Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to solve the problem that SpringBoot+Spring Security cannot achieve cross-domain
How to solve the problem that SpringBoot+Spring Security cannot achieve cross-domain
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-16 15:40:551216browse
SpringBoot Spring Security cannot achieve cross-domain
Cross-domain when Security is not used:
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureBefore;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.format.FormatterRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*;
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureBefore(SecurityConfig.class)
public class MyMvcConfigurer implements WebMvcConfigurer {
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry){
LOGGER.info("跨域已设置");
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowCredentials(true)
.maxAge(3600);
}
}When integrating Security, we found that there are still cross-domain problems when only using the above method to separate the front and back ends,
The solution is as follows:
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureBefore(Swagger2Configuration.class)
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@Order(-1)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/user/login")
.loginPage("/singIn.html")
.successHandler(moyuAuthenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(moyuAuthenticationFailureHandler)
.and()
.apply(moyuSocialSecurityConfig)
.and()
.rememberMe()
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
.tokenValiditySeconds(3600*24*7)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user/login","/login","/singIn.html","**","/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
.cors()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}Focus on adding code:
.and() .cors()//新加入 .and() .csrf().disable();
Quoting the cross-domain processing of the Spring Security project
The recent project adopts a framework of front-end and back-end separation. The front-end and back-end interfaces are not deployed to a site, and a cross-domain problem occurs. What is cross-domain, I will not go into details here, and just talk about the solution.
Spring has many ways to solve cross-domain problems. I personally use Crosfilter.
The specific code is as follows:
@Bean
public CorsFilter corsFilter() {
final UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource urlBasedCorsConfigurationSource = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
final CorsConfiguration corsConfiguration = new CorsConfiguration();
corsConfiguration.setAllowCredentials(true);
corsConfiguration.addAllowedOrigin("*");
corsConfiguration.addAllowedHeader("*");
corsConfiguration.addAllowedMethod("*");
urlBasedCorsConfigurationSource.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", corsConfiguration);
return new CorsFilter(urlBasedCorsConfigurationSource);
}After the configuration is completed, test the call and report an error 401, but it still doesn’t work. . After checking the information online, I learned that cross-domain requests will be made twice. The specific process is shown in the figure below:
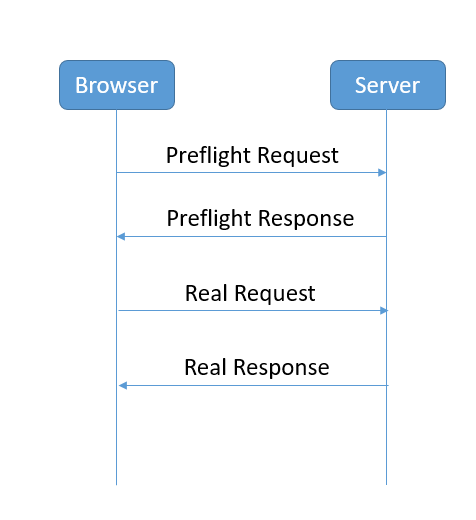
For each cross-domain request, before the actual request reaches the backend, the browser will first initiate a preflight request, and the request method is OPTIONS to query the server. Whether to accept the cross-domain request, the specific parameters are as follows:
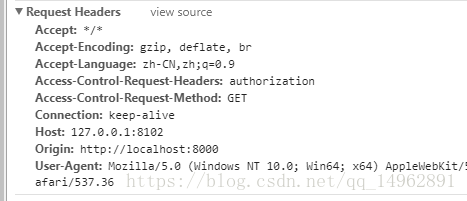
#But the request cannot carry cookies and self-defined headers.
Since Spring security was introduced in the project, the token delivery method I used was to use the authorization field in the header. In this way, I relied on Spring Security to intercept the preflight request and found that it did not carry a token, and an error 401 was reported, not authorized. .
Solving this problem is very simple. You can use the following configuration
to make Spring security not verify the preflight request.
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer<HttpSecurity>.ExpressionInterceptUrlRegistry registry
= http.authorizeRequests();
registry.requestMatchers(CorsUtils::isPreFlightRequest).permitAll();//让Spring security放行所有preflight request
}It will be fixed if you try again, but directly configuring the backend to support cross-domain will result in two requests. Another way is to use Nginx to forward the request.
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the problem that SpringBoot+Spring Security cannot achieve cross-domain. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

