Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to implement asymmetric encryption of strings in Springboot based on BCrypt
How to implement asymmetric encryption of strings in Springboot based on BCrypt
- PHPzforward
- 2023-05-22 08:25:051636browse
1: Introduction to BCrypt
In the user module, the user's password needs to be protected and usually encrypted.
We usually encrypt the password and store it in the database. When the user logs in, the password entered is encrypted and compared with the ciphertext stored in the database to verify whether the user password is correct.
Currently, MD5 and BCrypt are more popular. Relatively speaking, BCrypt is more secure than MD5.
2: Integrate BCrypt encryption and verification
2.1: Introduce POM
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mindrot</groupId>
<artifactId>jbcrypt</artifactId>
<version>0.3m</version>
</dependency>2.2: Tool class
PassWordUtil.java
package com.utils;
import org.mindrot.jbcrypt.BCrypt;
public class PassWordUtil {
/**
* 密码加密
*/
public static String encrypt(String source){
String salt = BCrypt.gensalt();
return BCrypt.hashpw(source, salt);
}
/**
* 密码校验
*/
public static boolean check(String source, String pwdCode){
return BCrypt.checkpw(source, pwdCode);
}
}2.3: Verification
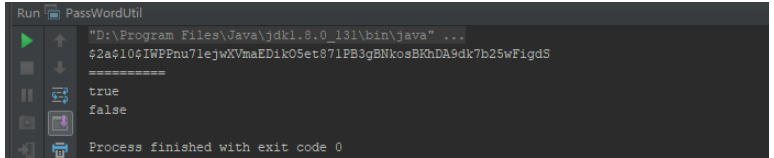
public static void main(String[] args) {
String password = "abc123&%*";
String crypt = encrypt(password);
System.out.println(crypt);
System.out.println("==========");
System.out.println(check(password, crypt));
System.out.println(check(password + "1", crypt));
}
The above is the detailed content of How to implement asymmetric encryption of strings in Springboot based on BCrypt. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:yisu.com. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete

