Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >How to operate MongoDB database with Python
How to operate MongoDB database with Python
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-28 09:31:102947browse
1. Connector installation and configuration
pymongo: The Python toolkit officially provided by MongoDB. Official documentation: https://pymongo.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ pip installation, the command is as follows:
pip install pymongo
Main steps to manage MongoDB As follows:
Connect to the MongoDB database system
Manage the MongoDB database
Management Collections in MongoDB
Manage documents in MongoDB
The first step is to connect to MongoDB:
# 方式一: 使用默认的配置 client = MongoClient() # 方式二: 指定主机地址和端口号 client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017) # 方式三: 使用URI连接参数 client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
The second step, manage the database:
#通过MongoClient对象来管理多个数据库获取数据库(逻辑库)对象 db = client.DATABASE_NAME db = client["DATABASE_NAME"] db = client.get_database(name=None, *args) # 查看所有的数据库(逻辑库) client.list_databases() # 删除数据库(逻辑库) client.drop_database(name_or_database, *args)
The third step, manage the collection
# 通过数据库对象db来管理集合 # 获取集合对象 db = client.DATABASE_NAME db.COLLECTION_NAME client.DATABASE_NAME.COLLECTION_NAME db.get_collection(name, *args) # 查看当前数据库下的集合列表 db.list_collection_names() # 删除集合 db.drop_collection(name_or_collection, *args)
Basic operation example:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2023-03-17 1:47
# @Author : AmoXiang
# @File : 1.数据库连接.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @Blog : https://blog.csdn.net/xw1680
from pymongo import MongoClient
# 使用默认配置连接到数据库
# client = MongoClient()
# print(client)
# client.close()
# 指定主机地址和端口号连接到数据库
# client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017)
# 使用URI连接参数连接到数据库
client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
print(client)
# client.close()
#
# # 访问数据库
# db = client.test
# db = client["test"]
# print(db)
# db = client.get_database('test')
# client.close()
# print(db)
#
# 查看有哪些数据库
db_list = client.list_databases()
# # db_list = client.list_database_names()
for item in db_list:
print(item)
#
# 查看数据库下有哪些集合
db_test = client["test"]
for item in db_test.list_collection_names():
print(item)
#
# # 集合对象操作
# data = db_test.students.find_one()
# data = client.test.students.find_one()
data = client.test.get_collection('students').find_one()
print(data)2. New document
Description: pymongo can convert python objects into BSON when inserting data
insert_one(): Insert a document
# 调用方法 result = db.COLLECTION_NAME.insert_one(doc) # 返回插入的文档ID result.inserted _id
insert_many(): Add documents in batches. Calling method:
doc_list = [doc1,doc2] result = db.COLLECTION_NAME.insert_many(doc_list)
Example:
3. Query documents
pymongo can convert the query results into objects in python
Common methods:
find_one(): 按条件查询一个文档 find(): 按条件查询多个文档 count_documents(): 统计满足条件的文档总数 aggregate(): 聚合统计 .sort(): 排序 .skip().limit(): 分页
Sample code:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2023-03-18 15:03
# @Author : AmoXiang
# @File : 5.查询文档.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @Blog : https://blog.csdn.net/xw1680
from bson.objectid import ObjectId
from pymongo import MongoClient, ASCENDING, DESCENDING
class LearnMongoDBSearch(object):
""" MongoDB查询练习 """
def __init__(self):
self.client = MongoClient()
def search_one(self):
""" 查询一个文档 """
temp_obj = self.client.test.newdb.find_one()
print(temp_obj)
print('喜欢分数:', temp_obj['likes'])
# print('注册时间:', temp_obj['reg_date'].date())
print('姓名:', temp_obj['uname'])
def search_user_by_pk(self, pk):
obj_id = ObjectId(pk)
# user_obj = self.client.test.newdb.find_one({'_id': obj_id})
# 面向对象的方法,有代码提示
db = self.client.get_database('test')
users = db.get_collection('newdb')
user_obj = users.find_one({'_id': obj_id})
print(user_obj)
def search_many(self):
""" 查询多个文档 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
students = db.get_collection('students')
# stu_list = students.find()
# for item in stu_list:
# print(item)
# 查询年龄大于12岁的学生
stu_list = students.find({'age': {'$gt': 12}}, {'stu_name': 1, 'class_name': 1, 'age': 1})
for item in stu_list:
# 注意: mongo中存储的整数转换成了浮点数
print(item)
def paginate(self, page=1, page_size=10):
"""
分页处理
:param page: 当前的页
:param page_size: 每一页数据大小
:return:
"""
db = self.client.get_database('test')
students = db.get_collection('students')
offset = (page - 1) * page_size
stu_list = students.find().skip(offset).limit(page_size)
return stu_list
def sort_data(self):
""" 排序 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
grades = db.get_collection('grades')
# // 将学生的语文成绩从高到低排序
# db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "语文"}).sort({"grade.score": -1});
#
# //将学生的语文成绩按照年龄和成绩排序
# db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "语文"}).sort({"age": -1, "grade.score": -1});
# db.grades.find({"grade.course_name": "语文"}).sort({"grade.score": -1, "age": -1});
# 按某一列排序
# data_list = grades.find({"grade.course_name": "语文"}).sort("grade.score", DESCENDING);
# for item in data_list:
# print(item)
# 按多列排序
data_list = grades.find({"grade.course_name": "语文"}).sort([('age', DESCENDING),("grade.score", DESCENDING),])
for item in data_list:
print(item)
def counter_students(self):
""" 统计newdb中文档总数 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
# result = newdb.count_documents({})
result = newdb.count_documents({"uname": {"$eq": "张三"}})
print(result)
def test_aggregate(self):
"""
聚合统计:及格的学生成绩
"""
db = self.client.get_database('test')
grades = db.get_collection('grades')
result = grades.aggregate([
# //where
{
'$match': {"grade.score": {'$gte': 60}}
},
# //group by
{
'$group': {
'_id': "$stu_no",
'total': {'$sum': 1}
}
},
# // having
{
'$match': {
'total': {'$eq': 3}
}
}
])
for item in result:
print(item)
if __name__ == '__main__':
obj = LearnMongoDBSearch()
# obj.search_one()
# obj.search_user_by_pk('6411ee77b6170000b4003f95')
# obj.search_many()
# stu_list = obj.paginate(page=3)
# for item in stu_list:
# print(item)
# obj.sort_data()
# obj.counter_students()
obj.test_aggregate()4. Update the document
Review, update the data expression, as shown in the following table:
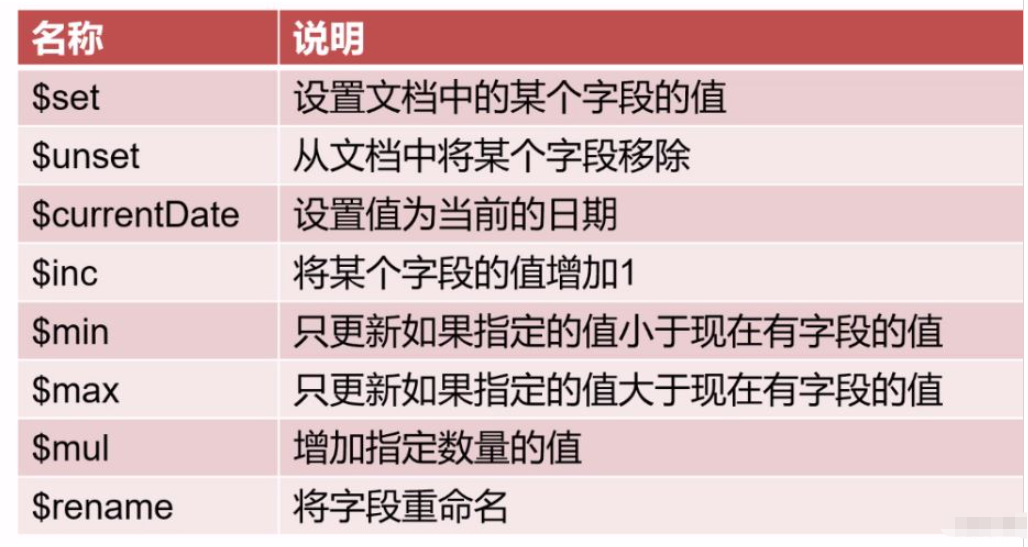
Modify a document and call the method:
update_one(filter, update, *args)
Replace a document and call the method:
replace_one(filter, replacement, *args)
Modify documents in batches and call the method:
