How to use redis in ThinkPHP5
- 王林forward
- 2023-06-02 18:25:311895browse
Premise: Because this article mainly focuses on using redis in thinkPHP5, there is no special explanation about the installation of redis, but here is a little reminder, after installing redis Be sure to enable the php.ini extension later, otherwise you will still be unable to use redis.
Configuration
1. Students who can use ThinkPHP5 all know that TinkPHP5 encapsulates the cache class. We only need to fill in the cache configuration items in the cache in /application/congfig.php It's ready to use (shown below).
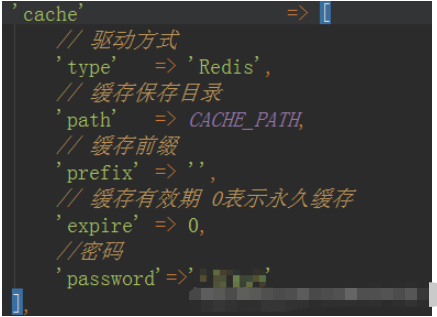
2. From the /thinkphp/library/think/cache/driver/Redis.php file we can see that the redis cache encapsulated here can only use the string basic type of redis. If you want This will not work if you use composite data types such as hashes or queues.
Looking at the cache class/thinkphp/library/think/cache/Driver.php, you will find that the handler method will return a handle, so we can use all data types of redis as long as we obtain this handle where we use redis. , so you can add the gethandle method getHandler
/**
* 返回句柄对象,可执行其它高级方法
*
* @access public
* @return object
*/
public function handler()
{
return $this->handler;
} /*
* 获取句柄
* @param
*/
public static function getHandler()
{
return self::init();
}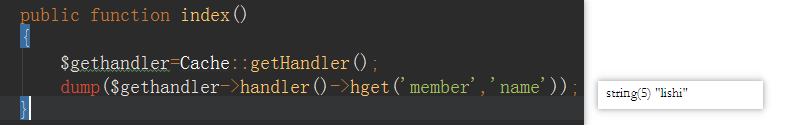
redis use
string(string)# in /thinkphp/library/think/Cache.php
##Basic type, one key corresponds to one value. A string type value can store up to 512MBIllustration:
// 创建数据
$redis->set('key', 'value');// 获取数据
$value = $redis->get('key');
echo $value . PHP_EOL;// 修改数据,与创建数据一致,即覆盖数据
$redis->set('key', 'value2');
echo $redis->get('key') . PHP_EOL;// 追加数据
$redis->append('key', '_value2');
echo $redis->get('key') . PHP_EOL;// 删除数据
$redis->del('key');
// $redis->delete('key');
var_dump($redis->get('key'));// 创建数据,带有效期
$redis->set('timeout_key', 'timeout_value', 5);
$redis->setex('timeout_key', 5, 'timeout_value');
// 获取数据的有效期
echo $redis->ttl('timeout_key') . PHP_EOL;// 判断是否已经写入,未写入则写入
$redis->set('unique_key', 'unique_value');
if (!$redis->setnx('unique_key', 'unique_value')) {
echo $redis->get('unique_key') . PHP_EOL;
}// 批量创建
$multi = ['key1' => 'value1', 'key2' => 'value2', 'key3' => 'value3'];
$redis->mset($multi);// 批量获取
$result = $redis->mget(array_keys($multi));
var_dump($result);Hash(Hash) Hash is a collection of key-value (key=>value) pairs; it is a mapping table of string type fields and values. Hash is particularly suitable for storing objects. Each hash can store 2^32 -1 key-value pairs (more than 4 billion) Illustration:
// 创建 hash 表 // 向名字叫 'hash' 的 hash表 中添加元素 ['key1' => 'val1'] $redis->hSet('hash', 'key1', 'val1');// 获取 hash表 中键名是 key1 的值 echo $redis->hGet('hash', 'key1') . PHP_EOL;// 获取 hash表的元素个数 echo $redis->hLen('hash') . PHP_EOL;// 获取 hash表 中所有的键 $keys = $redis->hKeys('hash'); var_dump($keys);// 获取 hash表 中所有的值 $vals = $redis->hVals('hash'); var_dump($vals);// 获取 hash表 中所有的键值对 // 不推荐使用这种方法获取全部数据,会导致服务器执行超时,推荐方法后边会详细介绍 // $all = $redis->hGetAll('hash'); // var_dump($all);// 判断 hash 表中是否存在键名是 key2 的元素 $bool = $redis->hExists('hash', 'key2'); echo $bool ? '存在' : '不存在' . PHP_EOL;// 批量添加元素 $redis->hMset('hash', ['key2' => 'val2', 'key3' => 'val3']);// 批量获取元素 $hashes = $redis->hMGet('hash', ['key1', 'key2', 'key3']); var_dump($hashes);// 删除 hash表 $redis->del('hash');List( List)A list is a simple list of strings, sorted in insertion order. You can add an element to the head (left) or tail (right) of the list. List types are commonly used in messaging queue services to facilitate message exchange between multiple programs. Each list can store up to about 4 billion elements, or 2^32-1 elements. Illustration:
