Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >What is the command to add a route in Linux?
What is the command to add a route in Linux?
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-16 20:35:1415439browse
The linux adding routing command is "route". The method of linux adding routing is: 1. Add "route add" in "/etc/rc.local" -net 192.168.2.0/24 gw 192.168.3.254"; 2. Add "GATEWAY=gw-ip" to the end of "/etc/sysconfig/network"; 3. Add "any net .." to "static-router". .” That’s it.
Detailed explanation of adding routing (route) command in linux
linux route command
route -nDisplay now All routes
root@Ubuntu:~# route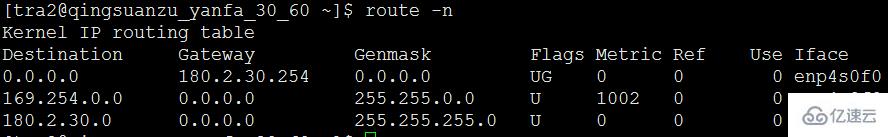
The result is from top to bottom. That is to say, whichever one is in front will have priority. There is no one in front. Use the last default
#添加一条路由(发往192.168.62这个网段的全部要经过网关192.168.1.1) route add -net 192.168.62.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.1.1 #删除一条路由 删除的时候不用写网关 route del -net 192.168.122.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
How to add a route under Linux:
1: Use the route command to add
Use the route command to add the route, machine The routing will become invalid after restarting or restarting the network card. Method:
#添加到主机的路由 # route add –host 192.168.168.110 dev eth0 # route add –host 192.168.168.119 gw 192.168.168.1 #添加到网络的路由 # route add –net IP netmask MASK eth0 # route add –net IP netmask MASK gw IP # route add –net IP/24 eth2 #添加默认网关 # route add default gw IP #删除路由 # route del –host 192.168.168.110 dev eth0
2: Method to set permanent routing under Linux:
1. In /etc/rc. Add
route add -net 192.168.3.0/24 dev eth0 route add -net 192.168.2.0/24 gw 192.168.3.254
in local 2. Add GATEWAY=gw-ip or GATEWAY=gw-dev# to the end of /etc/sysconfig/network
any net x.x.x.x/24 gw y.y.y.yCorrect usage of the Route commandUse the Route command line tool to view and edit the computer's IP routing table. The Route command and syntax are as follows:
route [-f] [-p] [Command [Destination] [mask Netmask] [Gateway] [metric Metric]] [if Interface]]
-f Clears the routing table for all gateway entries.
-p Makes a route persistent when used with the add command.
Command Specify the command you want to run (Add/Change/Delete/Print).
Destination Specifies the network destination for this route.
mask Netmask Specifies the network mask (also called a subnet mask) associated with the network target.
Gateway Specifies the forward or next hop IP addresses that can be reached by the address set and subnet mask defined by the network destination.
metric Metric Specifies an integer cost value for the route (from 1 to 9999), when in the routing table (with the destination address of the forwarded packet This can be used when selecting among multiple routes that best match).
if Interface Specifies the interface index for the interface through which the target can be reached. To obtain a list of interfaces and their corresponding interface indexes, use the display function of the route print command. Interface indexing can be done using decimal or hexadecimal values.
? Display help at the command prompt.
Example
route print Display the entire content of the IP routing table
route print 10.* Display starting from 10. Route in the original IP routing table
route add 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0 192.168.12.1 Add a default route with the 192.168.12.1 default gateway address
route add 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 10.27.0.1 Route add 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.1 with 255.255.0.0 subnet mask and 10.27.0.1 Add a route to the next hop address of 10.41.0.0
route -p add 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 10.27.0.1 to the target with # Add a permanent route to the 10.41.0.0 destination with ##255.255.0.0 subnet mask and 10.27.0.1 next hop address
route add 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 10.27.0.1 metric 7 Route with 255.255.0.0 subnet mask, 10.27.0.1 next hop address Add a route to the 10.41.0.0 target with a cost value of 7
route add 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 10.27.0.1 if 0x3 to with 255.255.0.0 subnet mask, 10.27.0.1 next hop address, and using 0x3 interface index 10.41.0.0 Add a route to the target
route delete 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 Delete to the one with 255.255.0.0 subnet mask 10.41.0.0 Target route
route delete 10.* Delete all routes in the IP routing table starting with 10.
route change 10.41.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 10.27.0.25 will have 10.41.0.0 destination and 255.255.0.0 subnet mask The next hop address is changed from 10.27.0.1 to 10.27.0.25
#示例1: 配置eth0的IP,同时激活设备:ifconfig eth0 192.168.4.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 up#示例2: 配置eth0别名设备 eth0:1 的IP,并添加路由ifconfig eth0:1 192.168.4.2 route add –host 192.168.4.2 dev eth0:1#示例3:激活(禁用)设备ifconfig eth0:1 up(down)#示例4:查看所有(指定)网络接口配置ifconfig (eth0)2. Use the route command to configure the routing table
示例1:添加到主机路由 route add –host 192.168.4.2 dev eth0:1 route add –host 192.168.4.1 gw 192.168.4.250 示例2:添加到网络的路由 route add –net IP netmask MASK eth0 route add –net IP netmask MASK gw IP route add –net IP/24 eth2 示例3:添加默认网关 route add default gw IP 示例4:删除路由 route del –host 192.168.4.1 dev eth0:1 示例5:查看路由信息 route 或 route -n (-n 表示不解析名字,列出速度会比route 快)3. ARP management command
示例1:查看ARP缓存 arp 示例2: 添加 arp –s IP MAC 示例3: 删除 arp –d IP4.
ipYes A powerful network configuration tool in the iproute2 software package, it can replace some traditional network management tools. For example: ifconfig, route, etc. The above example can be completely implemented using the following ip command, and the ip command can achieve more functions. Here are some examples: 4.0 Syntax of ip command
ip [OPTIONS] OBJECT [COMMAND [ARGUMENTS]]4.1 ip link set–change the attributes of the device. Abbreviation: set, s
示例1:up/down 起动/关闭设备。# ip link set dev eth0 up这个等于传统的 # ifconfig eth0 up(down)示例2:改变设备传输队列的长度。 参数:txqueuelen NUMBER或者txqlen NUMBER# ip link set dev eth0 txqueuelen 100示例3:改变网络设备MTU(最大传输单元)的值。# ip link set dev eth0 mtu 1500示例4: 修改网络设备的MAC地址。 参数: address LLADDRESS# ip link set dev eth0 address 00:01:4f:00:15:f1
4.2 ip link show–显示设备属性. 缩写:show、list、lst、sh、ls、l 、-s选项出现两次或者更多次,ip会输出更为详细的错误信息统计。
示例:# ip -s -s link ls eth0eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc cbq qlen 100 link/ether 00:a0:cc:66:18:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 2449949362 2786187 0 0 0 0 RX errors: length crc fifo missed 0 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 178558497 1783946 332 0 332 35172 TX errors: aborted fifo window heartbeat 0 0 0 332 这个命令等于传统的 ifconfig eth0
5.1 ip address add--添加一个新的协议地址. 缩写:add、a
示例1:为每个地址设置一个字符串作为标签。为了和Linux-2.0的网络别名兼容,这个字符串必须以设备名开头,接着一个冒号,# ip addr add local 192.168.4.1/28 brd + label eth0:1 dev eth0示例2: 在以太网接口eth0上增加一个地址192.168.20.0,掩码长度为24位(155.155.155.0),标准广播地址,标签为eth0:Alias:# ip addr add 192.168.4.2/24 brd + dev eth2 label eth2:1这个命令等于传统的: ifconfig eth2:1 192.168.4.2
5.2 ip address delete–删除一个协议地址. 缩写:delete、del、d
# ip addr del 192.168.4.1/24 brd + dev eth0 label eth0:Alias1
5.3 ip address show–显示协议地址. 缩写:show、list、lst、sh、ls、l