replace_one(filter, replacement, *args)
Shortcut method:
find_one_and_update(filter, update, *args) # 修改一个文档 find_one_and_replace(filter, replacement, *args) # 替换一个文档 # 注意返回值的不同
Return results:
acknowledged: whether the result has been confirmed
modified_count: the number of modified documents
matched_count: the number of documents that meet the conditions
raw_result: original data
upserted_id: updated ID (upsert=True)
Sample code:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2023-03-18 14:56
# @Author : AmoXiang
# @File : 4.修改文档.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @Blog : https://blog.csdn.net/xw1680
from pymongo import MongoClient
class LearnMongoDBUpdate(object):
""" MongoDB更新练习 """
def __init__(self):
self.client = MongoClient()
def test_update_one(self):
""" 更新一个文档 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
result = newdb.update_one({}, {'$set': {'likes': 70}})
print(result.modified_count)
def test_replace_one(self):
""" 替换一个文档 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
result = newdb.replace_one({}, {'uname': '张三'})
print(result.modified_count)
def test_update_many(self):
""" 批量更新文档 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
result = newdb.update_many({}, {'$set': {'likes': 90}})
print('修改的数量:', result.modified_count)
print('满足条件的数量:', result.matched_count)
def test_update_shortcut(self):
""" 更新文档的快捷方法 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
# 此处返回一个文档对象
result = newdb.find_one_and_update({}, {'$set': {'sex': '未知'}})
print(result['_id'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
obj = LearnMongoDBUpdate()
# obj.test_update_one()
# obj.test_replace_one()
# obj.test_update_many()
obj.test_update_shortcut()5. Delete documents
To delete a document, the calling method is as follows:
result = db.COLLECTION_NAME.delete_one(filter, *args) # 返回已经删除的记录数 result.deleted_count # 删除时返回文档对象 find_one_and_delete(filter, *args)
To delete documents in batches, the calling method is:
result = db.COLLECTION_NAME.delete_many(filter, *args) # 返回已经删除的记录数 result. deleted_count
Example Code:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2023-03-18 14:34
# @Author : AmoXiang
# @File : 3.删除文档.py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @Blog : https://blog.csdn.net/xw1680
from pymongo import MongoClient
class LearnMongoDBDelete(object):
""" MongoDB删除练习 """
def __init__(self):
self.client = MongoClient()
def test_delete_one(self):
""" 删除一个文档 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
result = newdb.delete_one({})
print(result.deleted_count)
def test_delete_many(self):
""" 批量删除文档 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
users = db.get_collection('newdb')
# 删除所有的数据
result = users.delete_many({"likes": {"$lte": 90}})
print(result.deleted_count)
def test_delete_shortcut(self):
""" 删除文档的快捷方法 """
db = self.client.get_database('test')
newdb = db.get_collection('newdb')
result = newdb.find_one_and_delete({})
print(result['title'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
obj = LearnMongoDBDelete()
# obj.test_delete_one()
# obj.test_delete_shortcut()
obj.test_delete_many()The above is the detailed content of How to operate MongoDB database with Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

