Spring basic idea IOC
The second is java reflection. The reflection mechanism is an important implementation core of spring. Today when I looked at spring’s third-level cache to solve the problem of circular references, I discovered the life cycle of a bean. It is highly similar to the generation process of Java objects. Then I went over the bean creation process and found that the process of a bean instance from scratch is very interesting. Spring uses extremely elegant code to realize the use of reflection and various methods. This map data structure realizes the pipeline production of beans, which is very elegant, so I tried to use reflection to write a gadget that reversely generates instance objects.
Then you need to understand the process of generating an object beforehand:
I summarize the object creation process as:
Check whether there is a symbolic reference to the object in the constant pool and determine Whether it has gone through the class loading process, if not, the class loading process will be carried out.
Allocate memory for new objects (two methods: pointer collision and free list
Set the object header.
Object initialization, this is the process of executing your constructor method and assigning the values you want to define to the fields you need.
Add some details: In the process of allocating memory for new objects, first of all, the memory size required by an object after the class loading is completed is completely determined. The process of allocating memory is actually in the Java heap. Divide a memory of equal size to it, but how to divide it? If the memory layout of the Java heap is allocated in a strict order, that is, one side is used and the other side is free, then the memory will be allocated by pointer collision. The so-called pointer is collected at the dividing line between the free area and the used area. When memory is required, the pointer moves backward until the length covered by the move is equal to the memory size required by the java object and stops and allocates. But what if the memory layout of the Java heap is fragmented and discontinuous? We can only maintain a list, which records the size and location information of all Java heap free areas. When allocating, we only need to find the most suitable area allocation for new objects.
The ability of the garbage collector and whether it can perform space compression and sorting determine whether the Java heap is regular. When the collectors we use are Serial and Parnew, they are allocated by pointer collision. When we use the CMS garbage collector, we need to use the troublesome free area table allocation.
Here we focus on filling in the properties and methods: the soul of an object is its properties and methods:
The core properties used by the entire tool:
private static volatile Constructor<?> constructor;
private static volatile Object newInstance;
private static volatile Map<String, Method> methodMap;Let’s first look at the functions of these methods:
public static Constructor<?> getConstructor(Object dataType) {
Class<?> typeClass = dataType.getClass();
try {
Constructor<?> constructor = typeClass.getConstructor();
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}Get the constructor of the type. Note that this is a no-parameter construct. If you don’t have a no-parameter construct, it is very likely to report an error, because we don’t know either. How many attributes does it have, right? (Always remember that we are reverse engineering!!! We don’t know what is in this type!!! Everything is information brought by reflection)
public static void fillValueToNewInstance(Object dataType, Map<String, Object> initialMap) throws Exception {
constructor = getConstructor(dataType);
Class<?> typeClass = dataType.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = typeClass.getDeclaredFields();
Iterator<Field> fieldIterator = Arrays.stream(declaredFields).iterator();
newInstance = constructor.newInstance();
while (fieldIterator.hasNext()) {
Field field = fieldIterator.next();
field.setAccessible(true);
if (initialMap != null)
field.set(newInstance, initialMap.get(field.getName()));
}
}Get the attributes and fill in the attribute values, The attributes are also included here.
public static Method[] getMethodArray(Object dataType) {
return dataType.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
}Get all methods to form a method array.
public static void fillMethodMap(Object dataType) {
methodMap = new HashMap<>();
Method[] methodArray = getMethodArray(dataType);
Iterator<Method> iterator = Arrays.stream(methodArray).iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Method method = iterator.next();
method.setAccessible(true);
methodMap.put(method.getName(), method);
}
}Save the method into the method collection for storage.
public static Object useMethod(String methodName, @Nullable Object... parameters) throws Exception {
return methodMap.get(methodName).invoke(newInstance, parameters);
}The method of use is to pass the name.
@SneakyThrows
public static Object getBean(Object dataType, Map<String, Object> parameterMap) {
fillValueToNewInstance(dataType, parameterMap);
fillMethodMap(dataType);
return newInstance;
}getBean method.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","xu");
map.put("age",Integer.valueOf(18));
map.put("sex",'女');
Person bean = (Person) getBean(new Person(), map);
System.out.println(bean.toString());
System.out.println(useMethod("toString"));
}Test method. The type information is as follows:
class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Character sex;
//无参构造绝对不能少
public Person() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=" + sex +
'}';
}
}The test results are as follows:

Here we do not use Person person = new Person(); to instantiate the object, use Reflection implements the instantiation of objects.
I will list the reflection methods used in it:
getDeclaredFields Get the domain attribute object
getName Get the attribute name
getType Get the word of the attribute type Section code file
setAccessible(true) Set brute force cracking and obtain the use of private attributes
getDeclaredMethods Get all method arrays
getClass Get bytecode file
getConstructor Get the parameterless constructor
The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot uses reflection to simulate IOC and getBean. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
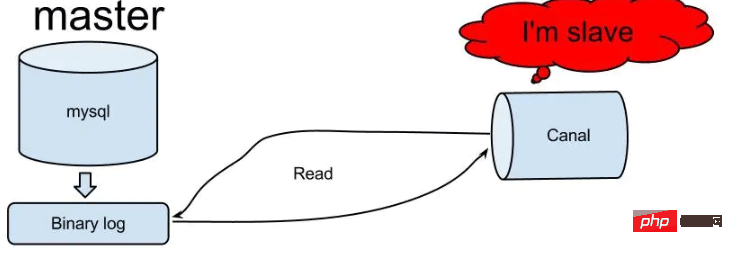 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
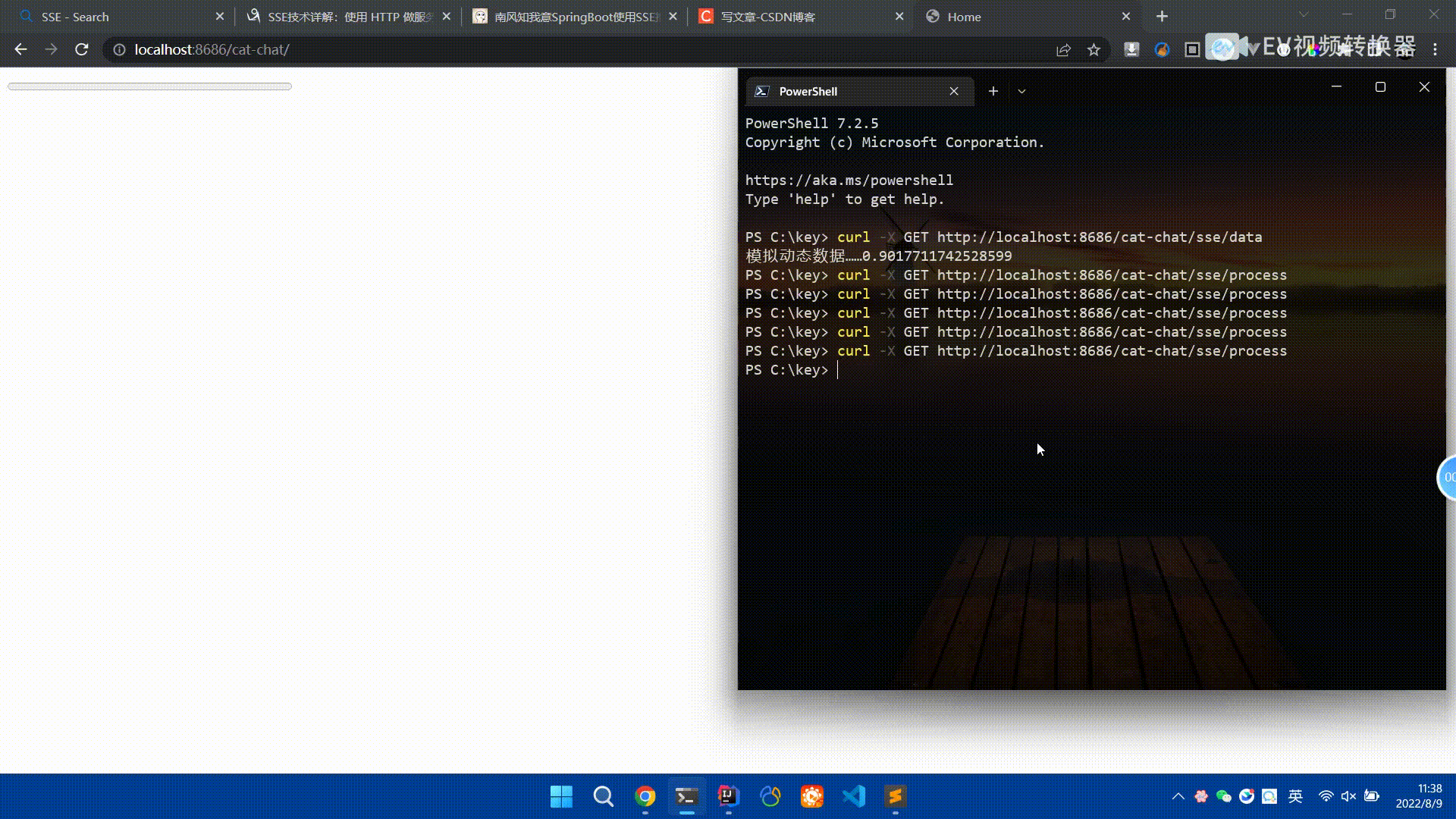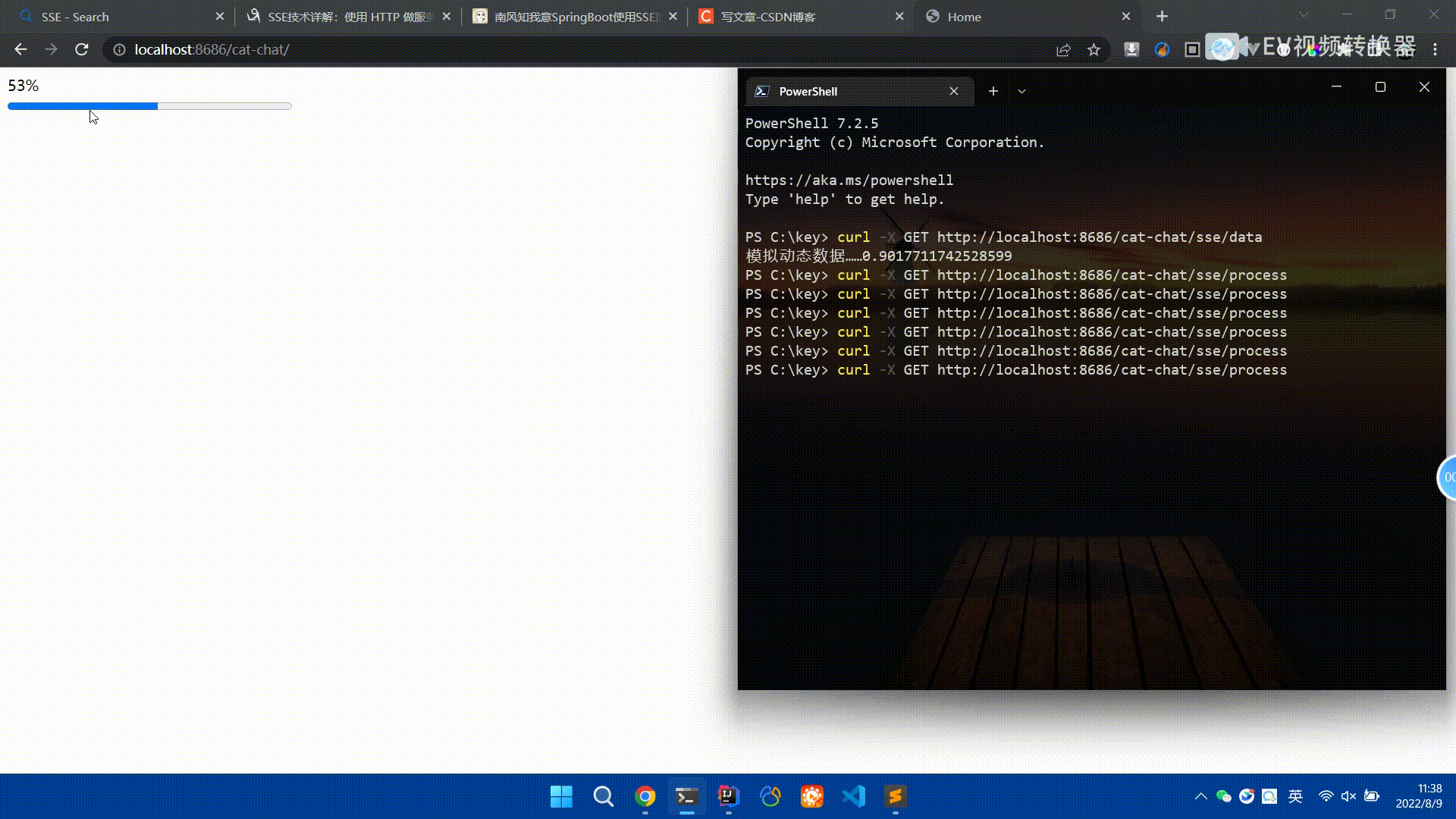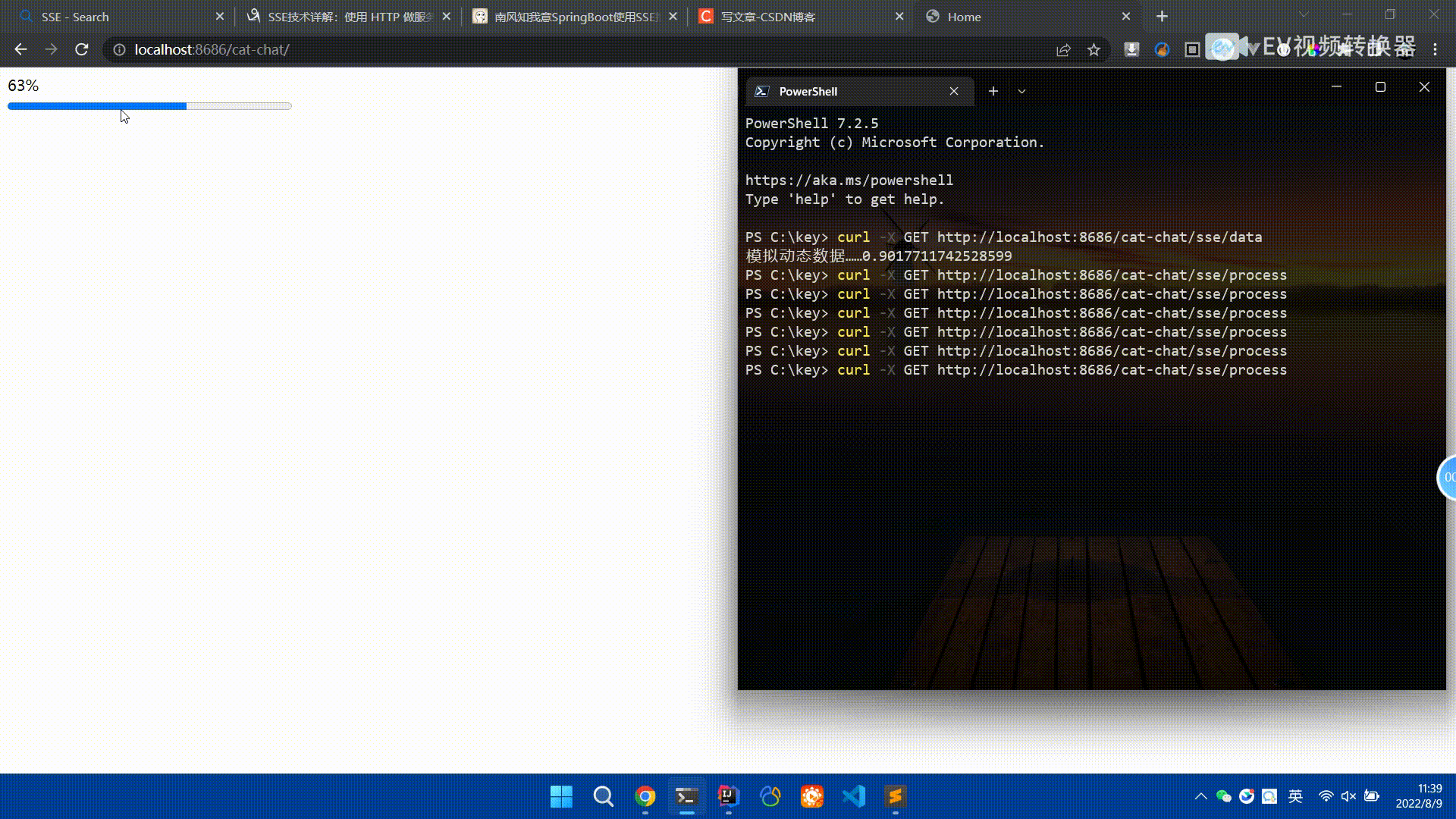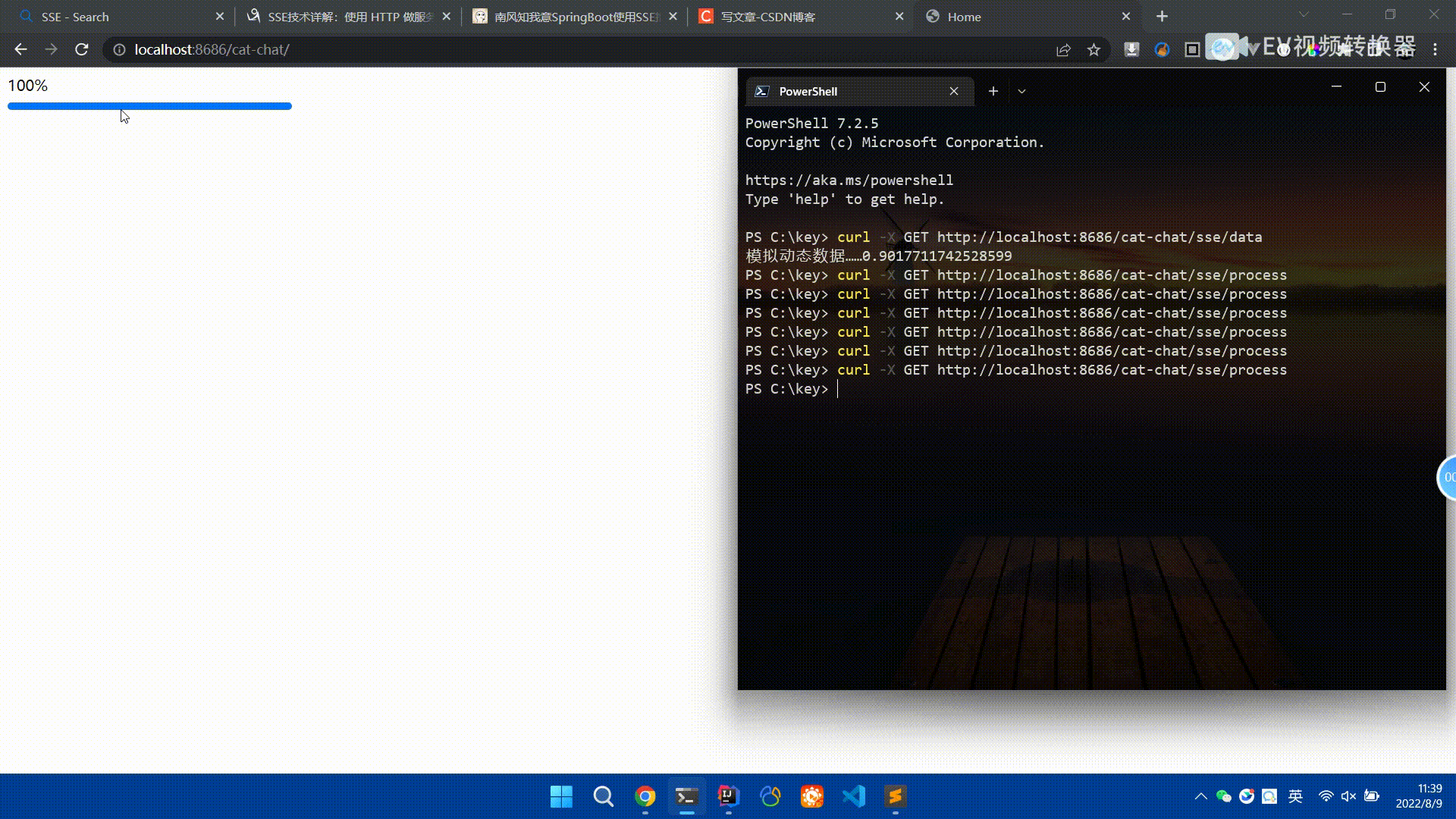 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
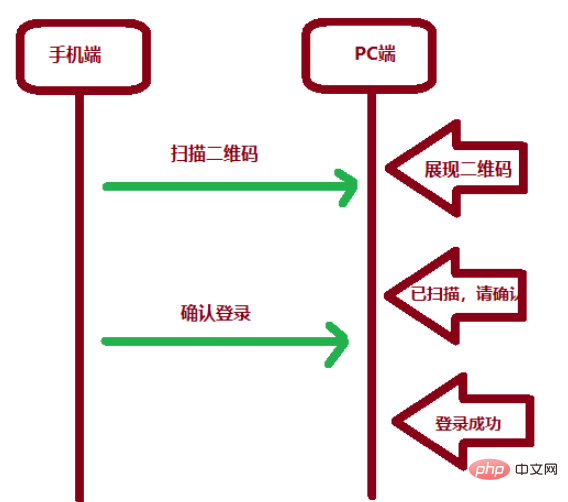 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
