Home >Java >javaTutorial >Example analysis of Java sequence table
Example analysis of Java sequence table
- PHPzforward
- 2023-05-23 16:58:12968browse
1. Foreword
Sequence table is a commonly used type. It is very important to learn and understand it. Sequence table lays the foundation for future learning.
2. Definition of sequence
The sequence represents a linear table saved in the form of an array in the computer memory, occupying a set of continuous storage units in the memory
, in Each element is stored in this sequence.

3. Implementing the sequence table
3.1 API design of the sequence table

3.2 Sequence table Code implementation
Define a generic class (the advantage of a generic class is that it can accept any type)
//定义一个泛型类
public class SequenceList<T> {}Define member variables in the generic class
//定义一个存储元素的数组(先定义为泛型)
private T[] eles;
//定义一个变量表示顺序表中的元素个数
private int N;Define the constructor Method, used to initialize member variables
//添加构造方法,用来初始化成员变量
public SequenceList(int capacity) {//接受一个容量长度
//初始化数组
this.eles = (T[]) new Object[capacity];//创建的是Object类型的所以需要强转为T[]
//初始化顺序表的长度
this.N = 0;
}The following functions are implemented:
Set the linear table to an empty table
// 将一个线性表置为空表
public void clear(){
//只需将顺序表的长度变为0即可
this.N=0;
}
//我们使用this的原因是:一定指的是成员变量,防止有局部变量和成员变量同名。
//只要涉及到成员变量尽量用this修饰Judge whether the linear table is an empty table
//判断当前线性表是否为空表
public boolean isEmpty(){
//是否为空只需要判断线性表中的元素个数
return this.N==0;
}Get the length of the linear table
//获取线性表的长度
public int length(){
//只需返回N即可
return this.N;
}Get the element at position i
//获取指定i位置的元素
public T get(int i){
//因为顺序表是一个数组,只需要通过索引找到该元素即可
return eles[i];
}Add element t to the linear table
//向线性表中添加元素t
public void insert(T t){//T表示的元素的类型
//这个表示非常的巧妙,将元素加1的同时又将索引N的位置赋值了元素
eles[N++]=t;
//这个表示等价于eles[N]=t;N++;
}Insert element t# at index i ##
//在i元素初插入元素t
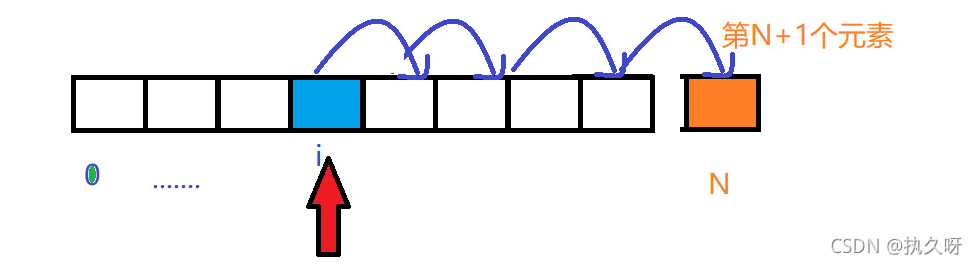
public void insert(int i,T t){
//先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向后移动一位
for (int index=N;index>i;index--){
//依次把前一位的值给后一位
eles[index]=eles[index-1];
}
//再把t元素放到i索引处,数组长度加1
eles[i]=t;
N++;
}Insertion diagram:
//删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i){
//先定义个一变量记录i位置的元素,后续用来返回该值
T current=eles[i];
//索引i后面元素依次向前移动一位
for (int index=0;index<N-1;index++){
//和前面的插入操作类似
eles[index]=eles[index+1];
}
//元素个数减1,返回被该(i覆盖)的值
N--;
return current;
}Return the first occurrence of element t The value of //查找元素t第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
for (int i=0;i<N;i++){
if(eles[i].equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
//for之后还没找到返回-1
return -1;
}3.3 Complete API overview: //定义一个泛型类
public class SequenceList {
//定义一个存储元素的数组(先定义为泛型)
private T[] eles;
//定义一个变量表示顺序表中的元素个数
private int N;
//添加构造方法,用来初始化成员变量
public SequenceList(int capacity) {//接受一个容量长度
//初始化数组
this.eles = (T[]) new Object[capacity];//创建的是Object类型的所以需要强转为T[]
//初始化顺序表的长度
this.N = 0;
}
// 将一个线性表置为空表
public void clear(){
//只需将顺序表的长度变为0即可
this.N=0;
//我们使用this的原因是:一定指的是成员变量,防止有局部变量和成员变量同名。
}
//判断当前线性表是否为空表
public boolean isEmpty(){
//是否为空只需要判断线性表中的元素个数
return this.N==0;
}
//获取线性表的长度
public int length(){
//只需返回N即可
return this.N;
}
//获取指定i位置的元素
public T get(int i){
//因为顺序表是一个数组,只需要通过索引找到该元素即可
return eles[i];
}
//向线性表中添加元素t
public void insert(T t){//T表示的元素的类型
//这个表示非常的巧妙,将元素加1的同时又将索引N的位置赋值了元素
eles[N++]=t;
//这个表示等价于eles[N]=t;N++;
}
//在i元素初插入元素t
public void insert(int i,T t){
//先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向后移动一位
for (int index=N;index>i;index--){
//依次把前一位的值给后一位
eles[index]=eles[index-1];
}
//再把t元素放到i索引处,数组长度加1
N++;eles[i]=t;
}
//删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i){
//先定义个一变量记录i位置的元素,后续用来返回该值
T current=eles[i];
//索引i后面元素依次向前移动一位
for (int index=0;index
4. Test of sequence table: public class SequenceListText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建对象,指定类型
SequenceList<String> sl=new SequenceList<String>(10);
//插入元素
sl.insert("孔超");
sl.insert("刘诗劲");
sl.insert(0,"孙嘉辉");
//获取元素
String s=sl.get(0);
System.out.println(s);//孙嘉辉
//删除元素
String remove1=sl.remove(0);
System.out.println(remove1);
//清空元素
sl.clear();
System.out.println(sl.length());//0
}
}
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of Java sequence table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

