Spring implements custom annotations
Implements custom annotations through interceptor AOP, where the interceptor acts as a method to be executed at the specified annotation , AOP is responsible for weaving the interceptor method and the place where the annotation takes effect (generating proxy class implementation through dynamic annotation).
1. Introduce related dependencies
spring-boot-starter: Some core basic dependencies of spring
spring-boot-starter-aop: Some related dependencies of spring to implement Aop
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>2. Related classes
1. Custom annotation class
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) //说明了Annotation所修饰的对象范围,这里,的作用范围是类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //自定义注解的有效期,Runtime:注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Documented //标注生成javadoc的时候是否会被记录
public @interface EasyExceptionResult {
}2.Interceptor class
/**
* MethodInterceptor是AOP项目中的拦截器(注:不是动态代理拦截器),
* 区别与HandlerInterceptor拦截目标时请求,它拦截的目标是方法。
*/
public class EasyExceptionIntercepter implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
AnnotatedElement element=invocation.getThis().getClass();
EasyExceptionResult easyExceptionResult=element.getAnnotation(EasyExceptionResult.class);
if (easyExceptionResult == null) {
return invocation.proceed();
}
try {
return invocation.proceed();
} catch (Exception rpcException) {
//不同环境下的一个异常处理
System.out.println("发生异常了");
return null;
}
}
}3. Pointcut aspect class
The implementation class of MethodInterceptor can be used as the execution method of the aspect because the parent class of Interceptor is Advice.
@Configuration
public class EasyExceptionAdvisor {
/**
* 放在最后执行
* 等待ump/日志等记录结束
*
* @return {@link DefaultPointcutAdvisor}对象
*/
@Bean
@Order(Integer.MIN_VALUE)
public DefaultPointcutAdvisor easyExceptionResultAdvisor() {
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor();
//针对EasyExceptionResult注解创建切点
AnnotationMatchingPointcut annotationMatchingPointcut = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(EasyExceptionResult.class, true);
EasyExceptionIntercepter interceptor = new EasyExceptionIntercepter();
advisor.setPointcut(annotationMatchingPointcut);
//在切点执行interceptor中的invoke方法
advisor.setAdvice(interceptor);
return advisor;
}
}4. Use of custom annotations
@Service
@EasyExceptionResult //自定义异常捕获注解
public class EasyServiceImpl {
public void testEasyResult(){
throw new NullPointerException("测试自定义注解");
}
}5. Effect
@SpringBootApplication
public class JdStudyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(JdStudyApplication.class, args);
EasyServiceImpl easyService=context.getBean(EasyServiceImpl.class);
easyService.testEasyResult();
}
}
So far, custom annotations have been implemented through spring.
Java implements custom annotations
Although custom annotations are implemented through Spring, there are still ways for us to implement custom annotations without using Spring. After all, annotations are earlier than Spring.
There are some meta-annotations in JDK, mainly @Target, @Retention, @Document, and @Inherited, which are used to modify annotations. The following is a custom annotation.
