Home >Java >javaTutorial >Example analysis of Java Fluent Mybatis aggregation query and apply method process
Example analysis of Java Fluent Mybatis aggregation query and apply method process
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-22 13:31:061794browse
Data preparation
In order to aggregate the query conditions, several pieces of data have been added.
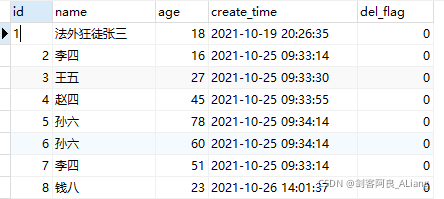
MIN
We try to get the minimum age.
Method implementation
@Override
public Integer getAgeMin() {
Map<String, Object> result =
testFluentMybatisMapper
.findOneMap(new TestFluentMybatisQuery().select.min.age("minAge").end())
.orElse(null);
return result != null ? Convert.toInt(result.get("minAge"), 0) : 0;
}Control layer code
@ApiOperation(value = "获取最小年龄", notes = "获取最小年龄")
@RequestMapping(value = "/getAgeMin", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Result<Integer> getAgeMin() {
try {
return Result.ok(aggregateService.getAgeMin());
} catch (Exception exception) {
return Result.error(ErrorCode.BASE_ERROR_CODE.getCode(), exception.getMessage(), null);
}
}Debug code
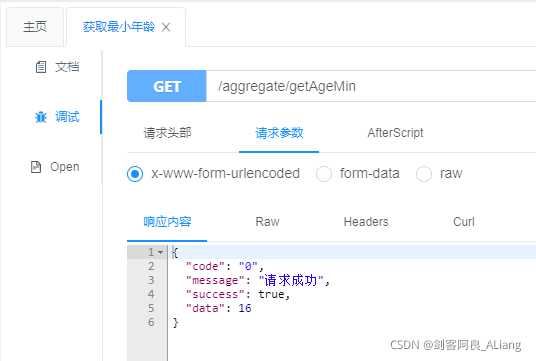
Code description:
1. Why does age("minAge") need to add a string? Is it okay not to add it? The answer is yes, but the results you see returned are like this.
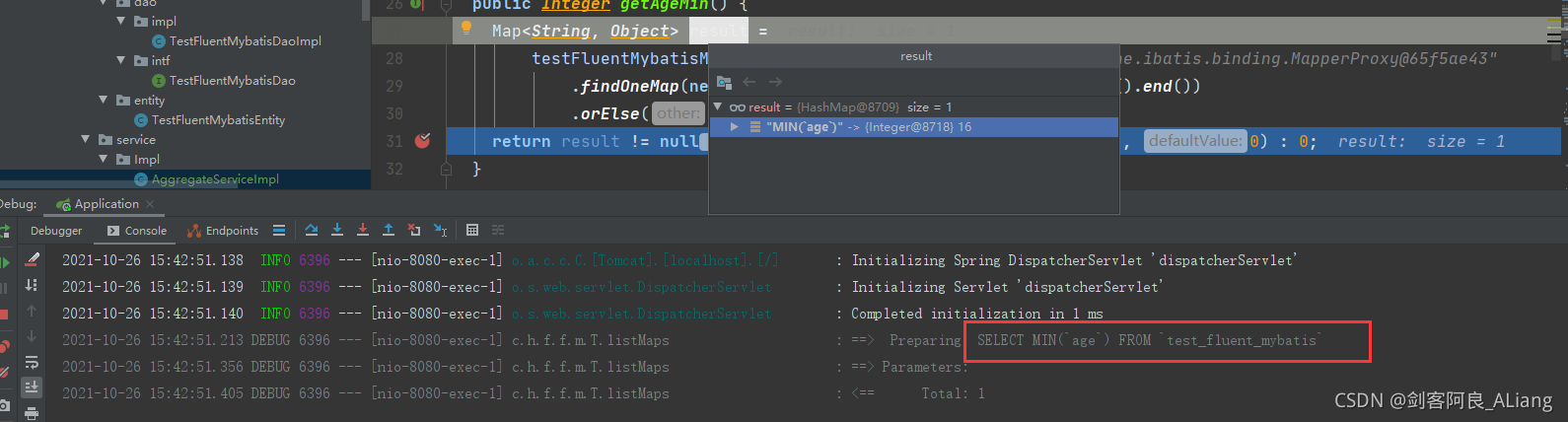
Yes, what’s in the parentheses is the alias of the aggregate query result. If you don’t pass it, the result will be embarrassing. It’s recommended to pass it.
MAX
When doing the max aggregation function, I will make it a little more complicated and add group by.
Define the return entity.
