preprocessing Using Cleanlab? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:15 AMData preprocessing is paramount for successful machine learning, yet real-world datasets often contain errors. Cleanlab offers an efficient solution, using its Python package to implement confident learning algorithms. It automates the detection and
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






