1. Multi-level caching
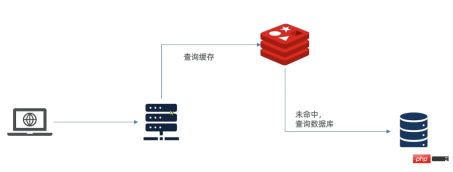
1. Traditional caching solution
After the request reaches tomcat, it first goes to redis to get the cache. If there is no hit, it goes to mysql to get it
2. Multi-level caching solution
# The number of concurrent requests of tomcatis much smaller than that of redis, so tomcat will become a bottleneckUse each link of request processing to add cache respectively to reduce the pressure on tomcat and improve service performance
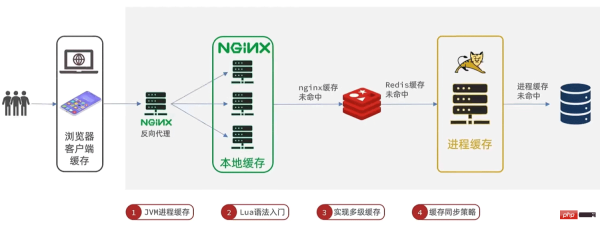
Distributed cache, Such as redis- Advantages: Large storage capacity, good reliability, can be shared in the cluster
- Disadvantages: There is network overhead for accessing the cache
- Scenario: Large amount of cached data, high reliability, needs to be in the cluster Shared data in
Process local cache, such as HashMap, GuavaCache1. Practical case- Advantages: Reading local memory, no network overhead, faster
- Disadvantages: Storage capacity Limited, low reliability (such as lost after restarting), cannot be shared in the cluster
- Scenario: high performance requirements, small amount of cached data
- Caffeine is a high-performance local cache library developed based on java8 that provides nearly the best hit rate.
- This is currently used for the internal cache of spring
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
</dependency>package com.erick.cache;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Cache;
import com.github.benmanes.caffeine.cache.Caffeine;
import java.time.Duration;
public final class CacheUtil {
private static int expireSeconds = 2;
public static Cache<String, String> cacheWithExpireSeconds;
private static int maxPairs = 1;
public static Cache<String, String> cacheWithMaxPairs;
static {
/*过期策略,写完60s后过期*/
cacheWithExpireSeconds = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(Duration.ofSeconds(expireSeconds))
.build();
/*过期策略,达到最大值后删除
* 1. 并不会立即删除,等一会儿才会删除
* 2. 会将之前存储的数据删除掉*/
cacheWithMaxPairs = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(maxPairs)
.build();
}
/*从缓存中获取数据
* 1. 如果缓存中有,则直接从缓存中返回
* 2. 如果缓存中没有,则去数据查询并返回结果*/
public static String getKeyWithExpire(String key) {
return cacheWithExpireSeconds.get(key, value -> {
return getResultFromDB();
});
}
public static String getKeyWithMaxPair(String key) {
return cacheWithMaxPairs.get(key, value -> {
return getResultFromDB();
});
}
private static String getResultFromDB() {
System.out.println("数据库查询");
return "db result";
}
}package com.erick.cache;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test01() throws InterruptedException {
CacheUtil.cacheWithExpireSeconds.put("name", "erick");
System.out.println(CacheUtil.getKeyWithExpire("name"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(CacheUtil.getKeyWithExpire("name"));
}
@org.junit.Test
public void test02() throws InterruptedException {
CacheUtil.cacheWithMaxPairs.put("name", "erick");
CacheUtil.cacheWithMaxPairs.put("age", "12");
System.out.println(CacheUtil.getKeyWithMaxPair("name"));
System.out.println(CacheUtil.getKeyWithMaxPair("age"));
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(CacheUtil.getKeyWithMaxPair("name")); // 查询不到了
System.out.println(CacheUtil.getKeyWithMaxPair("age"));
}
}3. Cache consistency1. Common solutions1.1 Set the validity period
- to the cache Set the validity period and automatically delete it after expiration. It can be updated when querying again
- Advantages: simple and convenient
- Disadvantages: poor timeliness, the cache may be inconsistent before it expires
- Scenario: Business with low update frequency and low timeliness requirements
- When modifying the database At the same time, directly modify the cache
- Advantages: code intrusion, strong consistency between cache and database
- Disadvantages: code intrusion, high coupling
- Scenario: Cache data with high consistency and invalidity requirements
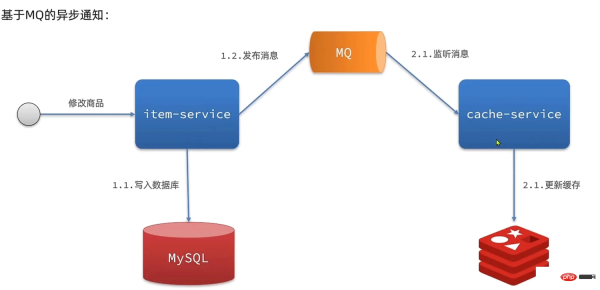
- Send an event notification when the database is modified, and the relevant services modify the cached data after listening to it
- Advantages: low coupling, multiple cache services can be notified at the same time
- Disadvantages: Timeliness is limited, there may be cache inconsistency issues
- Scenario: Timeliness is average, there are multiple services that need to be synchronized
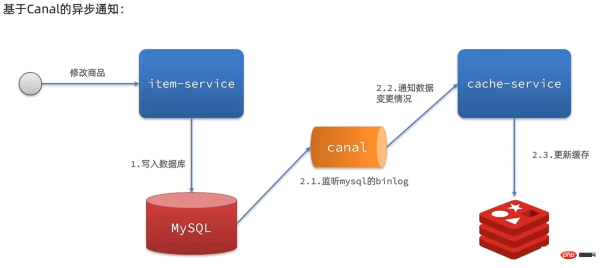
- is an open source project under Alibaba, based on java Development
- Based on database incremental log analysis, providing incremental data subscription and consumption
- The idea of master-slave backup based on mysql
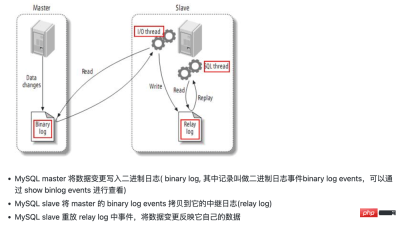
- canal simulates MySQL slave Interactive protocol, pretending to be a MySQL slave, sending dump protocol to MySQL master
- MySQL master receives the dump request and starts pushing the binary log to the slave (i.e. canal)
- canal parses the binary log object (originally a byte stream)
The above is the detailed content of How to implement Redis multi-level cache based on Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Java Platform Independence: Compatibility with different OSMay 13, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Java Platform Independence: Compatibility with different OSMay 13, 2025 am 12:11 AMJavaachievesplatformindependencethroughtheJavaVirtualMachine(JVM),allowingcodetorunondifferentoperatingsystemswithoutmodification.TheJVMcompilesJavacodeintoplatform-independentbytecode,whichittheninterpretsandexecutesonthespecificOS,abstractingawayOS
 What features make java still powerfulMay 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
What features make java still powerfulMay 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMJavaispowerfulduetoitsplatformindependence,object-orientednature,richstandardlibrary,performancecapabilities,andstrongsecurityfeatures.1)PlatformindependenceallowsapplicationstorunonanydevicesupportingJava.2)Object-orientedprogrammingpromotesmodulara
 Top Java Features: A Comprehensive Guide for DevelopersMay 13, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Top Java Features: A Comprehensive Guide for DevelopersMay 13, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe top Java functions include: 1) object-oriented programming, supporting polymorphism, improving code flexibility and maintainability; 2) exception handling mechanism, improving code robustness through try-catch-finally blocks; 3) garbage collection, simplifying memory management; 4) generics, enhancing type safety; 5) ambda expressions and functional programming to make the code more concise and expressive; 6) rich standard libraries, providing optimized data structures and algorithms.
 Is Java Truly Platform Independent? How 'Write Once, Run Anywhere' WorksMay 13, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Is Java Truly Platform Independent? How 'Write Once, Run Anywhere' WorksMay 13, 2025 am 12:03 AMJavaisnotentirelyplatformindependentduetoJVMvariationsandnativecodeintegration,butitlargelyupholdsitsWORApromise.1)JavacompilestobytecoderunbytheJVM,allowingcross-platformexecution.2)However,eachplatformrequiresaspecificJVM,anddifferencesinJVMimpleme
 Demystifying the JVM: Your Key to Understanding Java ExecutionMay 13, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Demystifying the JVM: Your Key to Understanding Java ExecutionMay 13, 2025 am 12:02 AMTheJavaVirtualMachine(JVM)isanabstractcomputingmachinecrucialforJavaexecutionasitrunsJavabytecode,enablingthe"writeonce,runanywhere"capability.TheJVM'skeycomponentsinclude:1)ClassLoader,whichloads,links,andinitializesclasses;2)RuntimeDataAr
 Is java still a good language based on new features?May 12, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Is java still a good language based on new features?May 12, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaremainsagoodlanguageduetoitscontinuousevolutionandrobustecosystem.1)Lambdaexpressionsenhancecodereadabilityandenablefunctionalprogramming.2)Streamsallowforefficientdataprocessing,particularlywithlargedatasets.3)ThemodularsystemintroducedinJava9im
 What Makes Java Great? Key Features and BenefitsMay 12, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What Makes Java Great? Key Features and BenefitsMay 12, 2025 am 12:11 AMJavaisgreatduetoitsplatformindependence,robustOOPsupport,extensivelibraries,andstrongcommunity.1)PlatformindependenceviaJVMallowscodetorunonvariousplatforms.2)OOPfeatureslikeencapsulation,inheritance,andpolymorphismenablemodularandscalablecode.3)Rich
 Top 5 Java Features: Examples and ExplanationsMay 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Top 5 Java Features: Examples and ExplanationsMay 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMThe five major features of Java are polymorphism, Lambda expressions, StreamsAPI, generics and exception handling. 1. Polymorphism allows objects of different classes to be used as objects of common base classes. 2. Lambda expressions make the code more concise, especially suitable for handling collections and streams. 3.StreamsAPI efficiently processes large data sets and supports declarative operations. 4. Generics provide type safety and reusability, and type errors are caught during compilation. 5. Exception handling helps handle errors elegantly and write reliable software.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.