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) //说明了Annotation所修饰的对象范围,这里,的作用范围是类、接口(包括注解类型) 或enum
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //自定义注解的有效期,Runtime:注解不仅被保存到class文件中,jvm加载class文件之后,仍然存在
@Documented //标注生成javadoc的时候是否会被记录
public @interface EasyExceptionResult {
}@Target
Indicates the java element type to which this annotation can be applied
| Target type | Description |
|---|---|
| ElementType.TYPE | Applies to classes, interfaces (including annotation types), and enumerations |
| ElementType.FIELD | Applies to properties (including constants in enumerations) |
| ElementType.METHOD | Applies to methods |
| ElementType.PARAMETER | Formal parameters applied to methods |
| ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR | Applied to constructors |
| ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE | Apply to local variables |
| ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE | Apply to annotation types |
| ElementType.PACKAGE | Apply to package |
| ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER | New in version 1.8, applied to type variables ) |
| ElementType.TYPE_USE | New in version 1.8, it applies to any statement that uses types (such as types in declaration statements, generics, and cast statements) |
@Retention
Indicates the life cycle of the annotation
| Lifecycle type | Description |
|---|---|
| RetentionPolicy.SOURCE | Discarded at compile time and not included in the class file |
| RetentionPolicy.CLASS | Discarded when the JVM loads, included in the class file, the default value |
| RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME | is determined by the JVM Loaded, included in the class file, and can be obtained at runtime |
@Document
indicates the element marked by the annotation Can be documented by Javadoc or similar tools
@Inherited
An annotation that indicates the use of the @Inherited annotation. Subclasses of the marked class will also have this annotation
Achieved through Cglib
After we define the annotations, we need to consider how to bind the annotations and classes together to achieve the effect we want during runtime. Here we can introduce dynamic proxies The mechanism of the annotation is to perform a weaving operation when the class is compiled before the method is executed, as follows.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class easyServiceImplClass=EasyServiceImpl.class;
//判断该对象是否有我们自定义的@EasyExceptionResult注解
if(easyServiceImplClass.isAnnotationPresent(EasyExceptionResult.class)){
final EasyServiceImpl easyService=new EasyServiceImpl();
//cglib的字节码加强器
Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer();
将目标对象所在的类作为Enhaner类的父类
enhancer.setSuperclass(EasyServiceImpl.class);
通过实现MethodInterceptor实现方法回调,MethodInterceptor继承了Callback
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
try{
method.invoke(easyService, args);
System.out.println("事务结束...");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("发生异常了");
}
return proxy;
}
});
Object obj= enhancer.create();;
EasyServiceImpl easyServiceProxy=(EasyServiceImpl)obj;
easyServiceProxy.testEasyResult();
}
}Running effect:

public class EasyServiceImplProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private EasyServiceImpl target;
public void setTarget(EasyServiceImpl target)
{
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 这里可以做增强
System.out.println("已经是代理类啦");
try{
return method.invoke(proxy, args);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("发生异常了");
return null;
}
}
/**
* 生成代理类
* @return 代理类
*/
public Object CreatProxyedObj()
{
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
}
The difference between Cglib and JDK dynamic proxy Java dynamic proxy uses the reflection mechanism to generate an anonymous class that implements the proxy interface, and calls InvokeHandler to process it before calling specific methods. The cglib dynamic proxy uses the asm open source package to load the class file of the proxy object class and modify its bytecode to generate a subclass for processing. 1. If the target object implements the interface, JDK's dynamic proxy will be used by default to implement AOP 2. If the target object implements the interface, CGLIB can be forced to be used to implement AOP 3. If the target object does not implement the interface, the CGLIB library must be used. Spring will automatically convert between JDK dynamic proxy and CGLIB.
How to force the use of CGLIB to implement AOP?
(1) Add the CGLIB library, SPRING_HOME/cglib/*.jar(2) AddWhat is the difference between JDK dynamic proxy and CGLIB bytecode generation?
(1) JDK dynamic proxy can only generate proxies for classes that implement interfaces, but not for classes (2) CGLIB implements proxies for classes, mainly for specified The class generates a subclass and overrides the methods Because it is inheritance, it is best not to declare the class or method as finalThe above is the detailed content of How to use AOP and interceptors to implement custom annotations in SpringBoot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
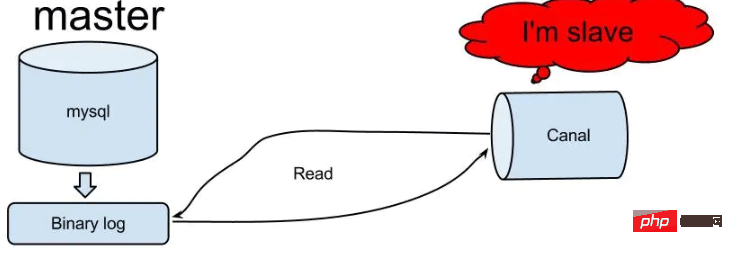 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
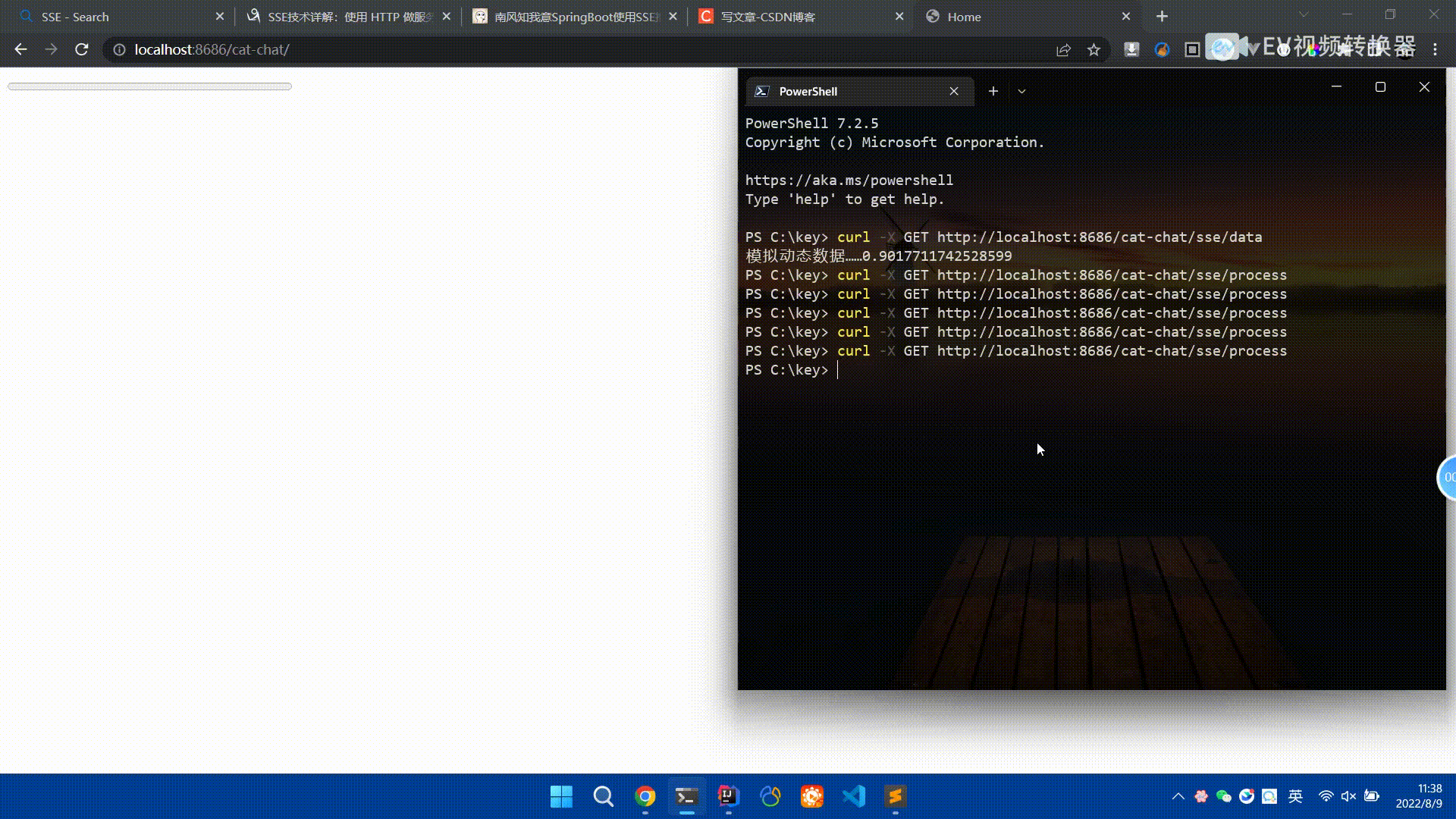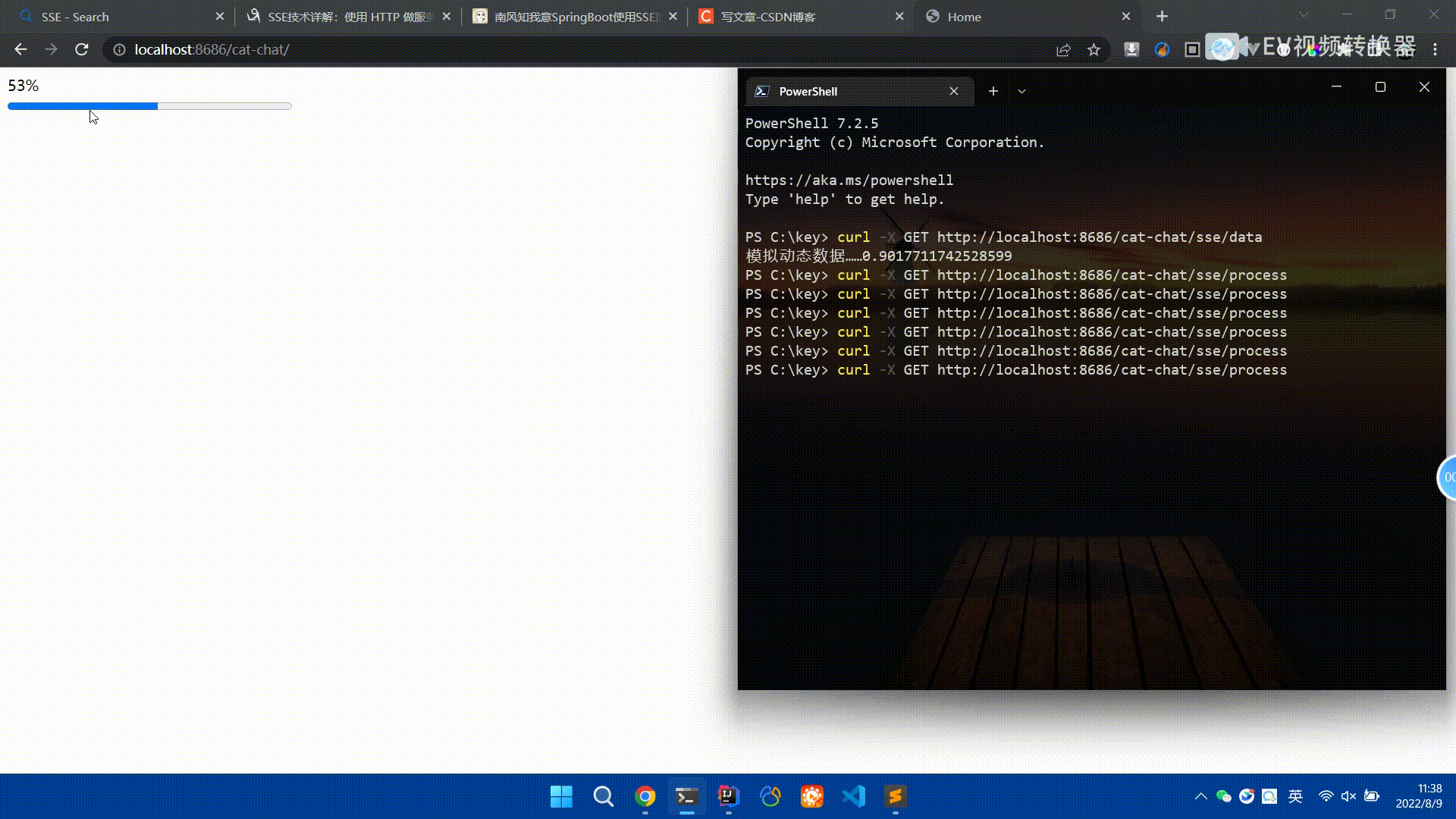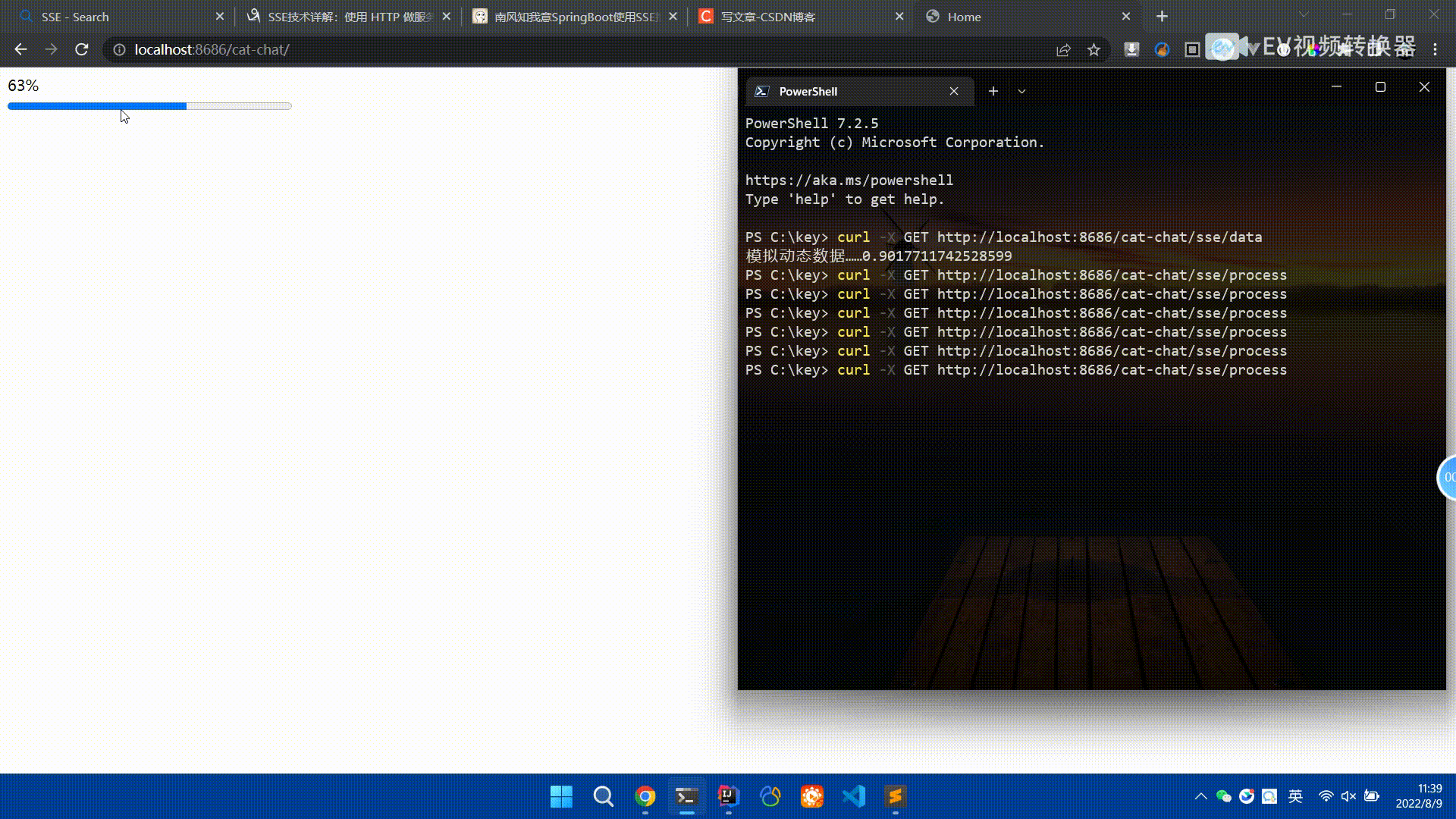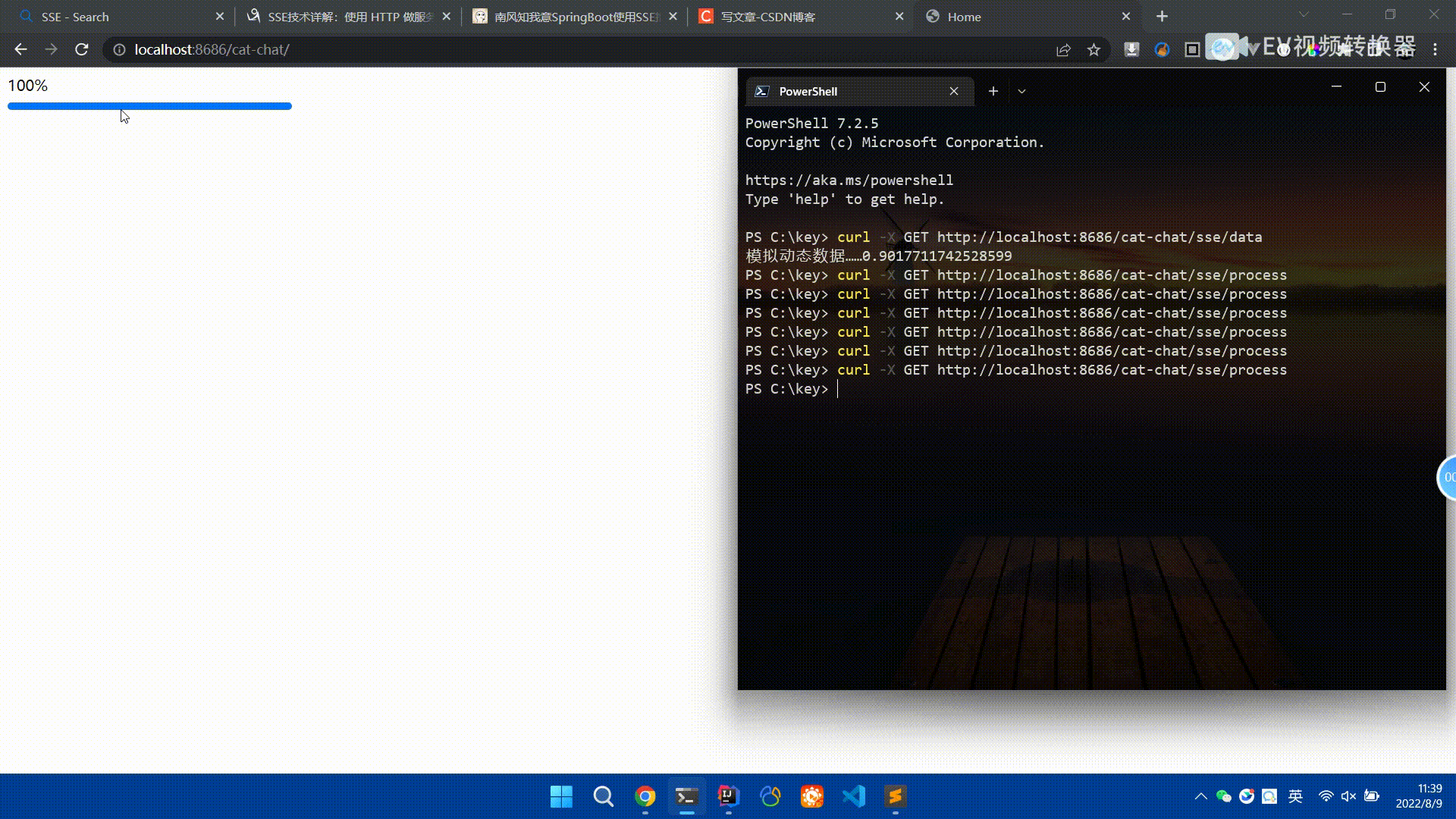 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
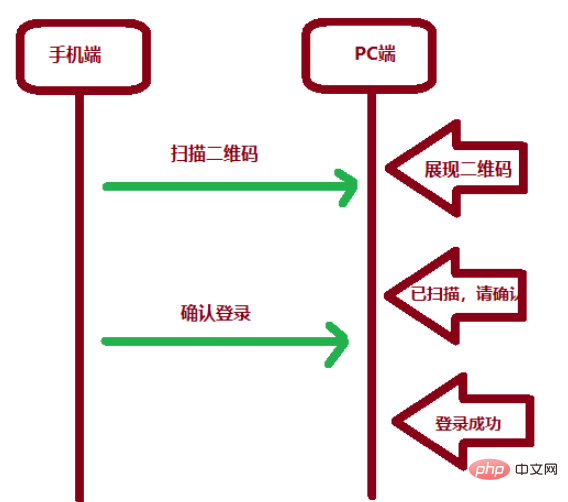 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
