Example analysis of master-slave replication, sentry, and clustering in Redis
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-29 13:52:54910browse
1. Redis master-slave replication
1. Overview of master-slave replication
Master-slave replication copies data from one Redis server to other Redis servers process. The former is called the master node (Master), and the latter is called the slave node (Slave); data replication is one-way, and can only be from the master node to the slave node.
By default, each Redis server is a master node; and a master node can have multiple slave nodes, but a slave node can only have one master node. [Related recommendation: Redis video tutorial]
2. The role of master-slave replication
● Data redundancy: Master-slave replication realizes data Hot backup is a data redundancy method other than persistence.
● Failure recovery: When a problem occurs on the master node, the slave node can provide services to achieve rapid failure recovery; it is actually a kind of service redundancy.
● Load balancing: Based on master-slave replication, combined with read-write separation, the master node can provide write services and the slave nodes can provide read services (that is, when writing Redis data, the application connects to the master node , when reading Redis data, apply the connection slave node) to share the server load; especially in the scenario of less writing and more reading, sharing the read load through multiple slave nodes can greatly increase the concurrency of the Redis server.
● Cornerstone of High Availability: In addition to the above functions, master-slave replication is also the basis for the implementation of sentinels and clusters. Therefore, master-slave replication is the basis of Redis high availability.
3. Master-slave replication process
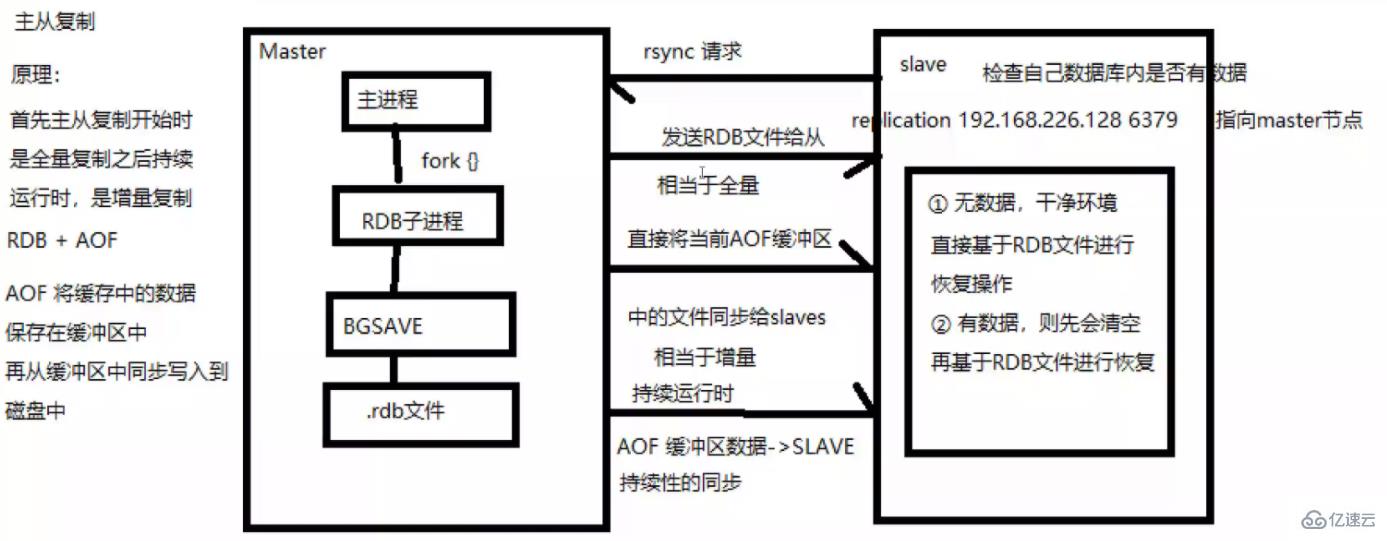
(1) If a Slave machine process is started, it will send data to the Master machine Send a "sync command" command to request a synchronous connection.
(2) Whether it is the first connection or reconnection, the Master machine will start a background process to save the data snapshot to the data file (perform RDB operation). At the same time, the Master will also record and cache all commands to modify the data. in the data file.
(3) After the background process completes the caching operation, the Master machine will send the data file to the Slave machine. The Slave machine will save the data file to the hard disk and then load it into the memory. Then the Master machine will modify the data file. All operations on the data are sent to the Slave machine at the same time. If the Slave fails and causes downtime, it will automatically reconnect when it returns to normal.
(4) After the Master machine receives the connection from the Slave machine, it sends its complete data file to the Slave machine. If the Master receives multiple synchronization requests from the Slave at the same time, the Master will start a synchronization request in the background. process to save the data file and then send it to all slave machines to ensure that all slave machines are normal.
4. Set up Redis master-slave replication
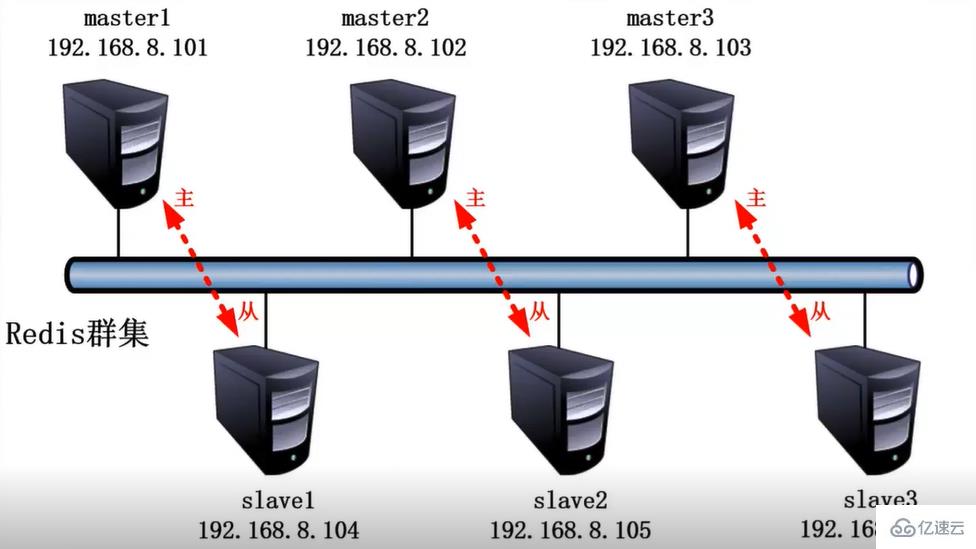
4.1 Server IP configuration
| Server | Host Name | IP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Master Node | master | 192.168 .122.10 | ||
| Slave1 node | slave1 | 192.168.122.11 | ||
| Slave2 node | slave2 | 192.168.122.12 |
| Server | Host Name | IP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| master | 192.168.122.10 | |||
| slave1 | 192.168.122.11 | |||
| slave2 | 192.168.122.12 |
| 服务器 | 主机名 | IP | 主端口 | 从端口 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node1节点 | node | 192.168.122.10 | 6001 | 6004 |
| Node2节点 | node | 192.168.122.10 | 6002 | 6005 |
| Node3节点 | node | 192.168.122.10 | 6003 | 6006 |
7.2 服务器防火墙环境
systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld setenforce 0
7.3 创建集群配置目录及文件
[root@node ~]# cd /etc/redis
[root@node redis]# mkdir -p redis-cluster/redis600{1..6}
[root@node redis]# for i in {1..6}
> do
> cp /opt/redis-5.0.7/redis.conf /etc/redis/redis-cluster/redis600$i
> cp /opt/redis-5.0.7/src/redis-cli /opt/redis-5.0.7/src/redis-server /etc/redis/redis-cluster/redis600$i
> done
[root@node redis]# ls -R redis-cluster/
redis-cluster/:
redis6001 redis6002 redis6003 redis6004 redis6005 redis6006
redis-cluster/redis6001:
redis-cli redis.conf redis-server
redis-cluster/redis6002:
redis-cli redis.conf redis-server
redis-cluster/redis6003:
redis-cli redis.conf redis-server
redis-cluster/redis6004:
redis-cli redis.conf redis-server
redis-cluster/redis6005:
redis-cli redis.conf redis-server
redis-cluster/redis6006:
redis-cli redis.conf redis-server7.4 开启群集功能
仅以redis6001为例,其他5个文件夹的配置文件以此类推修改,特别注意端口号的修改。
[root@node redis]# cd redis-cluster/redis6001 [root@node redis6001]# vim redis.conf ##69行,注释掉bind项,默认监听所有网卡 #bind 127.0.0.1 ##88行,修改,关闭保护模式 protected-mode no ##92行,修改,redis监听端口 port 6001 ##136行,开启守护进程,以独立进程启动 daemonize yes ##832行,取消注释,开启群集功能 cluster-enabled yes ##840行,注销注释,群集名称文件设置 cluster-config-file nodes-6001.conf ##846行,注销注释,群集超时时间设置 cluster-node-timeout 15000 ##700行,修改,开启AOF持久化 appendonly yes
7.5 启动redis节点
分别进入那六个文件夹,执行命令:“redis-server redis.conf”,来启动redis节点
[root@node redis6001]# for d in {1..6}
> do
> cd /etc/redis/redis-cluster/redis600$i
> ^C
[root@node redis6001]# for d in {1..6}
> do
> cd /etc/redis/redis-cluster/redis600$d
> redis-server redis.conf
> done
[root@node1 redis6006]# ps -ef | grep redis
root 992 1 0 13:45 ? 00:00:07 /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server 0.0.0.0:6379
root 2289 1 0 14:41 ? 00:00:00 redis-server *:6001 [cluster]
root 2294 1 0 14:41 ? 00:00:00 redis-server *:6002 [cluster]
root 2299 1 0 14:41 ? 00:00:00 redis-server *:6003 [cluster]
root 2304 1 0 14:41 ? 00:00:00 redis-server *:6004 [cluster]
root 2309 1 0 14:41 ? 00:00:00 redis-server *:6005 [cluster]
root 2314 1 0 14:41 ? 00:00:00 redis-server *:6006 [cluster]
root 2450 2337 0 14:50 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto redis7.6 启动集群
[root@node redis6006]# redis-cli --cluster create 127.0.0.1:6001 127.0.0.1:6002 127.0.0.1:6003 127.0.0.1:6004 127.0.0.1:6005 127.0.0.1:6006 --cluster-replicas 1
六个实例分为三组,每组一主一从,前面的做主节点,后面的做从节点。下面交互的时候需要输入yes才可以成功创建。
–replicas 1表示每个主节点有1个从节点。
7.7 测试集群
[root@node1 redis6006]# redis-cli -p 6001 -c
#加-c参数,节点之前就可以互相跳转
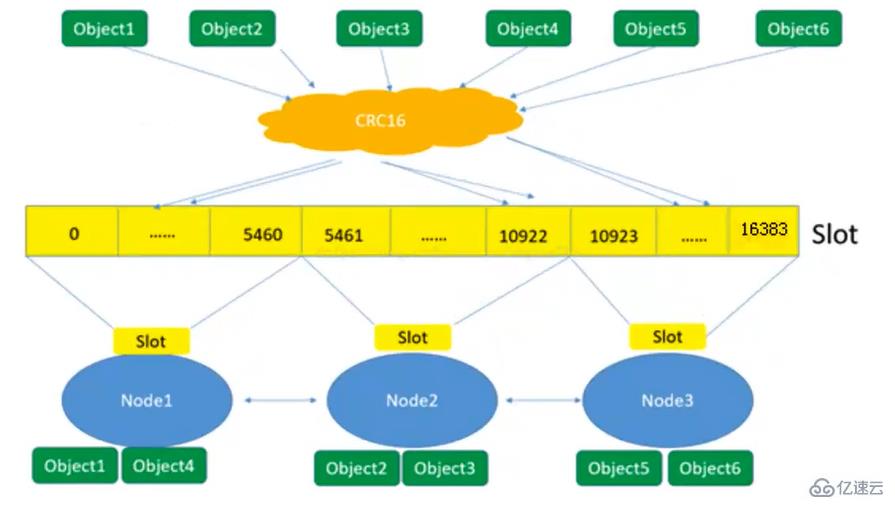
127.0.0.1:6001> cluster slots
#查看节点的哈希槽编号范围
1) 1) (integer) 0
#哈希槽起始编号
2) (integer) 5460
#哈希槽终止编号
3) 1) "127.0.0.1"
2) (integer) 6001
#node节点主
3) "18e59f493579facea29abf90ca4050f566d66339"
4) 1) "127.0.0.1"
2) (integer) 6004
#node节点从
3) "2635bf6a0c286ef910ec5da03dbdc7cde308c588"
2) 1) (integer) 10923
2) (integer) 16383
3) 1) "127.0.0.1"
2) (integer) 6003
3) "51460d417eb56537e5bd7e8c9581c66fdd817b3c"
4) 1) "127.0.0.1"
2) (integer) 6006
3) "51a75667dcf21b530e69a3242a3e9f81f577168d"
3) 1) (integer) 5461
2) (integer) 10922
3) 1) "127.0.0.1"
2) (integer) 6002
3) "6381d68c06ddb7ac43c8f7d7b8da0644845dcd59"
4) 1) "127.0.0.1"
2) (integer) 6005
3) "375ad927116d3aa845e95ad5f0586306e7ff3a96"
127.0.0.1:6001> set num 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6001> get num
"1"
127.0.0.1:6001> keys *
1) "num"
127.0.0.1:6001> quit
[root@node1 redis6006]# redis-cli -p 6002 -c
127.0.0.1:6002> keys *
#6002端口无键值对
(empty list or set)
127.0.0.1:6002> get num
-> Redirected to slot [2765] located at 127.0.0.1:6001
"1"
#6002端口获取到num键位于6001端口,切换到6001端口并显示键值
127.0.0.1:6001> set key1 11111
-> Redirected to slot [9189] located at 127.0.0.1:6002
OK
#6001端口创建键值对,将其存至6002端口,并切换至6002端口
127.0.0.1:6002>The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of master-slave replication, sentry, and clustering in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!