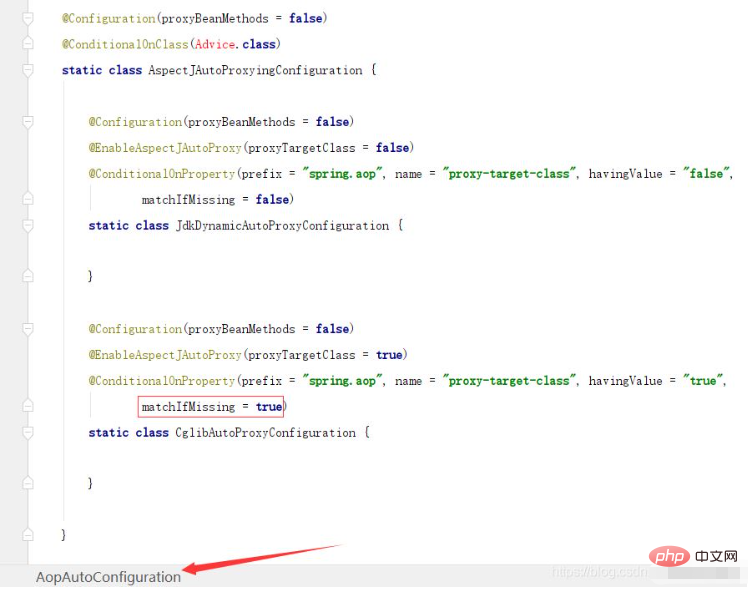 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
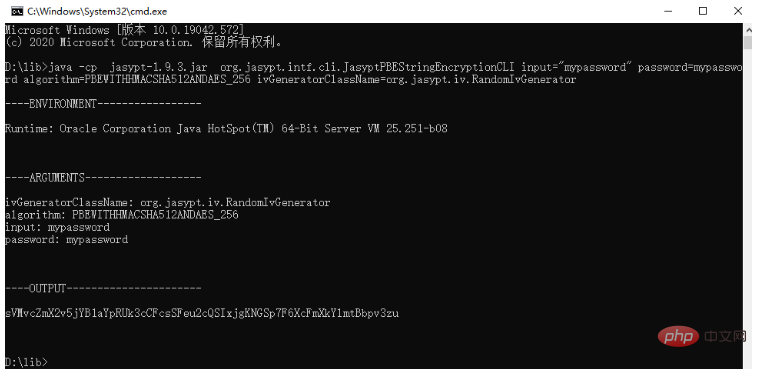 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
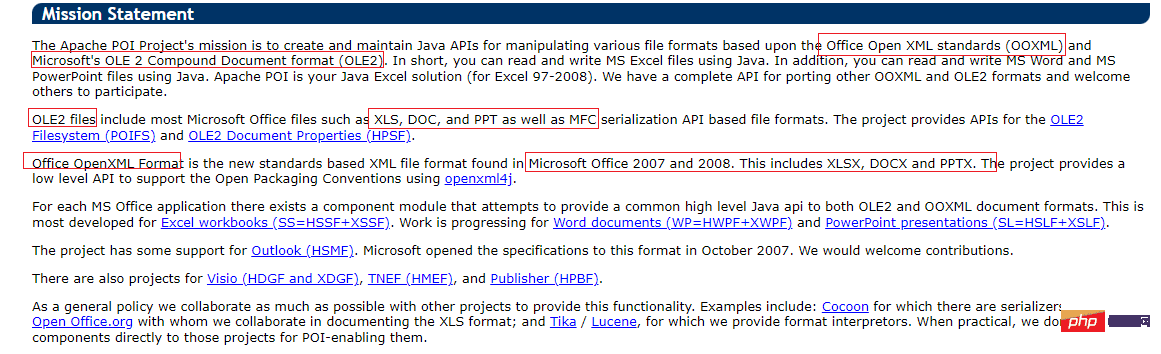
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM一、定义视频上传请求接口publicAjaxResultvideoUploadFile(MultipartFilefile){try{if(null==file||file.isEmpty()){returnAjaxResult.error("文件为空");}StringossFilePrefix=StringUtils.genUUID();StringfileName=ossFilePrefix+"-"+file.getOriginalFilename(


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft






