Foreshadowing
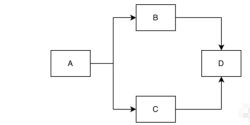
We will introduce algorithms related to directed graphs in this section, so we will first explain some concepts of directed graphs; subsequent articles These concepts will not be explained in detail. First, the nodes of the directed graph are connected by lines with arrows. The out-degree and in-degree of a node can be used to describe it. When the tail of a connection points to the node, its out-degree will increase by 1; and when the arrow of a connection points to the node, its in-degree will increase by 1. Look at the following example, A has an in-degree of 0 and an out-degree of 2, B has an in-degree of 1 and an out-degree of 1, C has an in-degree of 1 and an out-degree of 1, D has an in-degree of 2 and an out-degree is 0.
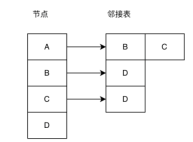
Adjacency list: The adjacency list is an effective way to store the graph structure. As shown in the figure below, the node array on the left stores all the nodes in the graph, and the adjacency list on the right stores the nodes. adjacent nodes.
Introduction
In this article we are going to talk about topological sorting, which is an algorithm for directed acyclic graphs, mainly to solve the problem of precursors The subsequent relationship, that is, what items we need to complete first when completing the current item, is actually used a lot in our process control. Looking at the picture below, we need to complete item A first, and then we can complete items B and C. Matters B and C are parallel and not in order, but item D can only be completed after items B and C are completed. Topological sorting can help us find a reasonable order for completing items. At the same time, let’s look at the example above. After item A is completed, items B and C are not in order. Whether B or C is completed first, the conditions are met, so topological sorting The sequence of is not entirely certain.
Working process
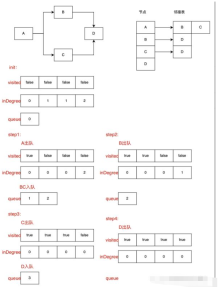
First, the corresponding operation of topological sorting is a directed acyclic graph. For an acyclic graph, there must be at least one node with indegree 0. In the current situation, we need to find a node with an in-degree of 0 for operation. An in-degree of 0 means that the current node has no predecessor node, or the predecessor node has been processed and can be operated directly. After the operation is completed, all the in-degrees of the current node's successor nodes are reduced by 1, and the node with an in-degree node of 0 is searched again for operation. After that, it is a recursive process, and the nodes with an in-degree of 0 under the current situation are continuously processed until all nodes are processed. complete.
Data structure
The following is the structure of a directed graph, in which node stores all the nodes in the current graph, and adj stores the corresponding subscript node. of adjacent points. When initializing the graph, you need to specify the number of nodes, create a node array and an adjacency array. Provides a method named addEdge, which is used to establish an edge between two nodes, that is, to add the successor node to the adjacency list of the predecessor node.
public static class Graph{
/**
* 节点个数
*/
private Integer nodeSize;
/**
* 节点
*/
private char[] node;
/**
* 邻接表
*/
private LinkedList[] adj;
public Graph(char[] node) {
this.nodeSize = node.length;
this.node = node;
this.adj = new LinkedList[nodeSize];
for (int i = 0 ; i < adj.length ; i++) {
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
}
/**
* 在节点之间加边,前驱节点指向后继节点
* @param front 前驱节点所在下标
* @param end 后继节点所在下标
*/
public void addEdge(int front, int end) {
adj[front].add(end);
}
}Topological sorting
Topological sorting first initializes two temporary arrays, a queue, and an inDegree array to store the in-degree of the corresponding subscript node, because each node visited requires that the predecessor node has already Completed, that is, the in-degree is 0. With this array, we can find these nodes relatively quickly; the other is the visited array, which marks whether the current node has been visited to prevent multiple visits; a nodes queue is saved in the current situation All nodes with indegree 0. (Note that for the convenience of access, we all store node subscripts. Step1: Initialize the inDegree array and visited array; step2: Traverse the inDegree array and put all nodes with an indegree of 0 into the nodes queue; step3: Exit the node nodes in sequence. Queue; Determine whether the current node has been visited based on visited, if yes, return to step3, if not, proceed to the next step; Set the in-degree of the adjacent node of the current node to -1, determine whether the in-degree of the adjacent node is 0, if it is 0, put it directly into the nodes queue , if it is not 0, return to step3;
/**
* @param graph 有向无环图
* @return 拓扑排序结果
*/
public List<Character> toPoLogicalSort(Graph graph) {
//用一个数组标志所有节点入度
int[] inDegree = new int[graph.nodeSize];
for (LinkedList list : graph.adj) {
for (Object index : list) {
++ inDegree[(int)index];
}
}
//用一个数组标志所有节点是否已经被访问
boolean[] visited = new boolean[graph.nodeSize];
//开始进行遍历
Deque<Integer> nodes = new LinkedList<>();
//将入度为0节点入队
for (int i = 0 ; i < graph.nodeSize; i++) {
if (inDegree[i] == 0) {
nodes.offer(i);
}
}
List<Character> result = new ArrayList<>();
//将入度为0节点一次出队处理
while (!nodes.isEmpty()) {
int node = nodes.poll();
if (visited[node]) {
continue;
}
visited[node] = true;
result.add(graph.node[node]);
//将当前node的邻接节点入度-1;
for (Object list : graph.adj[node]) {
-- inDegree[(int)list];
if (inDegree[(int)list] == 0) {
//前驱节点全部访问完毕,入度为0
nodes.offer((int) list);
}
}
}
return result;
}Test sample 1
public static void main(String[] args) {
ToPoLogicalSort toPoLogicalSort = new ToPoLogicalSort();
//初始化一个图
Graph graph = new Graph(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'});
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0,2);
graph.addEdge(1,3);
graph.addEdge(2,3);
List<Character> result = toPoLogicalSort.toPoLogicalSort(graph);
}Execution result
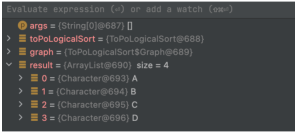
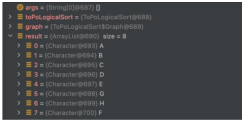
Test sample Example 2
public static void main(String[] args) {
ToPoLogicalSort toPoLogicalSort = new ToPoLogicalSort();
//初始化一个图
Graph graph = new Graph(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D','E','F','G','H'});
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(0,2);
graph.addEdge(0,3);
graph.addEdge(1,4);
graph.addEdge(2,4);
graph.addEdge(3,4);
graph.addEdge(4,7);
graph.addEdge(4,6);
graph.addEdge(7,5);
graph.addEdge(6,7);
List<Character> result = toPoLogicalSort.toPoLogicalSort(graph);
}Execution result
The above is the detailed content of How to implement topological sorting in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Is Java Platform Independent if then how?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Is Java Platform Independent if then how?May 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMJava is platform-independent because of its "write once, run everywhere" design philosophy, which relies on Java virtual machines (JVMs) and bytecode. 1) Java code is compiled into bytecode, interpreted by the JVM or compiled on the fly locally. 2) Pay attention to library dependencies, performance differences and environment configuration. 3) Using standard libraries, cross-platform testing and version management is the best practice to ensure platform independence.
 The Truth About Java's Platform Independence: Is It Really That Simple?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The Truth About Java's Platform Independence: Is It Really That Simple?May 09, 2025 am 12:10 AMJava'splatformindependenceisnotsimple;itinvolvescomplexities.1)JVMcompatibilitymustbeensuredacrossplatforms.2)Nativelibrariesandsystemcallsneedcarefulhandling.3)Dependenciesandlibrariesrequirecross-platformcompatibility.4)Performanceoptimizationacros
 Java Platform Independence: Advantages for web applicationsMay 09, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Java Platform Independence: Advantages for web applicationsMay 09, 2025 am 12:08 AMJava'splatformindependencebenefitswebapplicationsbyallowingcodetorunonanysystemwithaJVM,simplifyingdeploymentandscaling.Itenables:1)easydeploymentacrossdifferentservers,2)seamlessscalingacrosscloudplatforms,and3)consistentdevelopmenttodeploymentproce
 JVM Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to the Java Virtual MachineMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JVM Explained: A Comprehensive Guide to the Java Virtual MachineMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMTheJVMistheruntimeenvironmentforexecutingJavabytecode,crucialforJava's"writeonce,runanywhere"capability.Itmanagesmemory,executesthreads,andensuressecurity,makingitessentialforJavadeveloperstounderstandforefficientandrobustapplicationdevelop
 Key Features of Java: Why It Remains a Top Programming LanguageMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Key Features of Java: Why It Remains a Top Programming LanguageMay 09, 2025 am 12:04 AMJavaremainsatopchoicefordevelopersduetoitsplatformindependence,object-orienteddesign,strongtyping,automaticmemorymanagement,andcomprehensivestandardlibrary.ThesefeaturesmakeJavaversatileandpowerful,suitableforawiderangeofapplications,despitesomechall
 Java Platform Independence: What does it mean for developers?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AM
Java Platform Independence: What does it mean for developers?May 08, 2025 am 12:27 AMJava'splatformindependencemeansdeveloperscanwritecodeonceandrunitonanydevicewithoutrecompiling.ThisisachievedthroughtheJavaVirtualMachine(JVM),whichtranslatesbytecodeintomachine-specificinstructions,allowinguniversalcompatibilityacrossplatforms.Howev
 How to set up JVM for first usage?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AM
How to set up JVM for first usage?May 08, 2025 am 12:21 AMTo set up the JVM, you need to follow the following steps: 1) Download and install the JDK, 2) Set environment variables, 3) Verify the installation, 4) Set the IDE, 5) Test the runner program. Setting up a JVM is not just about making it work, it also involves optimizing memory allocation, garbage collection, performance tuning, and error handling to ensure optimal operation.
 How can I check Java platform independence for my product?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AM
How can I check Java platform independence for my product?May 08, 2025 am 12:12 AMToensureJavaplatformindependence,followthesesteps:1)CompileandrunyourapplicationonmultipleplatformsusingdifferentOSandJVMversions.2)UtilizeCI/CDpipelineslikeJenkinsorGitHubActionsforautomatedcross-platformtesting.3)Usecross-platformtestingframeworkss


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment