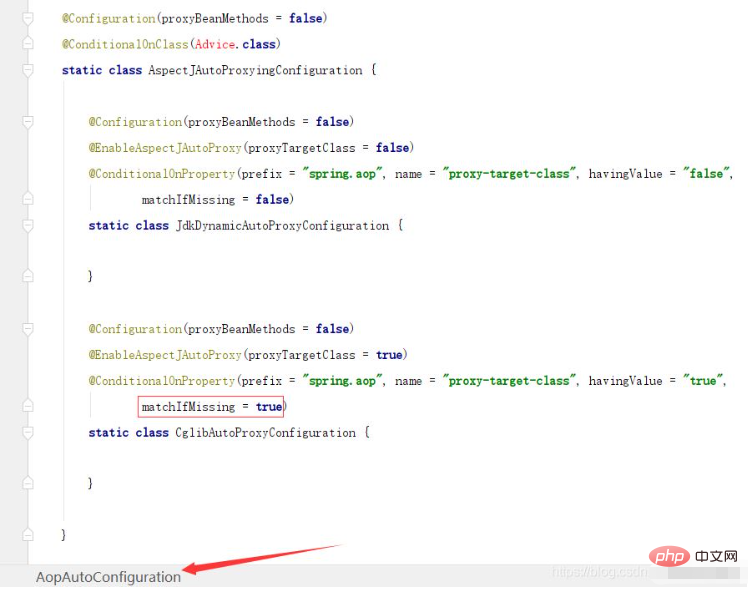 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
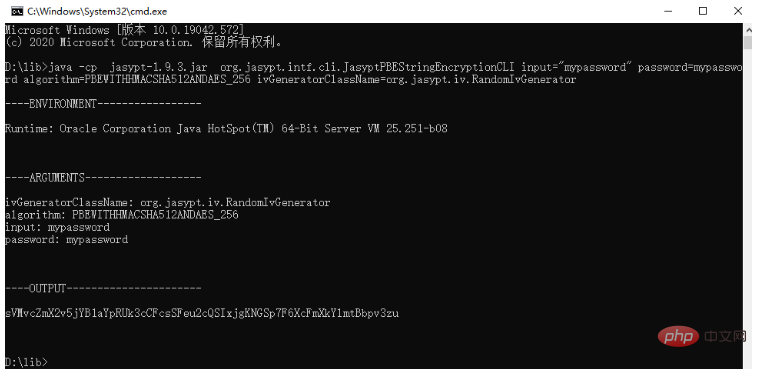 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 SpringBoot项目打包发布到外部tomcat遇到的问题怎么解决May 10, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
SpringBoot项目打包发布到外部tomcat遇到的问题怎么解决May 10, 2023 pm 05:49 PM先说遇到问题的情景:初次尝试使用springboot框架写了个小web项目,在IntellijIDEA中能正常启动运行。使用maven运行install,生成war包,发布到本机的tomcat下,出现异常,主要的异常信息是.......LifeCycleException。经各种搜索,找到答案。springboot因为内嵌tomcat容器,所以可以通过打包为jar包的方法将项目发布,但是如何将springboot项目打包成可发布到tomcat中的war包项目呢?1.既然需要打包成war包项目,首


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.







