Home >Java >javaTutorial >What is the method for SpringBoot to integrate tomcat?
What is the method for SpringBoot to integrate tomcat?
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-14 19:43:141356browse
spring boot supports current mainstream servlet containers, including tomcat, jetty, and undertow. These servlet containers can be easily integrated in our projects, reducing the workload of development and operation and maintenance. Traditional application development requires complicated steps: install tomcat –> modify tomcat configuration –> deploy war package –> start tomcat –> operation and maintenance... this workload Not small, especially when deploying clusters and migrating applications. After adopting spring boot, everything becomes so simple. Packaging - java -jar - operation and maintenance, you only need a jar package to deploy and install at will.
SPI
Before analyzing the source code, let’s first understand the SPI mechanism of spring. We know that jdk provides a default SPI implementation (ServiceLoader) to facilitate application expansion, and dubbo also has its own SPI. The same is true for spring. It provides us with SpringFactoriesLoader, which allows developers to extend through the META-INF/spring.factories file. Here is an example for easy understanding
If I want to add an ApplicationContextInitializer to the spring container to do some initialization work, we can use the SPI function provided by spring to complete this requirement.
First, create the META-INF/spring.factories file in the project. The file content is as follows:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer= \
We write another test case, and then we can obtain the ApplicationContextInitializer we defined through SPI. It seems to be a very simple function, but spring boot uses this powerful extension point to integrate commonly used open source frameworks for us on the basis of spring framework
@Test
public void testSpringSpi() {
List<ApplicationListener> listeners = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories( ApplicationListener.class,
ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader() );
System.out.println( listeners ); Let’s take a look at this SpringFactoriesLoader , the key code is as follows, it reads the META-INF/spring.factories file, finds the class specified by the method parameter, then creates the corresponding instance object, and returns it. In addition, sorting is also supported, which can be sorted in the following ways
org.springframework.core.Ordered: Implement this interface
org .springframework.core.annotation.Order: Annotation
javax.annotation.Priority: Annotation
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
List<String> factoryNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryClass, classLoaderToUse);
List<T> result = new ArrayList<T>(factoryNames.size());
for (String factoryName : factoryNames) {
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryName, factoryClass, classLoaderToUse));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;Next, let’s analyze spring How boot uses the SPI mechanism to integrate tomcat
SpringBoot for Tomcat
Before analyzing the source code of tomcat integration, let’s first understand EmbeddedServletContainer
EmbeddedServletContainer:
spring uses EmbeddedServletContainer to encapsulate the embedded servlet container, providing start, stop and other interfaces to control the life cycle of the container, and spring has built-in tomcat , jetty, undertow container implementation, as shown in the class diagram
Let’s take a look at the most commonly used SpringBootApplication annotations in spring boot. It turns out to be a complex of multiple annotations, and this EnableAutoConfiguration is the annotation used by spring boot for automatic configuration
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
// code...... We can see a large number of SPI configurations in the spring-boot-autoconfigure module, some of which are as follows
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\
Original EnableAutoConfiguration annotation introduced EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration, and this is the configuration class of the embedded servlet container. Tomcat, jetty, and undertow are all in this class, through @ConditionalOnClassAnnotation loads different servlet containers. However, this class only registers TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory, which is not enough to help us resolve all confusions. Don't worry, let's take a look at the class diagram of TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory first.
As can be seen from the above class diagram, it implements the following interface:
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory: It is a factory pattern used to create
EmbeddedServletContainer, That is, it is used to create an embedded Servlet container. There is only onegetEmbeddedServletContainermethod in this interface.- ##ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer: used to configure
EmbeddedServletContainer
, such as Talk about ports, context paths, etc.
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory, take a look at getEmbeddedServletContainerMethod call stack. The GenericWebApplicationContext#onRefresh() method is rewritten in EmbeddedWebApplicationContext, and the getEmbeddedServletContainer method is called to create a servlet container. We will analyze this creation process next.
EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
createEmbeddedServletContainer();
}
private void createEmbeddedServletContainer() {
EmbeddedServletContainer localContainer = this.embeddedServletContainer;
ServletContext localServletContext = getServletContext();
if (localContainer == null && localServletContext == null) {
// 从容器中获取bean,如果使用tomcat则返回TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory = getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
this.embeddedServletContainer = containerFactory.getEmbeddedServletContainer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (localServletContext != null) {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(localServletContext);
}
initPropertySources();Let’s draw the main flow chart first
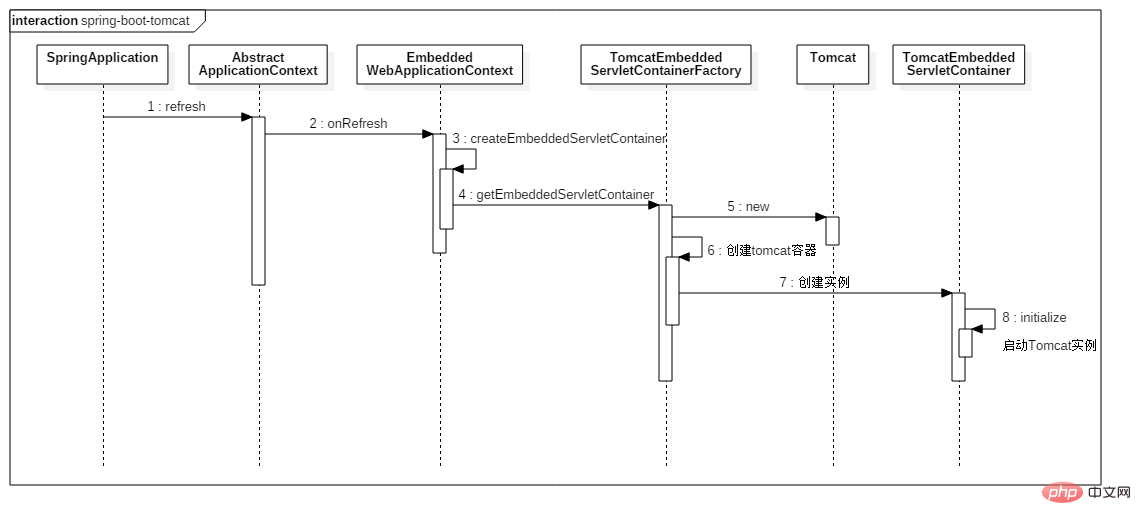
由上图可知,EmbeddedWebApplicationContext在执行onRefresh方法的时候,首先调用父类的onRefresh,然后从容器中获取EmbeddedServletContainerFactory的实现类。由于我们在 classpath 下面可以获取 tomcat 的 jar 包,因此EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration会在 spring 容器中注册TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory这个 bean。然后,由它创建TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer,我们来看看具体的创建过程,代码如下所示:
TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory.java
@Override
public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(
ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); // 实例化 apache Tomcat
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
// 创建 Connector 组件,默认使用org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
// 支持对 Connector 进行自定义设置,比如设置线程池、最大连接数等
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatEmbeddedServletContainer(tomcat);首先是实例化Tomcat对象,然后创建Connector组件,并且对Connector进行相关的参数设置,同时也允许我们通过TomcatConnectorCustomizer接口进行自定义的设置。OK,创建了Tomcat实例之后,需要创建TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer,它依赖Tomcat对象,在构造方法中便会启动 Tomcat 容器,从而完成各个组件的启动流程
public TomcatEmbeddedServletContainer(Tomcat tomcat, boolean autoStart) {
Assert.notNull(tomcat, "Tomcat Server must not be null");
this.tomcat = tomcat;
this.autoStart = autoStart;
initialize();
}
private void initialize() throws EmbeddedServletContainerException {
synchronized (this.monitor) {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
// Remove service connectors to that protocol binding doesn't happen yet
removeServiceConnectors();
// Start the server to trigger initialization listeners
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
Context context = findContext();
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, getNamingToken(context),
getClass().getClassLoader());
// Unlike Jetty, all Tomcat threads are daemon threads. We create a
// blocking non-daemon to stop immediate shutdown
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}The above is the detailed content of What is the method for SpringBoot to integrate tomcat?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