// 向队列左侧加入元素 $redis->lPush('lists', 'X'); $redis->lPush('lists', 'X'); // 向队列右侧加入元素 $redis->rPush('lists', 'Z');// 将索引为1的数据修改为 Y $redis->lSet('lists', 1, 'Y');// 获取 list 长度 $length = $redis->lLen('lists'); echo $length;// 遍历 list $lists = $redis->lRange('lists', 0, $length - 1); dump($lists);// 从左侧出队一个元素(获取并删除) $x = $redis->lPop('lists'); echo $x . PHP_EOL; // 从右侧出队一个元素(获取并删除) $z = $redis->rPop('lists'); echo $z . PHP_EOL;// 获取左侧第一个元素 $y = $redis->lIndex('lists', 0); echo $y . PHP_EOL;// 删除队列 $redis->del('lists');Set (set)Redis’ Set is an unordered collection of string type. Like lists, the efficiency is very high when performing insertion and deletion and determining whether an element exists. The biggest advantage of sets is that they can perform intersection, union, and difference operations. The maximum number of elements that a Set can contain is 4294967295 (more than 4 billion). Sets are implemented through hash tables, so the complexity of adding, deleting, and searching is O(1). Illustration:
// 创建集合 $redis->sAdd('sets', 'value1', 'value2'); // 以数组形式创建集合 $redis->sAddArray('sets2', ['value1', 'value2', 'value3']);// 取两个集合的并集 $union = $redis->sUnion('sets', 'sets2'); // 取两个集合的差集 $diff = $redis->sDiff('sets', 'sets2'); // 取两个集合的交集 $inter = $redis->sInter('sets', 'sets2');var_dump($union, $diff, $inter);// 获取集合数量 $card = $redis->sCard('sets'); echo $card . PHP_EOL;// 获取集合中全部元素 // 不推荐使用这种方法获取全部数据,会导致服务器执行超时,推荐方法后边会详细介绍 $sets = $redis->sMembers('sets'); var_dump($sets);// 判断元素是否是集合中的成员 $isMember = $redis->sIsMember('sets', 'value2'); var_dump($isMember);// 删除集合中的元素 $redis->sRem('sets', 'value2'); var_dump($redis->sMembers('sets'));// 随机获取一个元素 echo $redis->sRandMember('sets');// 随机获取一个元素并从集合中删除 echo $redis->sPop('sets');// 删除集合 $redis->del('sets', 'sets2');zset (ordered set)Redis zset is also a collection of string type elements like set, and does not Duplicate members are allowed. The difference is that each element is associated with a double type score. Redis uses scores to sort the members of the set from small to large.
// 添加成员 $redis->zAdd('zset', 95, '小明'); $redis->zAdd('zset', 99, '小刚'); $redis->zAdd('zset', 100, '小红');// 统计成员个数 echo $redis->zCard('zset') . PHP_EOL;// 获取某个成员的分数 $score = $redis->zScore('zset', '小明'); echo $score . PHP_EOL;// 获取某个成员的排名 $rank = $redis->zRank('zset', '小明'); // 从低到高排序的名次 $revRank = $redis->zRevRank('zset', '小明'); // 从高到低排序的名次 echo $rank . PHP_EOL; echo $revRank . PHP_EOL;// 给指定成员增加分数 $redis->zIncrBy('zset', 1, '小明'); // 给小明加一分// 返回指定排名范围的成员 $range = $redis->zRange('zset', 0, 9, true); // 返回分数从低到高排序的前10名及分数 $revRange = $redis-> zRevRange('zset', 0, 9, true); // 返回分数从高到低排序的前10名及分数 var_dump($range); var_dump($revRange);// 删除成员 $redis->zRem('zet', '小明');// 返回指定分数范围的成员 $rangeByScore = $redis->zRangeByScore('zet', 98, 100); // 返回指定分数范围内从低到高排序的成员 $revRangeByScore = $redis->zRevRangeByScore('zet', 98, 100); // 返回指定分数范围内从高到低排序的成员 var_dump($rangeByScore); var_dump($revRangeByScore);
The above is the detailed content of How to use redis in ThinkPHP5. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

