1. Let’s talk about an accident
Interface safety is a cliché talk
Before the Chinese New Year, I made an H5 mini-game about airplane battles. In the infinite mode, the user's points need to be saved. Because the Body is used to pass parameters, the parameters are visible. For the sake of interface security, I and the front end agreed that the parameters to be passed are: The points of the user in the infinite mode "a number we agreed on" "The user ID and are encrypted with Base64, and I decrypt the request to the server to get the user's unlimited mode points; as follows:
{
"integral": "MTExMTM0NzY5NQ==",
}However, during the Chinese New Year, the operation suddenly Tell me that the points in the infinite mode ranking list are wrong:
This is very strange. The second place only has more than 10,000 points, and the first place has more than 400,000 points! ! ! !
At first I thought there was a problem with my decryption, and I read it several times, but there couldn’t be a problem with just two or three lines of code! ! !
I had no choice but to look through the logs for a long time, only to find that this user had changed my interface parameters. . . .
He changed the Base64interface parameters
Now that the matter is over, I can’t blame the user. Who told me to think too simply, and the interface security is not in place?
So the first thing to do when I get to work after the new year is to start the interface encryption work
The currently commonly used encryption methods are symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. The encryption and decryption operations must be As you all know, the most important thing is what encryption and decryption method to use and what encryption strategy to formulate; considering my technical level and the speed of the interface, I use RAS asymmetric encryption and AES symmetric encryption together! ! ! !
2. Basic knowledge of RSA and AES
1. Asymmetric encryption and symmetric encryption
Asymmetric encryption
Asymmetric An encryption algorithm is a method of keeping a key secret. The asymmetric encryption algorithm requires two keys: public key (publickey: referred to as public key) and private key (privatekey: referred to as private key). Public keys and private keys appear in pairs. After using the public key to encrypt data, only the corresponding private key can decrypt it. Since two different keys are used for encryption and decryption, this algorithm is called an asymmetric encryption algorithm.
Symmetric encryption
The encryption key and decryption key are the same. When your key is known to others, there is no secret at all
AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm, advantages: fast encryption; disadvantages: if the secret key is lost, it is easy to decrypt the ciphertext, and the security is relatively poor
RSA is asymmetric Encryption algorithm, advantages: security; disadvantages: slow encryption speed
2. Basic knowledge of RSA
##RSA——Asymmetric encryption will produce public Key and private key, the public key is on the client side and the private key is on the server side. The public key is used for encryption and the private key is used for decryption.
The client sends a message to the server: The client encrypts the information with the public key and sends it to the server, and the server uses the private key to keep it secretThe server sends a message to the client: the server encrypts the information with the private key and sends it to the client, and the client uses the public key to keep it secretOf course, the security of the key must be ensured in the middle, and there are many more In order to ensure data security operations, such as digital signatures, certificate signatures, etc., we will not talk about them here;
RSA encryption and decryption algorithm supports three filling modes,
areENCRYPTION_OAEP, ENCRYPTION_PKCS1, ENCRYPTION_NONE respectively. The RSA padding is to be the same length as the public key.
ENCRYPTION_OAEP is the optimal asymmetric encryption padding mode and the latest and most secure recommended padding mode in RSA encryption and RSA decryption.
ENCRYPTION_PKCS1: Random padding data mode, the result of each encryption is different, it is the most widely used padding mode for RSA encryption and RSA decryption.
ENCRYPTION_NONE: No padding mode, which is a padding mode used less frequently for RSA encryption and RSA decryption.
RSA commonly used encryption padding modes
- RSA/None/PKCS1Padding
- RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding
- Java’s default RSA implementation is RSA/None/PKCS1Padding
- When creating an RSA key pair, it is best to choose an integer multiple of 2048 for the length. A length of 1024 is no longer very safe.
