 Web Front-end
Web Front-end H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial In-depth analysis of the method of controlling graphics matrix transformation in HTML5 Canvas_html5 tutorial skills
In-depth analysis of the method of controlling graphics matrix transformation in HTML5 Canvas_html5 tutorial skillsBefore introducing matrix transformation transform(), let’s talk about what a transformation matrix is. 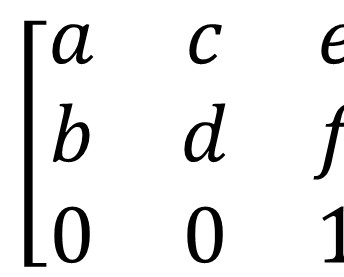
The above is the transformation matrix corresponding to the transform() method in Canvas. This method passes in the six parameters shown in the figure, specifically context.transform(a,b,c,d,e,f).
The meaning of each parameter corresponds to the following table:
| 参数 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| a | 水平缩放(1) |
| b | 水平倾斜(0) |
| c | 垂直倾斜(0) |
| d | 垂直缩放(1) |
| e | 水平位移(0) |
| f | 垂直位移(0) |
When we substitute the corresponding 0 or 1 into the matrix, we can find that this is an identity matrix (the default value of horizontal and vertical scaling is 1, which means scaling by 1 times, that is, no scaling). This method uses a new change matrix to multiply the current transformation matrix, and then obtains various change effects.
To put it simply, when we want to transform a graphic, we only need to operate the corresponding parameters of the transformation matrix. After the operation, multiply the coordinates of each fixed point of the graphic by this matrix to get a new The coordinates of the fixed point.
transform() method
Canvas drawing provides us with a method to change this transformation matrix, that is transform().
The default coordinate system is based on the upper left corner of the canvas as the coordinate origin (0, 0). The further to the right the X-axis value is, the greater the value is, and the further down the Y-axis value is the greater it is. In the default coordinate system, the coordinates of each point are directly mapped to a CSS pixel. Some specific operations and property settings on the canvas use the default coordinate system. However, in addition to the default coordinate system, each canvas also has a "current transformation matrix" as part of the graphics state. This matrix defines the current coordinate system of the canvas. When the coordinates of a point are specified, most operations on the canvas map the point to the current coordinate system, rather than the default coordinate system. The current transformation matrix is used to transform the specified coordinates into equivalent coordinates in the default coordinate system. The transformation of coordinates also affects the drawing of text and line segments.
Calling the translate() method simply moves the coordinate origin up, down, left, and right. The
rotate() method will rotate the coordinate axis clockwise according to the specified angle.
The scale() method implements extending and shortening the distance on the x-axis or the y-axis. Passing a negative value will achieve
scale to flip the coordinate axis using the coordinate origin as the reference point. Like a reflection in a mirror.
translate is used to move the coordinate origin to the lower left corner of the canvas, and then the scale method is used to flip the y-axis, so that the y-axis becomes larger as it goes up.
Understand coordinate system transformation from a mathematical perspective:
The translate, rotate and scale methods are easy to understand if you imagine them as transformations of the coordinate axes. It is easy to understand coordinate transformation from an algebraic perspective, that is, imagine the transformation as a point (x, y) in the transformed coordinate system, and the original coordinate system becomes (x`, y`).
Call c.translate(dx,dy). The method is equivalent to the following expression
x` = x dx; //new The 0 of the x-axis in the system is dx
y` = y dy;
c.scale(sx,sy);
x` = sx*x;
y` = in the original system sy*y;
c.rotate()
x` =x*cos(a)-y*sin(a);
y` = y*cos(a) x*sin(a) ;
It is recommended to use transform() in the following situations:
1. Use context.transform (1,0,0,1,dx,dy) instead of context.translate(dx,dy)
2. Use context.transform(sx,0,0,sy,0 ,0) instead of context.scale(sx, sy)
3. Use context.transform(0,b,c,0,0,0) to achieve the tilt effect (the most practical).
There is no need to use it to achieve rotation. In addition, there is no need to remember all these conclusions. Just write down the meaning of the six parameters of abcdef. The effect is the same.
Let’s look at a code to get familiar with it:
- nbsp;html>
- "zh">
- "UTF-8">
-
矩阵变换 - body { background: url("./images/bg3.jpg") repeat; }
- #canvas { border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; display: block; margin: 50px auto; }
-
"canvas-warp">
- 你的浏览器居然不支持Canvas?!赶快换一个吧!!
- <script> </script>
- window.onload = function(){
- var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
- canvas.width = 800;
- canvas.height = 600;
- var context = canvas.getContext("2d");
- context.fillStyle = "#FFF";
- context.fillRect(0,0,800,600);
- context.fillStyle = "yellow";
- context.strokeStyle = "#00AAAA";
- context.lineWidth = 5;
- context.save();
- //平移至(300,200)
- context.transform(1,0,0,1,300,200);
- //水平方向放大2倍,垂直方向放大1.5倍
- context.transform(2,0,0,1.5,0,0);
- //水平方向向右倾斜宽度10%的距离,垂直方向向上倾斜高度10%的距离
- context.transform(1,-0.1,0.1,1,0,0);
- context.fillRect(0,0,200,200);
- context.strokeRect(0,0,200,200);
- context.restore();
- };
运行结果:
setTransform()方法
transform()方法的行为相对于由 rotate(),scale(), translate(), or transform() 完成的其他变换。例如:如果我们已经将绘图设置为放到两倍,则 transform() 方法会把绘图放大两倍,那么我们的绘图最终将放大四倍。这一点和之前的变换是一样的。
但是setTransform()不会相对于其他变换来发生行为。它的参数也是六个,context.setTransform(a,b,c,d,e,f),与transform()一样。
这里我们通过一个例子来说明:
绘制一个矩形,通过 setTransform() 重置并创建新的变换矩阵,再次绘制矩形,重置并创建新的变换矩阵,然后再次绘制矩形。
- nbsp;html>
- "zh">
- "UTF-8">
-
矩阵变换 - body { background: url("./images/bg3.jpg") repeat; }
- #canvas { border: 1px solid #aaaaaa; display: block; margin: 50px auto; }
-
"canvas-warp">
- 你的浏览器居然不支持Canvas?!赶快换一个吧!!
- <script> </script>
- window.onload = function(){
- var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas");
- canvas.width = 800;
- canvas.height = 600;
- var context = canvas.getContext("2d");
- context.fillStyle = "#FFF";
- context.fillRect(0,0,800,600);
- context.fillStyle="yellow";
- context.fillRect(200,100,250,100)
- context.setTransform(1,0.5,-0.5,1,30,10);
- context.fillStyle="red";
- context.fillRect(200,100,250,100);
- context.setTransform(1,0.5,-0.5,1,30,10);
- context.fillStyle="blue";
- context.fillRect(200,100,250,100);
- };
运行结果: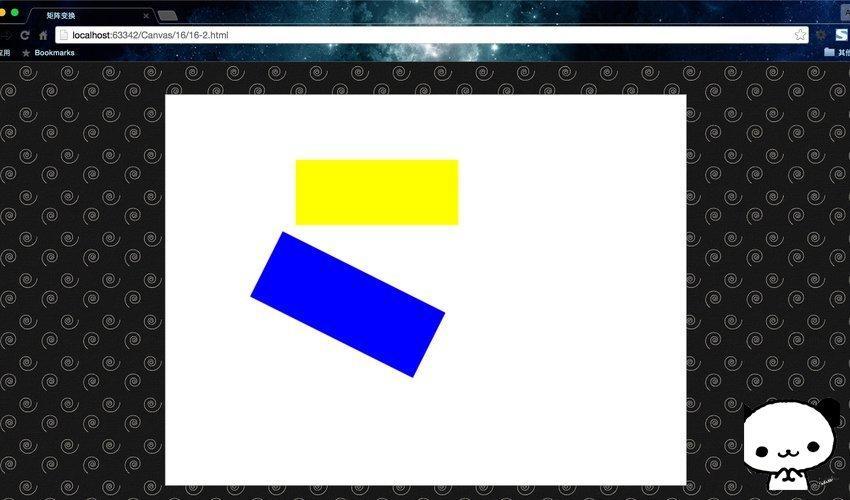
解释一下过程:每当我们调用 setTransform() 时,它都会重置前一个变换矩阵然后构建新的矩阵,因此在下面的例子中,不会显示红色矩形,因为它在蓝色矩形下面。
 html5的div一行可以放两个吗Apr 25, 2022 pm 05:32 PM
html5的div一行可以放两个吗Apr 25, 2022 pm 05:32 PMhtml5的div元素默认一行不可以放两个。div是一个块级元素,一个元素会独占一行,两个div默认无法在同一行显示;但可以通过给div元素添加“display:inline;”样式,将其转为行内元素,就可以实现多个div在同一行显示了。
 html5中列表和表格的区别是什么Apr 28, 2022 pm 01:58 PM
html5中列表和表格的区别是什么Apr 28, 2022 pm 01:58 PMhtml5中列表和表格的区别:1、表格主要是用于显示数据的,而列表主要是用于给数据进行布局;2、表格是使用table标签配合tr、td、th等标签进行定义的,列表是利用li标签配合ol、ul等标签进行定义的。
 html5怎么让头和尾固定不动Apr 25, 2022 pm 02:30 PM
html5怎么让头和尾固定不动Apr 25, 2022 pm 02:30 PM固定方法:1、使用header标签定义文档头部内容,并添加“position:fixed;top:0;”样式让其固定不动;2、使用footer标签定义尾部内容,并添加“position: fixed;bottom: 0;”样式让其固定不动。
 HTML5中画布标签是什么May 18, 2022 pm 04:55 PM
HTML5中画布标签是什么May 18, 2022 pm 04:55 PMHTML5中画布标签是“<canvas>”。canvas标签用于图形的绘制,它只是一个矩形的图形容器,绘制图形必须通过脚本(通常是JavaScript)来完成;开发者可利用多种js方法来在canvas中绘制路径、盒、圆、字符以及添加图像等。
 html5中不支持的标签有哪些Mar 17, 2022 pm 05:43 PM
html5中不支持的标签有哪些Mar 17, 2022 pm 05:43 PMhtml5中不支持的标签有:1、acronym,用于定义首字母缩写,可用abbr替代;2、basefont,可利用css样式替代;3、applet,可用object替代;4、dir,定义目录列表,可用ul替代;5、big,定义大号文本等等。
 html5废弃了哪个列表标签Jun 01, 2022 pm 06:32 PM
html5废弃了哪个列表标签Jun 01, 2022 pm 06:32 PMhtml5废弃了dir列表标签。dir标签被用来定义目录列表,一般和li标签配合使用,在dir标签对中通过li标签来设置列表项,语法“<dir><li>列表项值</li>...</dir>”。HTML5已经不支持dir,可使用ul标签取代。
 Html5怎么取消td边框May 18, 2022 pm 06:57 PM
Html5怎么取消td边框May 18, 2022 pm 06:57 PM3种取消方法:1、给td元素添加“border:none”无边框样式即可,语法“td{border:none}”。2、给td元素添加“border:0”样式,语法“td{border:0;}”,将td边框的宽度设置为0即可。3、给td元素添加“border:transparent”样式,语法“td{border:transparent;}”,将td边框的颜色设置为透明即可。
 html5是什么意思Apr 26, 2021 pm 03:02 PM
html5是什么意思Apr 26, 2021 pm 03:02 PMhtml5是指超文本标记语言(HTML)的第五次重大修改,即第5代HTML。HTML5是Web中核心语言HTML的规范,用户使用任何手段进行网页浏览时看到的内容原本都是HTML格式的,在浏览器中通过一些技术处理将其转换成为了可识别的信息。HTML5由不同的技术构成,其在互联网中得到了非常广泛的应用,提供更多增强网络应用的标准机。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools





