How to enter the BIOS in Windows 11
PC users can customize how they interact with Windows in a variety of ways. But some features can only be accessed from special screens like BIOS.
The BIOS is an important program that contains many core customizations, such as enabling Secure Boot or changing boot options, and can be accessed in a variety of ways. On this matter, we need to clarify the nature of this technology and how it differs from UEFI, while also understanding how to access it in Windows 11
What is BIOS?
BIOS is a program embedded in a small chip on the computer motherboard and is used for basic input and output operations. As the name suggests, it is a system that manages the flow of data between the operating system (Windows) and connected hardware (such as drives, monitors, mice, etc.) and prepares it for startup. It also contains some settings and customization options that are not accessible from any other screen.
The exact layout of the BIOS may vary depending on your OEM and motherboard manufacturer. However, the options available in all BIOS interfaces are more or less the same.
2 Ways to Enter the BIOS in Windows 11
There are several ways to access the BIOS. Let’s take a look one by one.
Method 1: Press the BIOS key at boot
To access the BIOS, a common method is to press a specific key when the computer starts, such as F2, F10, F12 or Del. Here's how to do it:
Turn on your computer. At the first sign that your computer is booting up, press the BIOS key repeatedly. There is only a small window of opportunity to register your keystrokes and run the BIOS. If you see the Windows logo, you're missing a window. Shut down the system and try again.
This is a tried and tested formula that has become the default way to access the BIOS. As mentioned before, the key may vary depending on your OEM or motherboard manufacturer.
Here is a list of some popular OEMs and their assigned BIOS hotkeys:
-
HP:
F10 -
Dell:
F2orF12 -
Gigabyte, MSI, Zotac:
Del -
ASUS:
Del,F10orF9 -
Acer :
DelorF2 -
Lenovo:
F2,Fn F2,F1, orEnterfollowed byF1 - Surface Pro: Press and hold to increase volume
If this is your first time accessing the BIOS, it may take a few attempts to properly access the BIOS screen.
Method 2: From Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
You can also enter the BIOS screen from Windows itself. To do this, you must first enter the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). Here are some ways to do this.
Step 1: Access WinRE (using any of the 4 methods)
Here are four methods of accessing the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). Once at this location, you can follow step 2 to enter the BIOS via WinRE.
Option 1: Access WinRE from Settings
Press Win I to open the Settings app. With System selected in the left pane, scroll down on the right and click Recovery.
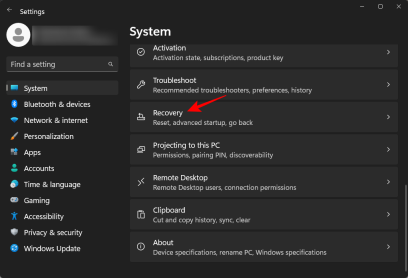
Click Restart Now next to Advanced Startup.
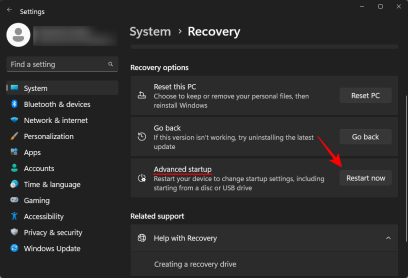
#This will restart your PC and boot into the recovery environment.
After entering the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE), follow step 2 below to enter the BIOS.
Option 2: Access WinRE from the Power Button (in the Start Menu and Login Screen)
The Restart button can be used as a shortcut to access WinRE to enter the BIOS. That's it:
Press Start and click the Power button.
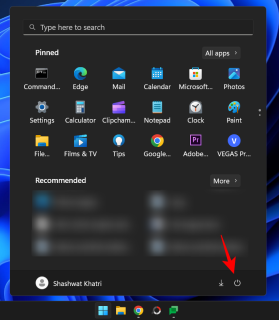
Then, while holding down the Shift key, click Restart.
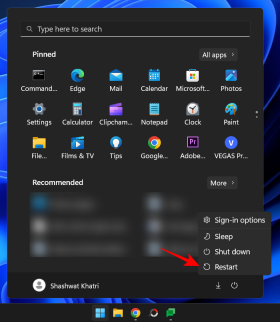
Alternatively, if you are on the login screen, click the Power button.

Now, while holding down the Shift key, click Restart.

#When you reboot using these advanced settings, the system enters directly into the Windows recovery environment. From here, the steps to access the BIOS are the same as shown above.
After entering the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE), follow step 2 below to enter the BIOS.
Option 3: Access WinRE from the Command Prompt (CMD)
You can also perform an advanced boot to access the BIOS by using a terminal application, such as Command Prompt or PowerShell. That's it:
Press Start, type cmd, and click "Command Prompt".

Note: You can also use PowerShell if you prefer, as the commands are the same for both command terminals.
Type the following command:
shutdown /r /o

New, and then click Shortcut.

shutdown /r /o
"Next".

Finish.

Win R to open the run box. Then type the same command:
shutdown /r /o
Troubleshoot".

Advanced Options.

UEFI Firmware Settings.

Restart.



UEFI can be regarded as an upgraded version of traditional BIOS. UEFI is a modern BIOS with larger memory space, more functions, and various customizable options.
UEFI also uses the GPT (GUID Partition Table) disk format, while BIOS uses the traditional MBR (Master Boot Record) format. This system frequently checks disk integrity and is expected to completely replace BIOS within the next few years.
How to check the BIOS version
If you want to check your BIOS version, please follow these steps:
Press start, enter CMD, then Press Enter.

Now type the following command:
wmic bios get smbiosbiosversion

Press the Enter key. You will now see your BIOS version.

Another way to check the BIOS version is to open the System Information tool. That's it:
Press Start, type msinfo32, and then press Enter.

After the System Information tool opens, find the BIOS version/date.

How to Enable Virtualization in BIOS
Virtualization allows users to install multiple guest operating systems on their PC. If you're going to use tools like VirtualBox, develop and test applications on different operating systems, or install old games, virtualization is something you can't live without. Enable Hyper-V functionality in the BIOS to run Windows 11. The operation method is as follows:
Enter the BIOS through the method given above. Then use the arrow keys to enter Configuration.

Note: Virtualization options may be in different tabs depending on your manufacturer. It might be under Security, Advanced, Device/System Configuration, or some such section.
Then select Virtualization Technology.

Enable it.

When finished, jump to the Exit tab and select Save changes and exit.

What is Secure Boot?
Secure Boot is a UEFI protocol that protects the Windows boot process by ensuring that only signed drivers are loaded at system startup. Starting with Windows 11, Microsoft has made this a prerequisite for system installation of Windows 11, although there are many workarounds for this.
However, if you want maximum security for your PC, it's best to enable it.
How to enable Secure Boot from the BIOS
Access the BIOS using the methods provided in this tutorial. Then, use the arrow keys to get to the Boot Options Options card (or a section with a similar title).

Then press Enter to select Secure Boot.

#Make sure it is enabled and press Enter.

Now go to the "Exit" tab and select "Save changes and exit".

FIX: Unable to access BIOS or Advanced Boot screen on Windows 11
If you are unable to access BIOS or even Advanced Boot screen on Windows 11, you may need to Change settings in the System Configuration application. That's it:
Press Start, type msconfig, and press Enter.

Now, under the "General" tab, select "Start normally" and click "OK".

You should now be able to access the BIOS from the boot screen or recovery environment.
FAQ
In this section, we will answer some frequently asked questions about the BIOS:
Can I access the BIOS without rebooting?
The BIOS can only be accessed before the operating system boots. Therefore, even if you reboot the system and enter the BIOS without using the WinRE environment, you still need to use the specified key during the boot process, so a reboot is inevitable.
Can you unlock the advanced menu hidden in the BIOS?
Although some online resources claim to be able to unlock advanced menus hidden in the BIOS, this is likely misleading information. There is no secret menu accessible in the BIOS. Even if there is a so-called "advanced" screen, it is just an additional BIOS screen provided by the OEM. But it certainly doesn't need to be unlocked to access.
The above is the detailed content of How to enter the BIOS in Windows 11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