- General A secret key pair is created by the server, the private key is saved on the server, and the public key is sent to the client
- DER is the binary format of the RSA key, and PEM is the character transcoded by DER into Base64 Format, since DER is a binary format, it is not easy to read and understand. Generally speaking, keys are stored in PEM format
/**
* 生成密钥对
* @param keyLength 密钥长度
* @return KeyPair
*/
public static KeyPair getKeyPair(int keyLength) {
try {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); //默认:RSA/None/PKCS1Padding
keyPairGenerator.initialize(keyLength);
return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("生成密钥对时遇到异常" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 获取公钥
*/
public static byte[] getPublicKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPublicKey rsaPublicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
return rsaPublicKey.getEncoded();
}
/**
* 获取私钥
*/
public static byte[] getPrivateKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
return rsaPrivateKey.getEncoded();
}3、AES基础知识
AES 简介 AES加密解密算法是一种可逆的对称加密算法,这类算法在加密和AES解密时使用相同的密钥,或是使用两个可以简单地相互推算的密钥,一般用于服务端对服务端之间对数据进行加密解密。它是一种为了替代原先DES、3DES而建立的高级加密标准(Advanced Encryption Standard)。作为可逆且对称的块加密,AES加密算法的速度比公钥加密等加密算法快很多,在很多场合都需要AES对称加密,但是要求加密端和解密端双方都使用相同的密钥是AES算法的主要缺点之一。
AES加密解密
AES加密需要:明文 + 密钥+ 偏移量(IV)+密码模式(算法/模式/填充) AES解密需要:密文 + 密钥+ 偏移量(IV)+密码模式(算法/模式/填充)
AES的算法模式一般为 AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding 或 AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding
AES常见的工作模式:
电码本模式(ECB)
密码分组链接模式(CBC)
计算器模式(CTR)
密码反馈模式(CFB)
输出反馈模式(OFB)
除了ECB无须设置初始化向量IV而不安全之外,其它AES工作模式都必须设置向量IV,其中GCM工作模式较为特殊。
AES填充模式
块密码只能对确定长度的数据块进行处理,而消息的长度通常是可变的,因此需要选择填充模式。
填充区别:在ECB、CBC工作模式下最后一块要在加密前进行填充,其它不用选择填充模式;填充模式:AES支持的填充模式为PKCS7和NONE不填充。其中PKCS7标准是主流加密算法都遵循的数据填充算法。AES标准规定的区块长度为固定值128Bit,对应的字节长度为16位,这明显和PKCS5标准规定使用的固定值8位不符,虽然有些框架特殊处理后可以通用PKCS5,但是从长远和兼容性考虑,推荐PKCS7。
AES密钥KEY和初始化向量IV
初始化向量IV可以有效提升安全性,但是在实际的使用场景中,它不能像密钥KEY那样直接保存在配置文件或固定写死在代码中,一般正确的处理方式为:在加密端将IV设置为一个16位的随机值,然后和加密文本一起返给解密端即可。
密钥KEY:AES标准规定区块长度只有一个值,固定为128Bit,对应的字节为16位。AES算法规定密钥长度只有三个值,128Bit、192Bit、256Bit,对应的字节为16位、24位和32位,其中密钥KEY不能公开传输,用于加密解密数据;初始化向量IV:该字段可以公开,用于将加密随机化。同样的明文被多次加密也会产生不同的密文,避免了较慢的重新产生密钥的过程,初始化向量与密钥相比有不同的安全性需求,因此IV通常无须保密。然而在大多数情况中,不应当在使用同一密钥的情况下两次使用同一个IV,一般推荐初始化向量IV为16位的随机值。
三、加密策略
RAS、AES加密解密的操作都是一样,如果有效的结合到一起才能达到更好的加密效果很重要;
上面说到:
AES 是对称加密算法,优点:加密速度快;缺点:如果秘钥丢失,就容易解密密文,安全性相对比较差
RSA 是非对称加密算法 , 优点:安全 ;缺点:加密速度慢
1、主要思路:
那么我们就结合2个加密算法的优点来操作:
1、因为接口传递的参数有多有少,当接口传递的参数过多时,使用RSA加密会导致加密速度慢,所以我们使用AES加密加密接口参数
2、因为AES的密钥key和偏移量VI都是固定的所以可以使用RSA加密
3、客户端将AES加密后的密文和RSA加密后的密文,传递给服务器即可。
2、涉及工具类:
util包下:
ActivityRSAUtilAES256UtilRequestDecryptionUtil
3、加密策略

4、交互方式
前端:
1、客户端随机生成2个16为的AES密钥和AES偏移量
2、使用AES加密算法加密真实传递参数,得到参数密文“asy”
3、将AES密钥、AES偏移量和当前时间戳,格式如下:
key:密钥
keyVI:偏移量
time:请求时间,用户判断是否重复请求
{
"key":"0t7FtCDKofbEVpSZS",
"keyVI":"0t7WESMofbEVpSZS",
"time":211213232323323
}
//转成JSON字符串4、AES信息密钥信息,再使用RSA公钥加密,得到AES密钥的密文“sym”
5、将“sym”和“asy”作为body参数,调用接口

后端:
1、在接口接收参数中,多增加2个字段接收加密后的“sym”和“asy” (名字可以自己定,能接收到就行)
2、使用RequestDecryptionUtil.getRequestDecryption()方法解密,返回解密后的真实传递参数
四、服务器自动解密
因为不是每个接口都需求加密解密,我们可以自定义一个注解,将需要解密的接口上加一个这个注解,
1、自定义解密注解:@RequestRSA
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestRSA {
}2、创建一个aop切片
1、AOP判断controller接收到请求是否带有@RequestRSA注解
2、如果带有注解,通过ProceedingJoinPoint类getArgs()方法获取请求的body参数,
3、将body参数,传为JSONObject类,获取到"asy"和"sym"属性,再调用RequestDecryptionUtil解密获取接口传递的真实参数
4、获取接口入参的类
5、将获取解密后的真实参数,封装到接口入参的类中
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import app.activity.common.interceptor.RequestRSA;
import app.activity.util.RequestDecryptionUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Parameter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-08 16:41
* @copyright 请求验证RSA & AES 统一验证切面
**/
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(2)
@Slf4j
public class RequestRSAAspect {
/**
* 1> 获取请求参数
* 2> 获取被请求接口的入参类型
* 3> 判断是否为get请求 是则跳过AES解密判断
* 4> 请求参数解密->封装到接口的入参
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * app.activity.controller.*.*(..))")
public void requestRAS() {
}
@Around("requestRAS()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//=======AOP解密切面通知=======
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method methods = methodSignature.getMethod();
RequestRSA annotation = methods.getAnnotation(RequestRSA.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(annotation)){
//获取请求的body参数
Object data = getParameter(methods, joinPoint.getArgs());
String body = JSONObject.toJSONString(data);
//获取asy和sym的值
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(body);
String asy = jsonObject.get("asy").toString();
String sym = jsonObject.get("sym").toString();
//调用RequestDecryptionUtil方法解密,获取解密后的真实参数
JSONObject decryption = RequestDecryptionUtil.getRequestDecryption(sym, asy);
//获取接口入参的类
String typeName = joinPoint.getArgs()[0].getClass().getTypeName();
System.out.println("参数值类型:"+ typeName);
Class<?> aClass = joinPoint.getArgs()[0].getClass();
//将获取解密后的真实参数,封装到接口入参的类中
Object o = JSONObject.parseObject(decryption.toJSONString(), aClass);
Object[] as = {o};
return joinPoint.proceed(as);
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
/**
* 根据方法和传入的参数获取请求参数 获取的是接口的入参
*/
private Object getParameter(Method method, Object[] args) {
List<Object> argList = new ArrayList<>();
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
//将RequestBody注解修饰的参数作为请求参数
RequestBody requestBody = parameters[i].getAnnotation(RequestBody.class);
if (requestBody != null) {
argList.add(args[i]);
}
}
if (argList.size() == 0) {
return null;
} else if (argList.size() == 1) {
return argList.get(0);
} else {
return argList;
}
}
}3、RequestDecryptionUtil 解密类
1、使用privateKey私钥对”sym“解密获取到客户端加密的AES密钥,偏移量、时间等信息
{
"key":"0t7FtSMofbEVpSZS",
"keyVI":"0t7FtSMofbEVpSZS",
"time":211213232323323
}2、获取当前时间戳,与time比较是否超过一分钟(6000毫秒),超过就抛出“Request timed out, please try again”异常
3、没有超时,将获取的到AES密钥和偏移量,再对“asy”解密获取接口传递的真实参数
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import app.activity.common.rsa.RSADecodeData;
import app.common.exception.ServiceException;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-09 17:43
* @copyright
**/
public class RequestDecryptionUtil {
private final static String publicKey = "RSA生成的公钥";
private final static String privateKey = "RSA生成的私钥";
private final static Integer timeout = 60000;
/**
*
* @param sym RSA 密文
* @param asy AES 密文
* @param clazz 接口入参类
* @return Object
*/
public static <T> Object getRequestDecryption(String sym, String asy, Class<T> clazz){
//验证密钥
try {
//解密RSA
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = ActivityRSAUtil.getRSAPrivateKeyByString(privateKey);
String RSAJson = ActivityRSAUtil.privateDecrypt(sym, rsaPrivateKey);
RSADecodeData rsaDecodeData = JSONObject.parseObject(RSAJson, RSADecodeData.class);
boolean isTimeout = Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData) && Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData.getTime()) && System.currentTimeMillis() - rsaDecodeData.getTime() < timeout;
if (!isTimeout){
throw new ServiceException("Request timed out, please try again."); //请求超时
}
//解密AES
String AESJson = AES256Util.decode(rsaDecodeData.getKey(),asy,rsaDecodeData.getKeyVI());
System.out.println("AESJson: "+AESJson);
return JSONObject.parseObject(AESJson,clazz);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("RSA decryption Exception: " +e.getMessage());
}
}
public static JSONObject getRequestDecryption(String sym, String asy){
//验证密钥
try {
//解密RSA
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = ActivityRSAUtil.getRSAPrivateKeyByString(privateKey);
String RSAJson = ActivityRSAUtil.privateDecrypt(sym, rsaPrivateKey);
RSADecodeData rsaDecodeData = JSONObject.parseObject(RSAJson, RSADecodeData.class);
boolean isTimeout = Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData) && Objects.nonNull(rsaDecodeData.getTime()) && System.currentTimeMillis() - rsaDecodeData.getTime() < timeout;
if (!isTimeout){
throw new ServiceException("Request timed out, please try again."); //请求超时
}
//解密AES
String AESJson = AES256Util.decode(rsaDecodeData.getKey(),asy,rsaDecodeData.getKeyVI());
System.out.println("AESJson: "+AESJson);
return JSONObject.parseObject(AESJson);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("RSA decryption Exception: " +e.getMessage());
}
}
}4、ActivityRSAUtil 工具类
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.security.*;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey;
import java.security.interfaces.RSAPublicKey;
import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-07 16:54
* @copyright
**/
public class ActivityRSAUtil {
/**
* 字符集
*/
public static String CHARSET = "UTF-8";
/**
* 生成密钥对
* @param keyLength 密钥长度
* @return KeyPair
*/
public static KeyPair getKeyPair(int keyLength) {
try {
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); //默认:RSA/None/PKCS1Padding
keyPairGenerator.initialize(keyLength);
return keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("生成密钥对时遇到异常" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 获取公钥
*/
public static byte[] getPublicKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPublicKey rsaPublicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic();
return rsaPublicKey.getEncoded();
}
/**
* 获取私钥
*/
public static byte[] getPrivateKey(KeyPair keyPair) {
RSAPrivateKey rsaPrivateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate();
return rsaPrivateKey.getEncoded();
}
/**
* 公钥字符串转PublicKey实例
* @param publicKey 公钥字符串
* @return PublicKey
* @throws Exception e
*/
public static PublicKey getPublicKey(String publicKey) throws Exception {
byte[] publicKeyBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKey.getBytes());
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
}
/**
* 私钥字符串转PrivateKey实例
* @param privateKey 私钥字符串
* @return PrivateKey
* @throws Exception e
*/
public static PrivateKey getPrivateKey(String privateKey) throws Exception {
byte[] privateKeyBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKey.getBytes());
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKeyBytes);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
}
/**
* 获取公钥字符串
* @param keyPair KeyPair
* @return 公钥字符串
*/
public static String getPublicKeyString(KeyPair keyPair){
RSAPublicKey publicKey = (RSAPublicKey) keyPair.getPublic(); // 得到公钥
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64(publicKey.getEncoded()));
}
/**
* 获取私钥字符串
* @param keyPair KeyPair
* @return 私钥字符串
*/
public static String getPrivateKeyString(KeyPair keyPair){
RSAPrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); // 得到私钥
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64((privateKey.getEncoded())));
}
/**
* 公钥加密
* @param data 明文
* @param publicKey 公钥
* @return 密文
*/
public static String publicEncrypt(String data, RSAPublicKey publicKey) {
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
byte[] bytes = rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, data.getBytes(CHARSET), publicKey.getModulus().bitLength());