# ip addr ls eth0
5.4.ip address flush–清除协议地址. 缩写:flush、f
示例1 : 删除属于私网10.0.0.0/8的所有地址:# ip -s -s a f to 10/8示例2 : 取消所有以太网卡的IP地址# ip -4 addr flush label "eth0"
ip neighbour--neighbour/arp表管理命令
缩写 neighbour、neighbor、neigh、n
命令 add、change、replace、delete、fulsh、show(或者list)
6.1ip neighbour add– 添加一个新的邻接条目ip neighbour change–修改一个现有的条目ip neighbour replace–替换一个已有的条目
缩写:add、a;change、chg;replace、repl
示例1: 在设备eth0上,为地址10.0.0.3添加一个permanent ARP条目:# ip neigh add 10.0.0.3 lladdr 0:0:0:0:0:1 dev eth0 nud perm示例2:把状态改为reachable# ip neigh chg 10.0.0.3 dev eth0 nud reachable
6.2.ip neighbour delete–删除一个邻接条目
示例1:删除设备eth0上的一个ARP条目10.0.0.3
# ip neigh del 10.0.0.3 dev eth0
6.3.ip neighbour show–显示网络邻居的信息. 缩写:show、list、sh、ls
# ip -s n ls 193.233.7.254 193.233.7.254. dev eth0 lladdr 00:00:0c:76:3f:85 ref 5 used 12/13/20 nud reachable
6.4.ip neighbour flush–清除邻接条目. 缩写:flush、f
示例1: (-s 可以显示详细信息)
# ip -s -s n f 193.233.7.254
路由表管理
7.1.缩写 route、ro、r
7.2.路由表
从Linux-2.2开始,内核把路由归纳到许多路由表中,这些表都进行了编号,编号数字的范围是1到255。另外,为了方便,还可以在/etc/iproute2/rt_tables中为路由表命名。
默认情况下,所有的路由都会被插入到表main(编号254)中。在进行路由查询时,内核只使用路由表main。
7.3.ip route add– 添加新路由ip route change– 修改路由ip route replace– 替换已有的路由
缩写:add、a;change、chg;replace、repl
示例1: 设置到网络10.0.0/24的路由经过网关193.233.7.65
# ip route add 10.0.0/24 via 193.233.7.65
示例2: 修改到网络10.0.0/24的直接路由,使其经过设备dummy
# ip route chg 10.0.0/24 dev dummy
示例3: 实现链路负载平衡.加入缺省多路径路由,让ppp0和ppp1分担负载(注意:scope值并非必需,它只不过是告诉内核,
这个路由要经过网关而不是直连的。实际上,如果你知道远程端点的地址,使用via参数来设置就更好了)。
# ip route add default scope global nexthop dev ppp0 nexthop dev ppp1 # ip route replace default scope global nexthop dev ppp0 nexthop dev ppp1
示例4: 设置NAT路由。在转发来自192.203.80.144的数据包之前,先进行网络地址转换,把这个地址转换为193.233.7.83
# ip route add nat 192.203.80.142 via 193.233.7.83
示例5: 实现数据包级负载平衡,允许把数据包随机从多个路由发出。weight 可以设置权重.
# ip route replace default equalize nexthop via 211.139.218.145 dev eth0 weight 1 nexthop via 211.139.218.145 dev eth2 weight 1
7.4.ip route delete– 删除路由
缩写:delete、del、d
示例1:删除上一节命令加入的多路径路由
# ip route del default scope global nexthop dev ppp0 nexthop dev ppp1
7.5.ip route show – 列出路由
缩写:show、list、sh、ls、l
示例1: 计算使用gated/bgp协议的路由个数
# ip route ls proto gated/bgp |wc 1413 9891 79010
示例2: 计算路由缓存里面的条数,由于被缓存路由的属性可能大于一行,以此需要使用-o选项
# ip -o route ls cloned |wc 159 2543 18707
示例3: 列出路由表TABLEID里面的路由。缺省设置是table main。TABLEID或者是一个真正的路由表ID或者是/etc/iproute2/rt_tables文件定义的字符串,
或者是以下的特殊值:all – 列出所有表的路由;cache – 列出路由缓存的内容。
ip ro ls 193.233.7.82 tab cache
示例4: 列出某个路由表的内容
# ip route ls table fddi153
示例5: 列出默认路由表的内容
# ip route ls
这个命令等于传统的: route
7.6.ip route flush – 擦除路由表
示例1: 删除路由表main中的所有网关路由(示例:在路由监控程序挂掉之后):
# ip -4 ro flush scope global type unicast
示例2:清除所有被克隆出来的IPv6路由:
# ip -6 -s -s ro flush cache
示例3: 在gated程序挂掉之后,清除所有的BGP路由:
# ip -s ro f proto gated/bgp
示例4: 清除所有ipv4路由cache
# ip route flush cache *** IPv4 routing cache is flushed.
7.7 ip route get – 获得单个路由 .缩写:get、g
使用这个命令可以获得到达目的地址的一个路由以及它的确切内容。
ip route get命令和ip route show命令执行的操作是不同的。ip route show命令只是显示现有的路由,而ip route get命令在必要时会派生出新的路由。
示例1: 搜索到193.233.7.82的路由
# ip route get 193.233.7.82 193.233.7.82 dev eth0 src 193.233.7.65 realms inr.ac cache mtu 1500 rtt 300
示例2: 搜索目的地址是193.233.7.82,来自193.233.7.82,从eth0设备到达的路由(这条命令会产生一条非常有意思的路由,这是一条到193.233.7.82的回环路由)
# ip r g 193.233.7.82 from 193.233.7.82 iif eth0 193.233.7.82 from 193.233.7.82 dev eth0 src 193.233.7.65 realms inr.ac/inr.accachemtu 1500 rtt 300 iif eth0
ip route– 路由策略数据库管理命令
命令
add、delete、show(或者list)
注意:策略路由(policy routing)不等于路由策略(rouing policy)。
在某些情况下,我们不只是需要通过数据包的目的地址决定路由,可能还需要通过其他一些域:源地址、IP协议、传输层端口甚至数据包的负载。
这就叫做:策略路由(policy routing)。
8.1. ip rule add – 插入新的规则
ip rule delete – 删除规则
缩写:add、a;delete、del、d
示例1: 通过路由表inr.ruhep路由来自源地址为192.203.80/24的数据包 ip ru add from 192.203.80/24 table inr.ruhep prio 220 示例2:把源地址为193.233.7.83的数据报的源地址转换为192.203.80.144,并通过表1进行路由 ip ru add from 193.233.7.83 nat 192.203.80.144 table 1 prio 320 示例3:删除无用的缺省规则 ip ru del prio 32767
8.2. ip rule show – 列出路由规则
缩写:show、list、sh、ls、l
示例1: # ip ru ls 0: from all lookup local 32762: from 192.168.4.89 lookup fddi153 32764: from 192.168.4.88 lookup fddi153 32766: from all lookup main 32767: from all lookup 253
ip maddress – 多播地址管理
缩写:show、list、sh、ls、l
9.1.ip maddress show – 列出多播地址
示例1: # ip maddr ls dummy
9.2. ip maddress add – 加入多播地址
ip maddress delete – 删除多播地址
缩写:add、a;delete、del、d
使用这两个命令,我们可以添加/删除在网络接口上监听的链路层多播地址。这个命令只能管理链路层地址。
示例1: 增加 # ip maddr add 33:33:00:00:00:01 dev dummy示例2: 查看 # ip -O maddr ls dummy2: dummylink 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 2 staticlink 01:00:5e:00:00:01 示例3: 删除 # ip maddr del 33:33:00:00:00:01 dev dummy
10.ip mroute – 多播路由缓存管理
10.1. ip mroute show – 列出多播路由缓存条目
缩写:show、list、sh、ls、l
示例1:查看 # ip mroute ls(193.232.127.6, 224.0.1.39) Iif: unresolved(193.232.244.34, 224.0.1.40) Iif: unresolved(193.233.7.65, 224.66.66.66) Iif: eth0 Oifs: pimreg 示例2:查看 # ip -s mr ls 224.66/16(193.233.7.65, 224.66.66.66) Iif: eth0 Oifs: pimreg 9383 packets, 300256 bytes
ip tunnel – 通道配置
缩写
tunnel、tunl
11.1.ip tunnel add – 添加新的通道
ip tunnel change – 修改现有的通道
ip tunnel delete – 删除一个通道
缩写:add、a;change、chg;delete、del、d
示例1:建立一个点对点通道,最大TTL是32
# ip tunnel add Cisco mode sit remote 192.31.7.104 local 192.203.80.1 ttl 32
11.2.ip tunnel show – 列出现有的通道
缩写:show、list、sh、ls、l
示例1: # ip -s tunl ls Cisco
12.ip monitor和rtmon – 状态监视
ip命令可以用于连续地监视设备、地址和路由的状态。这个命令选项的格式有点不同,命令选项的名字叫做monitor,接着是操作对象:
ip monitor [ file FILE ] [ all | OBJECT-LIST ]
示例1: # rtmon file /var/log/rtmon.log
示例2: # ip monitor file /var/log/rtmon.log r
The above is the detailed content of What is the command to add a route in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

