Usage 1: The attributes of the annotation are aliases for each other
Introduction
It can be annotated to two attributes of the custom annotation, indicating that the two attributes are aliases for each other, that is to say, this The two attributes actually have the same meaning.
One of the attribute names must be "value"
No matter which attribute name is specified to set the attribute value, the other attribute name is also the same attribute value, or the default attribute name.
If both specify attribute values, the required values must be the same, otherwise an error will be reported.
Use concisely. After using it like this, @MyAnno(location="shanghai") can be written directly as: @MyAnno("shanghai");
The reason for this function:
If the custom annotation has an attribute, and the attribute is named to reflect its meaning, the caller must write the attribute and then set it every time he uses the custom annotation, which is a little troublesome.
Example
Annotation
package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface MyAnnotation {
@AliasFor(attribute = "location")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor(attribute = "value")
String location() default "";
}Controller
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@MyAnnotation(value = "location")
/*//下边这两种写法结果与上边是相同的
@MyAnnotation("location")
@MyAnnotation(location = "location")*/
@RequestMapping("/test1")
public String test1() {
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = null;
try {
myAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test1"), MyAnnotation.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "value:" + myAnnotation.value() + ";loation:" + myAnnotation.location();
}
}Test
Front-end access: http://localhost:8080/hello/test1
Front-end result (value and location are both the same value)
value:location; loation:location
Usage 2. Inherit the attributes of the parent annotation without rewriting the attribute name
Introduction
The reading and writing of the attribute value of the child annotation is actually Read and write the attribute value of the parent annotation. (For inherited properties)
At this time, only inherited property values can be read and written.
Code
Annotations
package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface MyAnnotation {
@AliasFor(attribute = "location")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor(attribute = "value")
String location() default "";
}package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Inherited
@MyAnnotation
public @interface SubMyAnnotation {
@AliasFor(annotation = MyAnnotation.class)
String location() default "";
// 这个不能写,只能有一个与父属性名同名的属性,否则报错
// @AliasFor(annotation = MyAnnotation.class)
// String value() default "";
}Controller
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import com.example.annotation.SubMyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotatedElementUtils;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@SubMyAnnotation(location = "location(my)")
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test() {
SubMyAnnotation subMyAnnotation = null;
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = null;
MyAnnotation myAnnotation1 = null;
try {
subMyAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test"), SubMyAnnotation.class);
myAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test"), MyAnnotation.class);
myAnnotation1 = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test"), MyAnnotation.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "loation(sub):" + subMyAnnotation.location() + "\n" +
"location:" + myAnnotation.location() + "\n" +
"location:" + myAnnotation1.location();
}
}Test
Front-end access: http://localhost:8080/hello/test
Result
##loation(sub):location(my)Usage 3: Inherit the attributes of the parent annotation and rewrite the attribute nameIntroduction The reading and writing of the attribute value of the child annotation is actually the reading and writing of the attribute value of the parent annotation. (For overridden attributes) No matter which attribute name is specified to set the attribute value, the other attribute name also has the same attribute value, and the default attribute name cannot be used. If both specify attribute values, the required values must be the same, otherwise an error will be reported. Codelocation:
location:location(my)
Annotations
package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface MyAnnotation {
@AliasFor(attribute = "location")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor(attribute = "value")
String location() default "";
}package com.example.annotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Inherited
@MyAnnotation
public @interface SubMyAnnotation {
@AliasFor(attribute = "value", annotation = MyAnnotation.class)
String subValue() default "";
@AliasFor(attribute = "location", annotation = MyAnnotation.class)
String subLocation() default "";
// subLocation属性写成下边这两种结果是一样的
// @AliasFor(attribute = "value", annotation = MyAnnotation.class)
// String subLocation() default "";
// @AliasFor(value = "location", annotation = MyAnnotation.class)
// String subLocation() default "";
//
}
Controller
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.annotation.MyAnnotation;
import com.example.annotation.SubMyAnnotation;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotatedElementUtils;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@SubMyAnnotation(subValue = "subLocation")
// @SubMyAnnotation(subLocation = "subLocation") //这个与上边结果相同
// @SubMyAnnotation("subLocation") //缺省属性名会报错
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test() {
SubMyAnnotation subMyAnnotation = null;
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = null;
MyAnnotation myAnnotation1 = null;
try {
subMyAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test"), SubMyAnnotation.class);
myAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test"), MyAnnotation.class);
myAnnotation1 = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(this.getClass().getMethod("test"), MyAnnotation.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "subValue:" + subMyAnnotation.subValue() + ";subLoation:" + subMyAnnotation.subLocation() + "\n" +
"value:" + myAnnotation.value() + ";location:" + myAnnotation.location() + "\n" +
"value:" + myAnnotation1.value() + ";location:" + myAnnotation1.location();
}
}
Test
Front-end access: http://localhost:8080/hello/testResult
##subValue:subLocation;subLoation:subLocationvalue:;location:value:subLocation;location:subLocation
The above is the detailed content of How to use the @AliasFor annotation in SpringBoot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
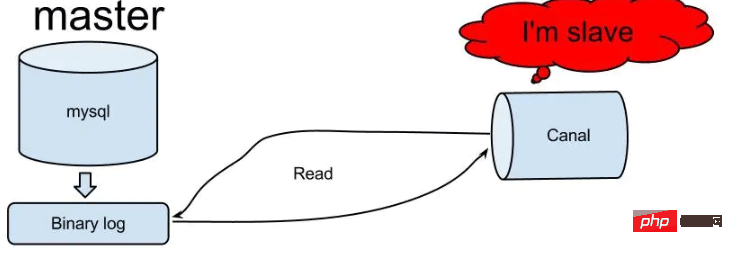 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
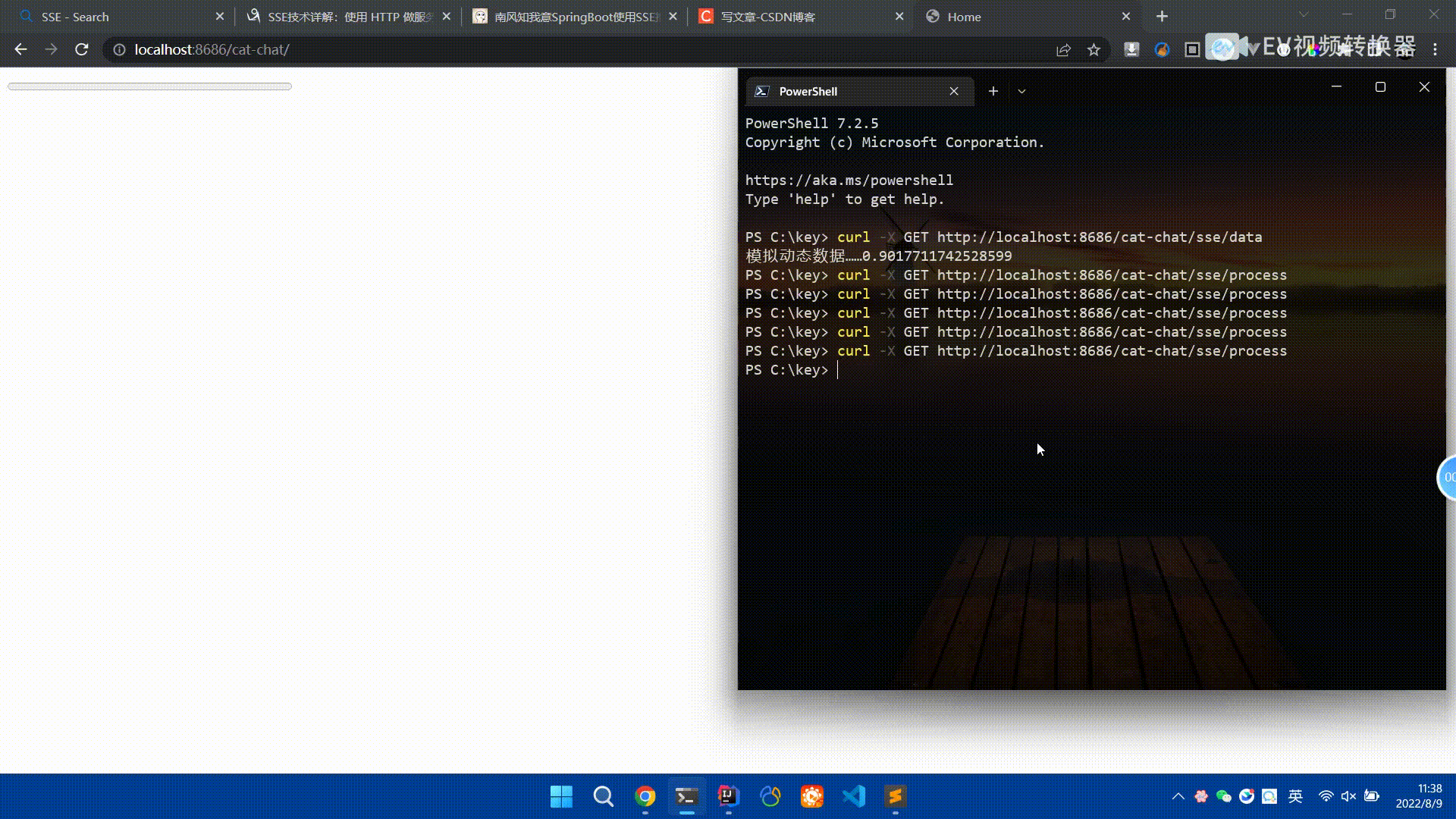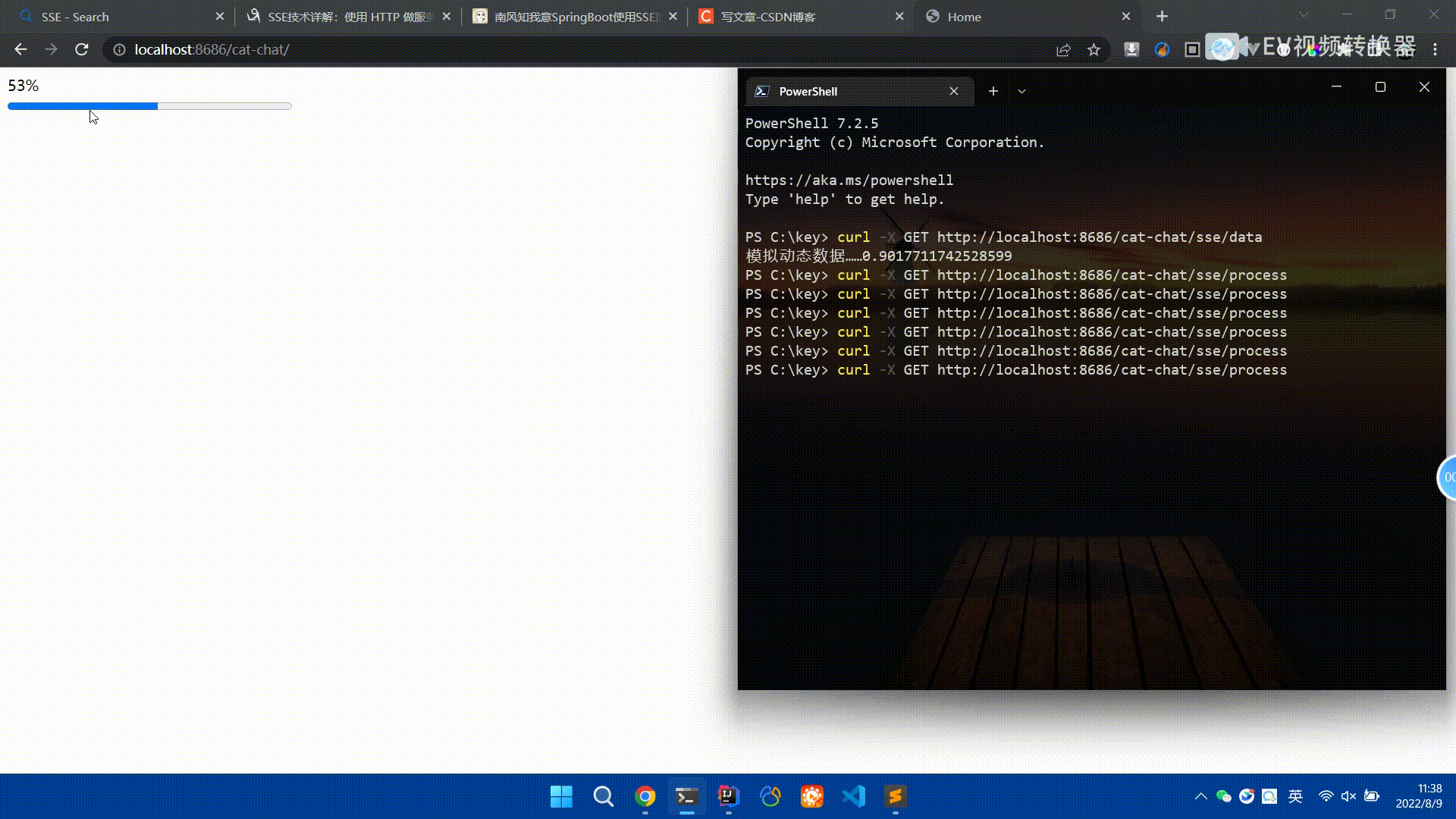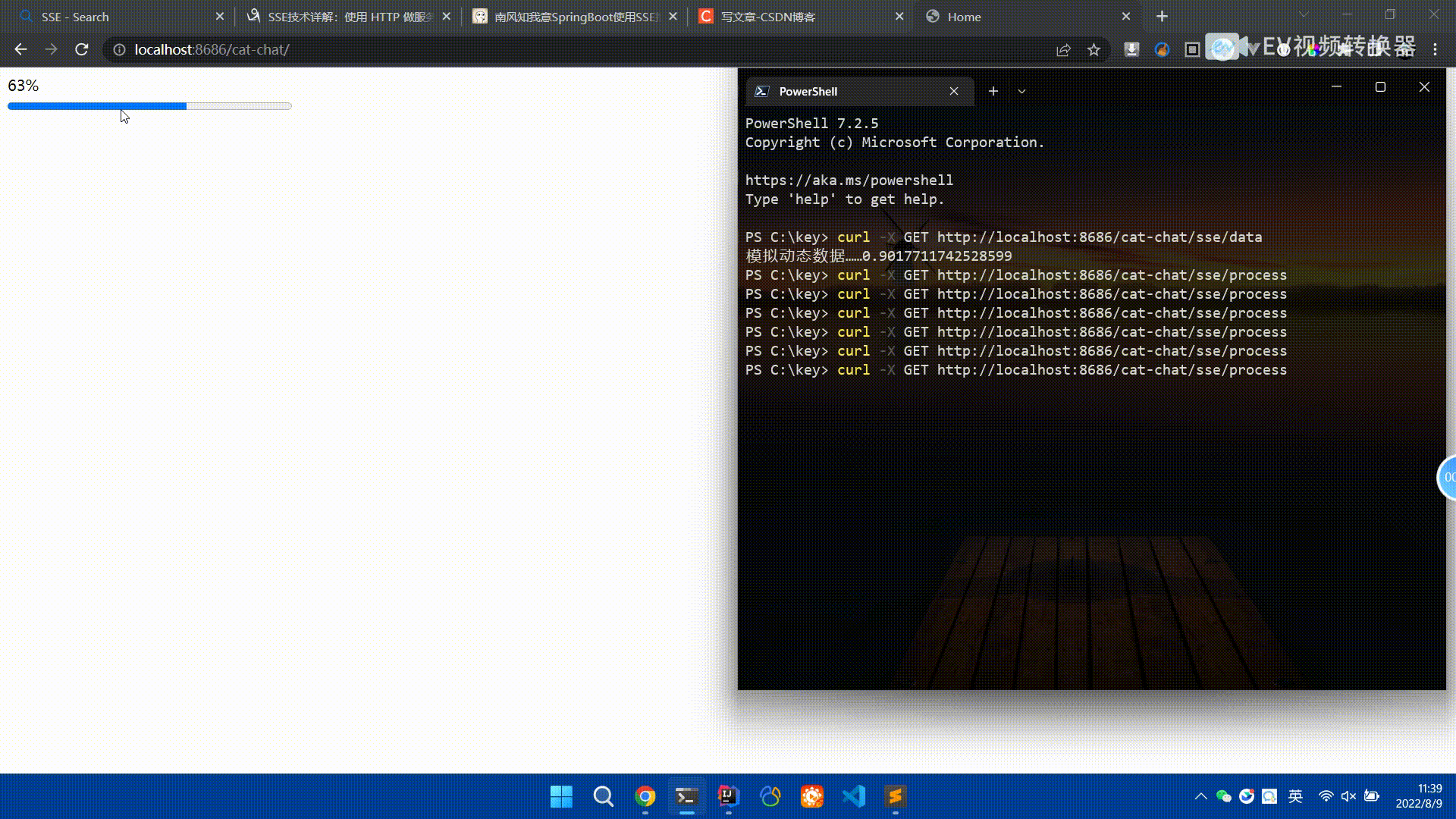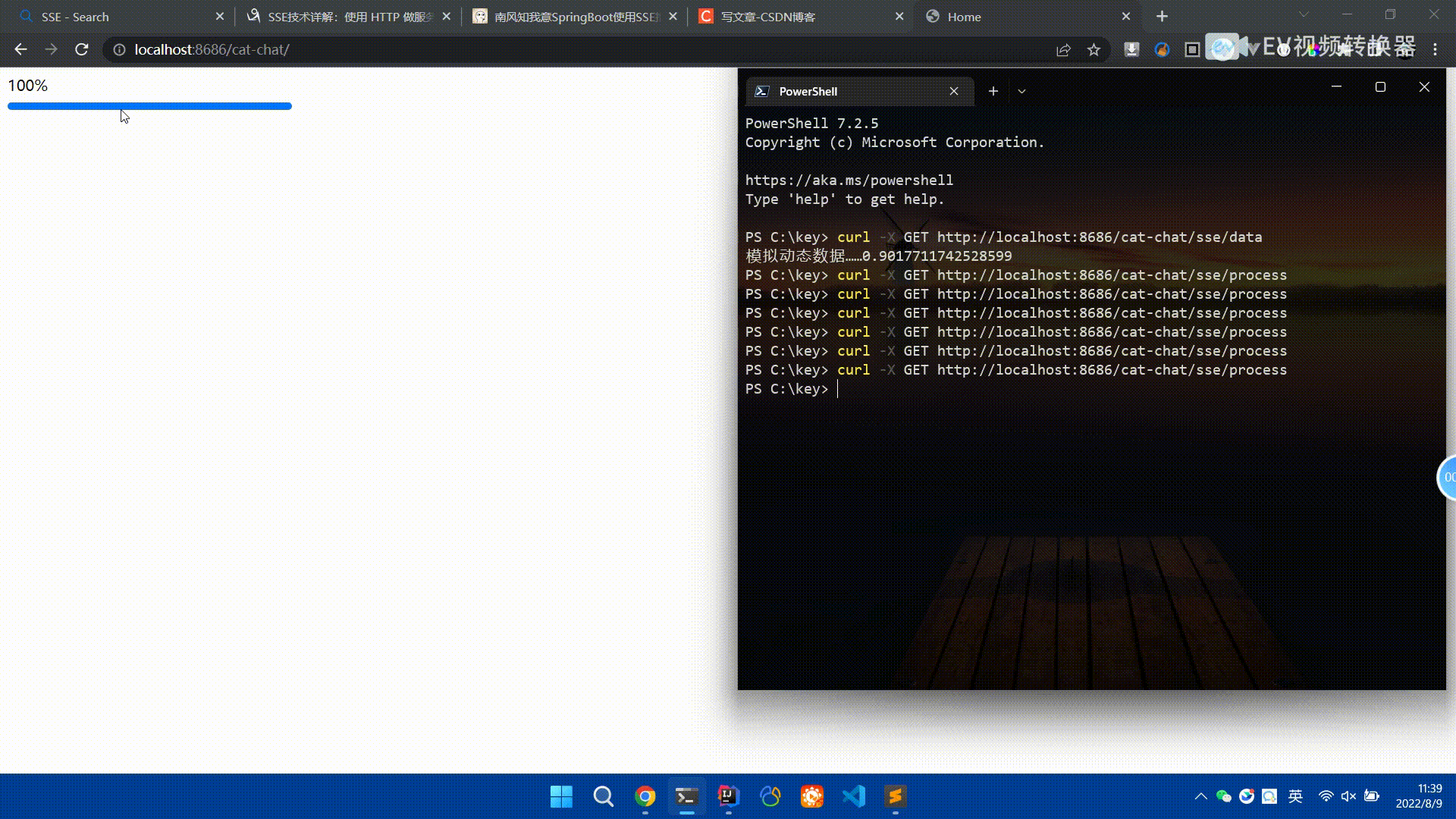 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
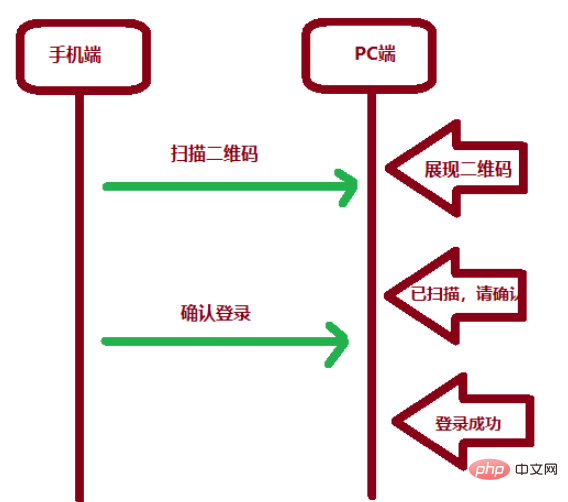 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
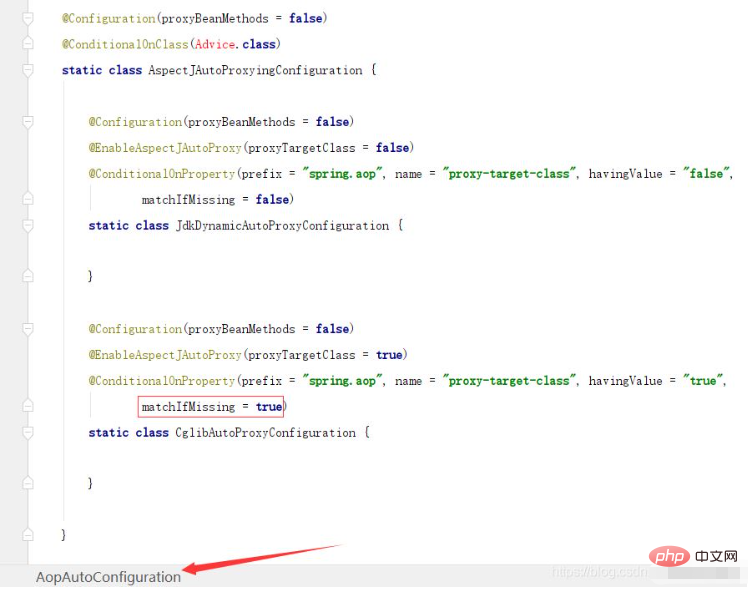 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
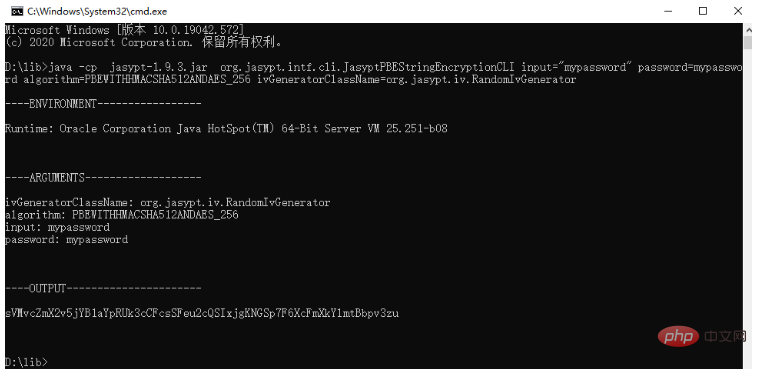 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM一、定义视频上传请求接口publicAjaxResultvideoUploadFile(MultipartFilefile){try{if(null==file||file.isEmpty()){returnAjaxResult.error("文件为空");}StringossFilePrefix=StringUtils.genUUID();StringfileName=ossFilePrefix+"-"+file.getOriginalFilename(


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools