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64(bytes));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("加密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常"+ e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 私钥解密
* @param data 密文
* @param privateKey 私钥
* @return 明文
*/
public static String privateDecrypt(String data, RSAPrivateKey privateKey) {
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return new String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, Base64.getDecoder().decode(data), privateKey.getModulus().bitLength()), CHARSET);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("privateKey解密字符串[" + data + "]时遇到异常"+ e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 私钥加密
* @param content 明文
* @param privateKey 私钥
* @return 密文
*/
public static String encryptByPrivateKey(String content, RSAPrivateKey privateKey){
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
byte[] bytes = rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE,content.getBytes(CHARSET), privateKey.getModulus().bitLength());
return new String(org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64.encodeBase64(bytes));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("privateKey加密字符串[" + content + "]时遇到异常" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 公钥解密
* @param content 密文
* @param publicKey 私钥
* @return 明文
*/
public static String decryByPublicKey(String content, RSAPublicKey publicKey){
try {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return new String(rsaSplitCodec(cipher, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, Base64.getDecoder().decode(content), publicKey.getModulus().bitLength()), CHARSET);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("publicKey解密字符串[" + content + "]时遇到异常" +e.getMessage());
}
}
public static RSAPublicKey getRSAPublicKeyByString(String publicKey){
try {
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKey));
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return (RSAPublicKey)keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("String转PublicKey出错" + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static RSAPrivateKey getRSAPrivateKeyByString(String privateKey){
try {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec pkcs8EncodedKeySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKey));
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
return (RSAPrivateKey)keyFactory.generatePrivate(pkcs8EncodedKeySpec);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("String转PrivateKey出错" + e.getMessage());
}
}
//rsa切割解码 , ENCRYPT_MODE,加密数据 ,DECRYPT_MODE,解密数据
private static byte[] rsaSplitCodec(Cipher cipher, int opmode, byte[] datas, int keySize) {
int maxBlock = 0; //最大块
if (opmode == Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE) {
maxBlock = keySize / 8;
} else {
maxBlock = keySize / 8 - 11;
}
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int offSet = 0;
byte[] buff;
int i = 0;
try {
while (datas.length > offSet) {
if (datas.length - offSet > maxBlock) {
//可以调用以下的doFinal()方法完成加密或解密数据:
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, maxBlock);
} else {
buff = cipher.doFinal(datas, offSet, datas.length - offSet);
}
out.write(buff, 0, buff.length);
i++;
offSet = i * maxBlock;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("加解密阀值为[" + maxBlock + "]的数据时发生异常: " + e.getMessage());
}
byte[] resultDatas = out.toByteArray();
IOUtils.closeQuietly(out);
return resultDatas;
}
}5、AES256Util 工具类
import org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.Security;
import java.util.Base64;
/**
* @module
* @author: qingxu.liu
* @date: 2023-02-07 16:14
* @copyright
**/
public class AES256Util {
private static final String AES = "AES";
/**
* 初始向量IV, 初始向量IV的长度规定为128位16个字节, 初始向量的来源为随机生成.
*/
/**
* 加密解密算法/加密模式/填充方式
*/
private static final String CIPHER_ALGORITHM = "AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding";
private static final Base64.Encoder base64Encoder = java.util.Base64.getEncoder();
private static final Base64.Decoder base64Decoder = java.util.Base64.getDecoder();
//通过在运行环境中设置以下属性启用AES-256支持
static {
Security.setProperty("crypto.policy", "unlimited");
}
/*
* 解决java不支持AES/CBC/PKCS7Padding模式解密
*/
static {
Security.addProvider(new BouncyCastleProvider());
}
/**
* AES加密
*/
public static String encode(String key, String content,String keyVI) {
try {
javax.crypto.SecretKey secretKey = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), AES);
javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = javax.crypto.Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(javax.crypto.Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(keyVI.getBytes()));
// 获取加密内容的字节数组(这里要设置为utf-8)不然内容中如果有中文和英文混合中文就会解密为乱码
byte[] byteEncode = content.getBytes(java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// 根据密码器的初始化方式加密
byte[] byteAES = cipher.doFinal(byteEncode);
// 将加密后的数据转换为字符串
return base64Encoder.encodeToString(byteAES);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* AES解密
*/
public static String decode(String key, String content,String keyVI) {
try {
javax.crypto.SecretKey secretKey = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), AES);
javax.crypto.Cipher cipher = javax.crypto.Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(javax.crypto.Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, new javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec(keyVI.getBytes()));
// 将加密并编码后的内容解码成字节数组
byte[] byteContent = base64Decoder.decode(content);
// 解密
byte[] byteDecode = cipher.doFinal(byteContent);
return new String(byteDecode, java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* AES加密ECB模式PKCS7Padding填充方式
* @param str 字符串
* @param key 密钥
* @return 加密字符串
* @throws Exception 异常信息
*/
public static String aes256ECBPkcs7PaddingEncrypt(String str, String key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS7Padding");
byte[] keyBytes = key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, AES));
byte[] doFinal = cipher.doFinal(str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(doFinal));
}
/**
* AES解密ECB模式PKCS7Padding填充方式
* @param str 字符串
* @param key 密钥
* @return 解密字符串
* @throws Exception 异常信息
*/
public static String aes256ECBPkcs7PaddingDecrypt(String str, String key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS7Padding");
byte[] keyBytes = key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, AES));
byte[] doFinal = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(str));
return new String(doFinal);
}
}The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot implements RAS+AES automatic interface decryption. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
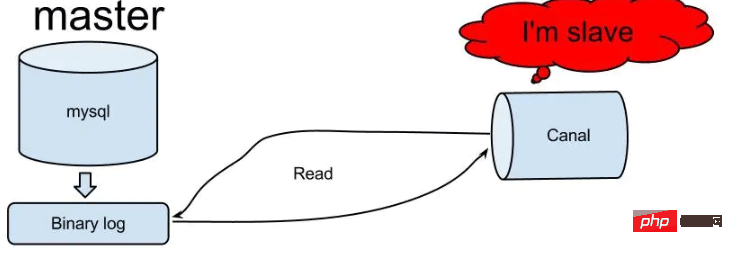 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
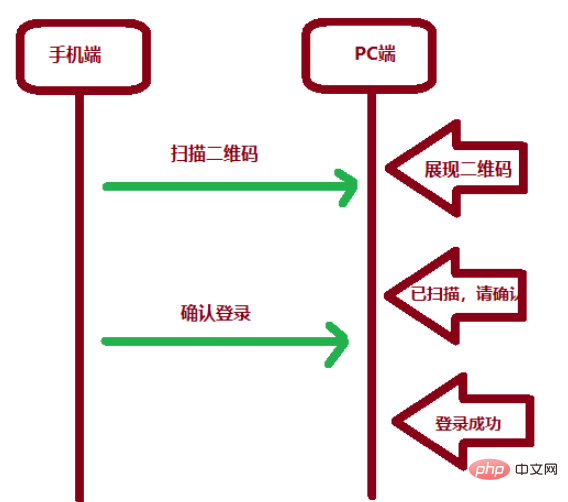 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM一、定义视频上传请求接口publicAjaxResultvideoUploadFile(MultipartFilefile){try{if(null==file||file.isEmpty()){returnAjaxResult.error("文件为空");}StringossFilePrefix=StringUtils.genUUID();StringfileName=ossFilePrefix+"-"+file.getOriginalFilename(


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