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/** @Author huyi @Date 2021/10/26 14:15 @Description: 聚合最大年龄返回体 */
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class AggregateMaxAgeRsp {
private String name;
private Integer maxAge;
}Method implementation
@Override
public List<AggregateMaxAgeRsp> getAgeMaxByName() {
List<Map<String, Object>> result =
testFluentMybatisMapper.listMaps(
new TestFluentMybatisQuery()
.select
.name()
.max
.age("maxAge")
.end()
.groupBy
.name()
.end());
if (result != null && result.size() != 0) {
List<AggregateMaxAgeRsp> list = new ArrayList<>();
result.forEach(
x -> list.add(BeanUtil.fillBeanWithMapIgnoreCase(x, new AggregateMaxAgeRsp(), false)));
return list;
} else {
return null;
}
}Control layer code
@ApiOperation(value = "根据年龄分组并获取最大年龄", notes = "根据年龄分组并获取最大年龄")
@RequestMapping(value = "/getAgeMaxByName", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Result<List<AggregateMaxAgeRsp>> getAgeMaxByName() {
try {
return Result.ok(aggregateService.getAgeMaxByName());
} catch (Exception exception) {
return Result.error(ErrorCode.BASE_ERROR_CODE.getCode(), exception.getMessage(), null);
}
}Debug code
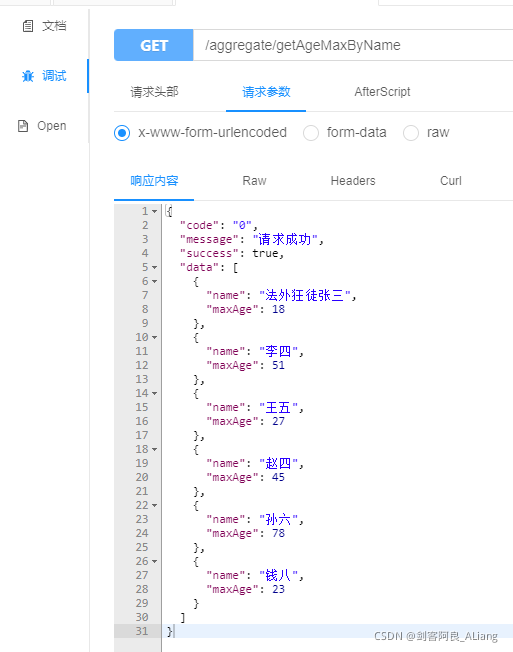
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/** @Author huyi @Date 2021/10/26 14:50 @Description: 聚合平均总和返回体 */
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class AggregateAgeSumAvgAndCountRsp {
private String name;
private Integer sum;
private Integer avg;
private Integer count;
}Method implementation @Override
public List<AggregateAgeSumAvgAndCountRsp> getAgeSumAvgCountByName() {
List<Map<String, Object>> result =
testFluentMybatisMapper.listMaps(
new TestFluentMybatisQuery()
.select
.name()
.sum
.age("sum")
.avg
.age("avg")
.count("count")
.end()
.groupBy
.name()
.end());
if (result != null && result.size() != 0) {
List<AggregateAgeSumAvgAndCountRsp> list = new ArrayList<>();
result.forEach(
x ->
list.add(
BeanUtil.fillBeanWithMapIgnoreCase(
x, new AggregateAgeSumAvgAndCountRsp(), false)));
return list;
} else {
return null;
}
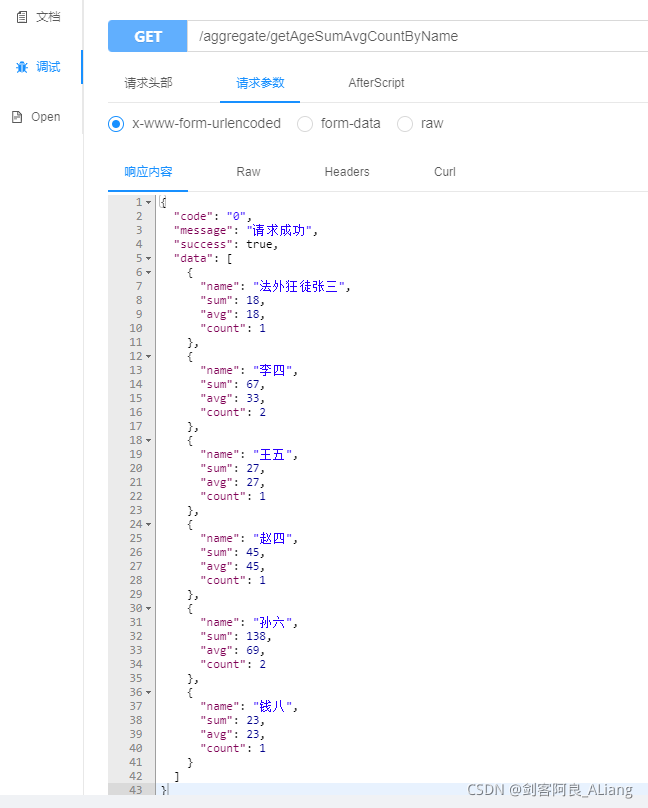
}Control layer code @ApiOperation(value = "根据年龄分组并获取年龄和、平均年龄、数量", notes = "根据年龄分组并获取年龄和、平均年龄、数量")
@RequestMapping(value = "/getAgeSumAvgCountByName", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Result<List<AggregateAgeSumAvgAndCountRsp>> getAgeSumAvgCountByName() {
try {
return Result.ok(aggregateService.getAgeSumAvgCountByName());
} catch (Exception exception) {
return Result.error(ErrorCode.BASE_ERROR_CODE.getCode(), exception.getMessage(), null);
}
}Debugging code
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.Date;
/** @Author huyi @Date 2021/10/26 15:10 @Description: 聚合应用返回体 */
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class AggregateApplyRsp {
private String name;
private Date createTime;
private Integer minAge;
private Date maxTime;
}Method implementation @Override
public List<AggregateApplyRsp> getApply() {
List<Map<String, Object>> result =
testFluentMybatisMapper.listMaps(
new TestFluentMybatisQuery()
.select
.apply("name")
.createTime("createTime")
.apply("min(age) as minAge", "max(create_time) as maxTime")
.end()
.groupBy
.name()
.createTime()
.end());
if (result != null && result.size() != 0) {
List<AggregateApplyRsp> list = new ArrayList<>();
result.forEach(
x -> list.add(BeanUtil.fillBeanWithMapIgnoreCase(x, new AggregateApplyRsp(), false)));
return list;
} else {
return null;
}
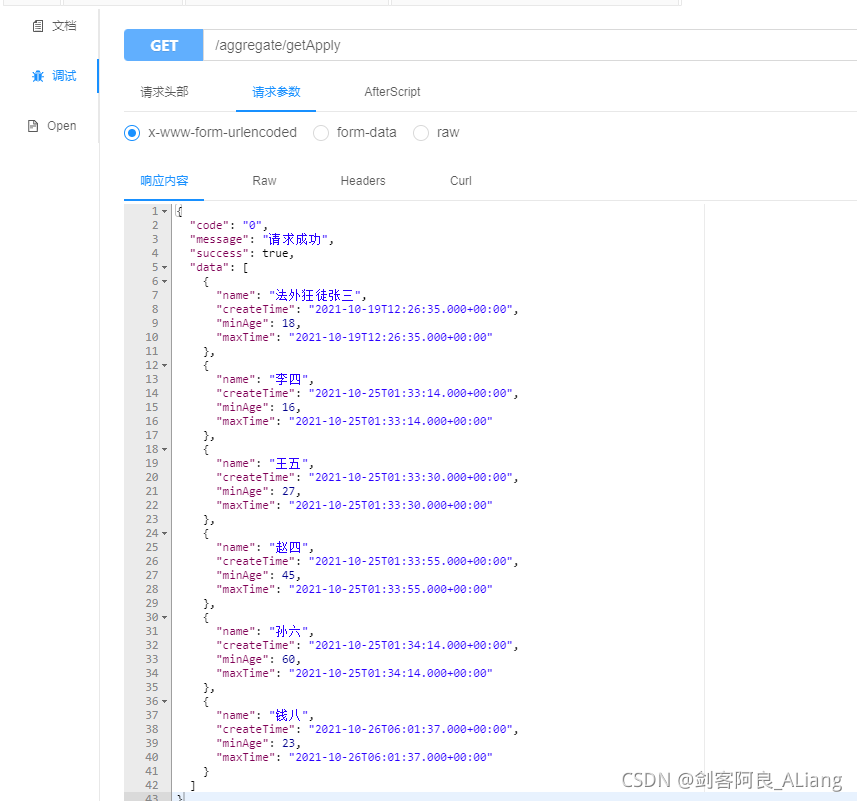
}Control layer code @ApiOperation(value = "根据名字获取最小年龄,使用语句", notes = "根据名字获取最小年龄,使用语句")
@RequestMapping(value = "/getApply", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Result<List<AggregateApplyRsp>> getApply() {
try {
return Result.ok(aggregateService.getApply());
} catch (Exception exception) {
return Result.error(ErrorCode.BASE_ERROR_CODE.getCode(), exception.getMessage(), null);
}
}Debugging code
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of Java Fluent Mybatis aggregation query and apply method process. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

