Home >Java >javaTutorial >Example Analysis of Java Reflection Mechanism Principle
Example Analysis of Java Reflection Mechanism Principle
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-19 21:13:041189browse
What is reflection?
The reflection mechanism is in the running state. It provides Java with the ability to "operate objects". In the running state, through the Class file object, the properties, methods, and structures in any class can be called. Methods, including private ones, are transparent to all classes in front of the reflection mechanism
My own summary: Everything in this class can be seen through the Class file object, and can be used and modified
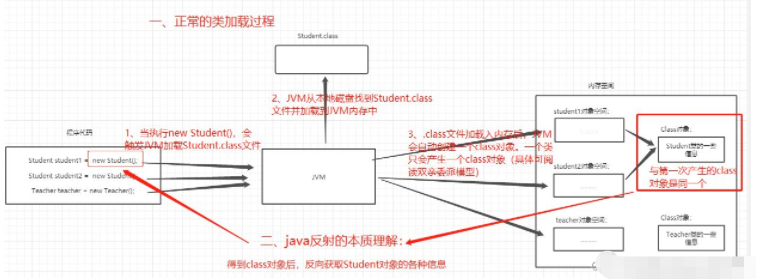
The premise of reflection is to obtain the Class file object ((bytecode object)), then there are three ways to obtain it:
Class.forName ("Full class name") ---- Through the static method of the Class class (most commonly used)
Class name.class
Object .getClass()
//方式1:获取字节码对象,Class.forName("全类名")
Class cla1 = Class.forName("Study01.Person");
//方式2: 类名.Class
Class cla2 = Person.class;
//方式3:对象.getClass();
Person per = new Person();
Class cla3 = per.getClass();
//这三个class对象都是由Person这个类生成的
//那么我们看一下这三个字节码对象是不是同一个:
System.out.println(cla1==cla2);
System.out.println(cla2==cla3);//Output result: two true
Conclusion:
The bytecode object is generated when the class is loaded, and there is only one
No matter which way the bytecode object is obtained, it is the same bytecode object
Get the attributes in the class through reflection:
After getting the Class bytecode object, we can get the attributes of the class we want to get through the bytecode object. , methods, construction methods, and private modifications.
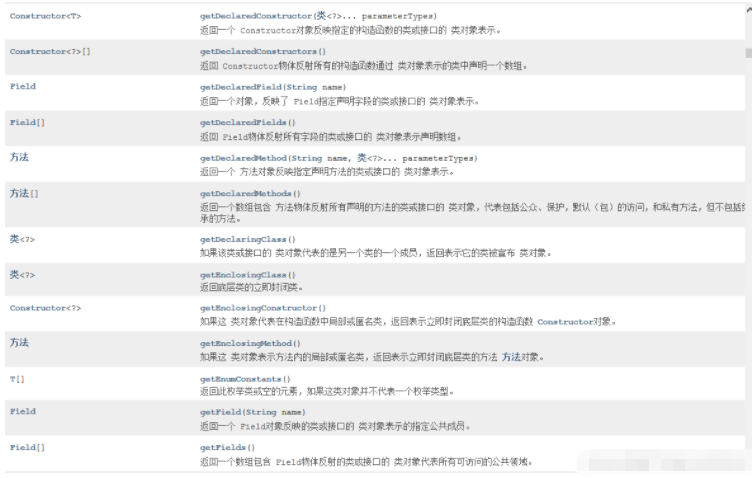
Part of the Class methods:
public class Person {
private String name; //名字
private int age = 18; //年龄
public int ID = 123; //身份证
public String Sex; //性别
@Override
public String toString(){
return "姓名"+name+"年龄:"+age+"ID:"+ID+"性别:"+Sex;
}
}Test class: public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取Class文件对象,用最常用的通过Class类的静态方法
Class per = Class.forName("Test01.Person"); //这里是传入全路径!!从最外层的包名开始!
//使用getFields()方法获取全部被public修饰的属性(方法上面的截图有)
//并且返回的是Field类型的数组
Field fields[] = per.getFields();
for (Field field:fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
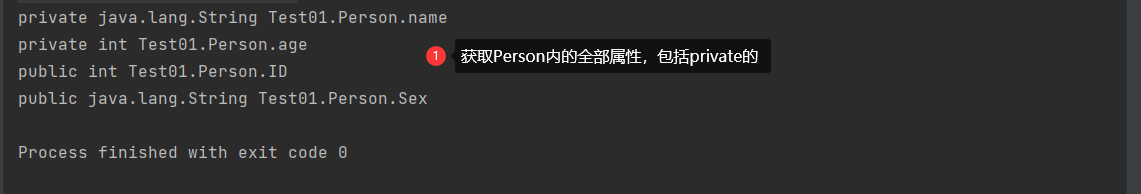
}Output :We successfully obtained all public attributes in the Person class

for (Field field : per.getDeclaredFields()) {
System.out.println(field);
}Output:
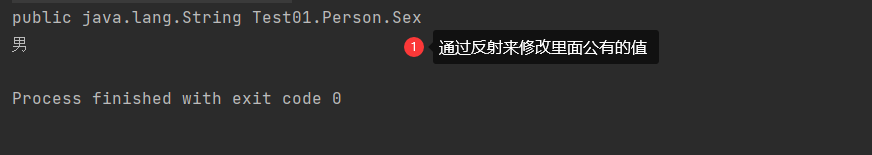
Field f = per.getField("Sex");
System.out.println(f);
//获取一个对象:
Object obj = per.getConstructor().newInstance();
//修改值:
f.set(obj,"男");
Person p = (Person)obj;
System.out.println(p.Sex);Output:
Person p = (Person)obj;
//获取公有字段并调用,并修改
Field f = per.getField("Sex");
//获取一个对象:
Object obj = per.getConstructor().newInstance();
f.set(obj,"男"); //将Sex的属性修改成了 男
//调用私有的属性,并修改
f = per.getDeclaredField("name");
//在访问私有的属性的值之前,先要设置运行访问↓
//在访问之前忽略访问权限的检查,叫暴力反射
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(obj,"张三");
System.out.println("Person里面的信息是:"+p.toString());
}
}Output:
public class Person {
private String name; //名字
private int age = 18; //年龄
public int ID = 123; //身份证
public String Sex ; //性别
//构造:
public Person() {}
public Person(String name, int age, int ID, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.ID = ID;
Sex = sex;
}
//无参公有方法:
public void eat(){
System.out.println("我会吃饭");
}
//有参公有方法:
public void eat(String food){
System.out.println("我在吃:"+food);
}
//有参私有方法
private void play(String name){
System.out.println(name+"在玩");
}
}Test class: public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//获取到Person以及父类Object里面的public方法:
System.out.println("-----获取到Person以及父类Object里面的public方法↓-----");
for (Method method : Person.class.getMethods()) {
System.out.println(method);
System.out.println("方法名:"+ method.getName());
}
//获取到Person里面的方法,包括私有
System.out.println("-----获取到Person里面的方法,包括私有↓-----");
for (Method method:Person.class.getDeclaredMethods()) {
System.out.println(method.getName()+" ");
}
//按照方法名获取到Person中的eat方法:
System.out.println("-----根据方法名获取到Person类中的eat方法↓-----");
Method earMethod1 = Person.class.getMethod("eat");
Person per = new Person();
//通过invoke(Object,param...)来调用指定的方法
earMethod1.invoke(per);
//使用反射调用有参方法;
System.out.println("-----使用反射调用有参方法(传入参数)↓-----");
Method earMethod2 = Person.class.getMethod("eat",String.class);
earMethod2.invoke(per,"牛肉");
//通过暴力反射获取到私有的play方法:
System.out.println("-----通过暴力反射获取到私有的play方法传入参数)↓-----");
Method earMethod3 = Person.class.getDeclaredMethod("play", String.class);
//在访问私有的属性的方法之前,先要设置运行访问
earMethod3.setAccessible(true);
earMethod3.invoke(per,"小王");
}Output:
-----Get the public methods in Person and parent class Object↓-----public void Test02.Person.eat(java .lang.String)
Method name: eat
public void Test02.Person.eat()
Method name: eat
public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang .InterruptedException
Method name: wait
public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
Method name: wait
public final native void java.lang .Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
Method name: wait
public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
Method name: equals
public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()
Method name: toString
public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
Method name: hashCode
public final native java .lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()
Method name: getClass
public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()
Method name: notify
public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()
Method name: notifyAll
The above is the detailed content of Example Analysis of Java Reflection Mechanism Principle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

