What is kafka?
Kafka is an open source stream processing platform developed by the Apache Software Foundation and written in Scala and Java. Kafka is a high-throughput distributed publish-subscribe messaging system that can process all action streaming data of consumers in the website. Such actions (web browsing, searches and other user actions) are a key factor in many social functions on the modern web. This data is typically addressed by processing logs and log aggregation due to throughput requirements. This is a feasible solution for log data and offline analysis systems like Hadoop, but requiring real-time processing constraints. The purpose of Kafka is to unify online and offline message processing through Hadoop's parallel loading mechanism, and to provide real-time messages through the cluster.
Application scenarios
Message system: Kafka and traditional message systems (also called message middleware) both have system decoupling, redundant storage, and traffic peak shaving. , buffering, asynchronous communication, scalability, recoverability and other functions. At the same time, Kafka also provides message sequence guarantee and retroactive consumption functions that are difficult to achieve in most messaging systems.
Storage system: Kafka persists messages to disk, which effectively reduces the risk of data loss compared to other memory storage-based systems. It is precisely thanks to Kafka's message persistence function and multi-copy mechanism that we can use Kafka as a long-term data storage system. We only need to set the corresponding data retention policy to "permanent" or enable the topic's log compression function. That’s it.
Streaming processing platform: Kafka not only provides a reliable data source for each popular streaming framework, but also provides a complete streaming class library, such as windows, Various operations such as joins, transformations and aggregations.
Let’s take a look at the detailed code of SpringBoot integrating Kafka tool class.
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.12.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>fastjson</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.83</version>
</dependency>Tool Class
package com.bbl.demo.utils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.exception.ExceptionUtils;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.admin.*;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerRecords;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;
import org.apache.kafka.common.KafkaFuture;
import org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TopicExistsException;
import org.apache.kafka.common.errors.UnknownTopicOrPartitionException;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class KafkaUtils {
private static AdminClient admin;
/**
* 私有静态方法,创建Kafka生产者
* @author o
* @return KafkaProducer
*/
private static KafkaProducer<String, String> createProducer() {
Properties props = new Properties();
//声明kafka的地址
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"node01:9092,node02:9092,node03:9092");
//0、1 和 all:0表示只要把消息发送出去就返回成功;1表示只要Leader收到消息就返回成功;all表示所有副本都写入数据成功才算成功
props.put("acks", "all");
//重试次数
props.put("retries", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//批处理的字节数
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
//批处理的延迟时间,当批次数据未满之时等待的时间
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
//用来约束KafkaProducer能够使用的内存缓冲的大小的,默认值32MB
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// properties.put("value.serializer",
// "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializer");
// properties.put("key.serializer",
// "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializer");
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
return new KafkaProducer<String, String>(props);
}
/**
* 私有静态方法,创建Kafka消费者
* @author o
* @return KafkaConsumer
*/
private static KafkaConsumer<String, String> createConsumer() {
Properties props = new Properties();
//声明kafka的地址
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,"node01:9092,node02:9092,node03:9092");
//每个消费者分配独立的消费者组编号
props.put("group.id", "111");
//如果value合法,则自动提交偏移量
props.put("enable.auto.commit", "true");
//设置多久一次更新被消费消息的偏移量
props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000");
//设置会话响应的时间,超过这个时间kafka可以选择放弃消费或者消费下一条消息
props.put("session.timeout.ms", "30000");
//自动重置offset
props.put("auto.offset.reset","earliest");
// properties.put("value.serializer",
// "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializer");
// properties.put("key.serializer",
// "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializer");
props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
return new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(props);
}
/**
* 私有静态方法,创建Kafka集群管理员对象
* @author o
*/
public static void createAdmin(String servers){
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(AdminClientConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,servers);
admin = AdminClient.create(props);
}
/**
* 私有静态方法,创建Kafka集群管理员对象
* @author o
* @return AdminClient
*/
private static void createAdmin(){
createAdmin("node01:9092,node02:9092,node03:9092");
}
/**
* 传入kafka约定的topic,json格式字符串,发送给kafka集群
* @author o
* @param topic
* @param jsonMessage
*/
public static void sendMessage(String topic, String jsonMessage) {
KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = createProducer();
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>(topic, jsonMessage));
producer.close();
}
/**
* 传入kafka约定的topic消费数据,用于测试,数据最终会输出到控制台上
* @author o
* @param topic
*/
public static void consume(String topic) {
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = createConsumer();
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(topic));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(100));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records){
System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s",record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/**
* 传入kafka约定的topic数组,消费数据
* @author o
* @param topics
*/
public static void consume(String ... topics) {
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = createConsumer();
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(topics));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(100));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records){
System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s",record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/**
* 传入kafka约定的topic,json格式字符串数组,发送给kafka集群
* 用于批量发送消息,性能较高。
* @author o
* @param topic
* @param jsonMessages
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void sendMessage(String topic, String... jsonMessages) throws InterruptedException {
KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = createProducer();
for (String jsonMessage : jsonMessages) {
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>(topic, jsonMessage));
}
producer.close();
}
/**
* 传入kafka约定的topic,Map集合,内部转为json发送给kafka集群 <br>
* 用于批量发送消息,性能较高。
* @author o
* @param topic
* @param mapMessageToJSONForArray
*/
public static void sendMessage(String topic, List<Map<Object, Object>> mapMessageToJSONForArray) {
KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = createProducer();
for (Map<Object, Object> mapMessageToJSON : mapMessageToJSONForArray) {
String array = JSONObject.toJSON(mapMessageToJSON).toString();
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>(topic, array));
}
producer.close();
}
/**
* 传入kafka约定的topic,Map,内部转为json发送给kafka集群
* @author o
* @param topic
* @param mapMessageToJSON
*/
public static void sendMessage(String topic, Map<Object, Object> mapMessageToJSON) {
KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = createProducer();
String array = JSONObject.toJSON(mapMessageToJSON).toString();
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>(topic, array));
producer.close();
}
/**
* 创建主题
* @author o
* @param name 主题的名称
* @param numPartitions 主题的分区数
* @param replicationFactor 主题的每个分区的副本因子
*/
public static void createTopic(String name,int numPartitions,int replicationFactor){
if(admin == null) {
createAdmin();
}
Map<String, String> configs = new HashMap<>();
CreateTopicsResult result = admin.createTopics(Arrays.asList(new NewTopic(name, numPartitions, (short) replicationFactor).configs(configs)));
//以下内容用于判断创建主题的结果
for (Map.Entry<String, KafkaFuture<Void>> entry : result.values().entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getValue().get();
System.out.println("topic "+entry.getKey()+" created");
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
if (ExceptionUtils.getRootCause(e) instanceof TopicExistsException) {
System.out.println("topic "+entry.getKey()+" existed");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 删除主题
* @author o
* @param names 主题的名称
*/
public static void deleteTopic(String name,String ... names){
if(admin == null) {
createAdmin();
}
Map<String, String> configs = new HashMap<>();
Collection<String> topics = Arrays.asList(names);
topics.add(name);
DeleteTopicsResult result = admin.deleteTopics(topics);
//以下内容用于判断删除主题的结果
for (Map.Entry<String, KafkaFuture<Void>> entry : result.values().entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getValue().get();
System.out.println("topic "+entry.getKey()+" deleted");
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
if (ExceptionUtils.getRootCause(e) instanceof UnknownTopicOrPartitionException) {
System.out.println("topic "+entry.getKey()+" not exist");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 查看主题详情
* @author o
* @param names 主题的名称
*/
public static void describeTopic(String name,String ... names){
if(admin == null) {
createAdmin();
}
Map<String, String> configs = new HashMap<>();
Collection<String> topics = Arrays.asList(names);
topics.add(name);
DescribeTopicsResult result = admin.describeTopics(topics);
//以下内容用于显示主题详情的结果
for (Map.Entry<String, KafkaFuture<TopicDescription>> entry : result.values().entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getValue().get();
System.out.println("topic "+entry.getKey()+" describe");
System.out.println("\t name: "+entry.getValue().get().name());
System.out.println("\t partitions: ");
entry.getValue().get().partitions().stream().forEach(p-> {
System.out.println("\t\t index: "+p.partition());
System.out.println("\t\t\t leader: "+p.leader());
System.out.println("\t\t\t replicas: "+p.replicas());
System.out.println("\t\t\t isr: "+p.isr());
});
System.out.println("\t internal: "+entry.getValue().get().isInternal());
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
if (ExceptionUtils.getRootCause(e) instanceof UnknownTopicOrPartitionException) {
System.out.println("topic "+entry.getKey()+" not exist");
}
}
}
}
/**
* 查看主题列表
* @author o
* @return Set<String> TopicList
*/
public static Set<String> listTopic(){
if(admin == null) {
createAdmin();
}
ListTopicsResult result = admin.listTopics();
try {
result.names().get().stream().map(x->x+"\t").forEach(System.out::print);
return result.names().get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(listTopic());
}
}The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot integrates Kafka tool classes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
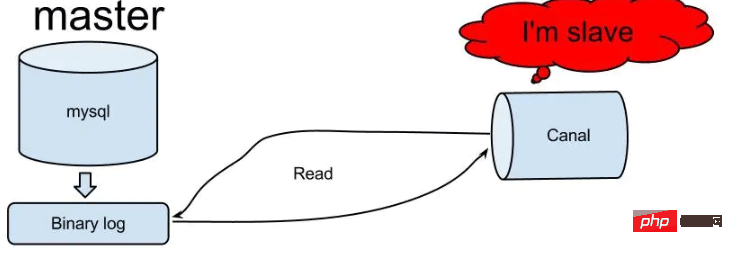 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
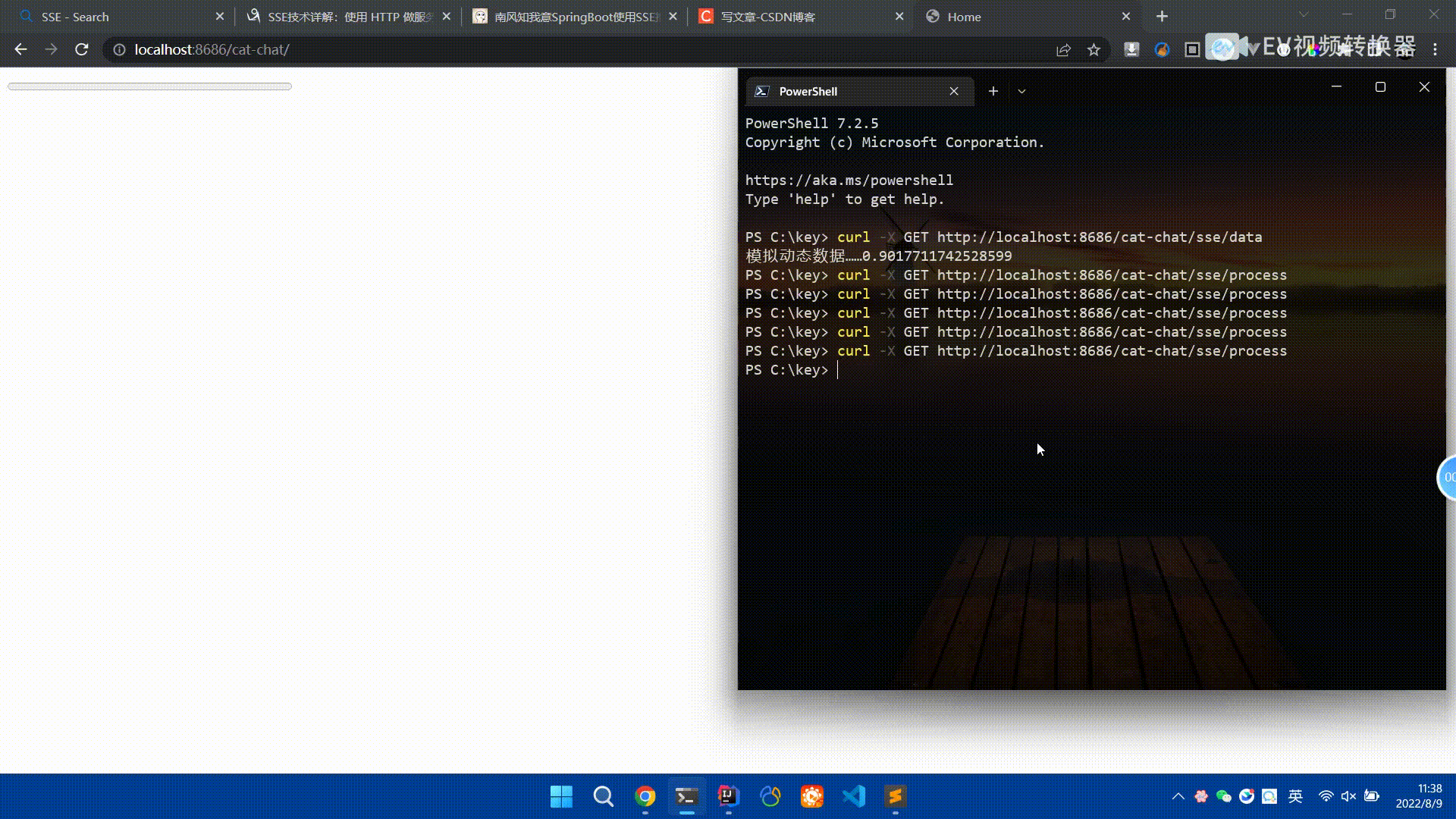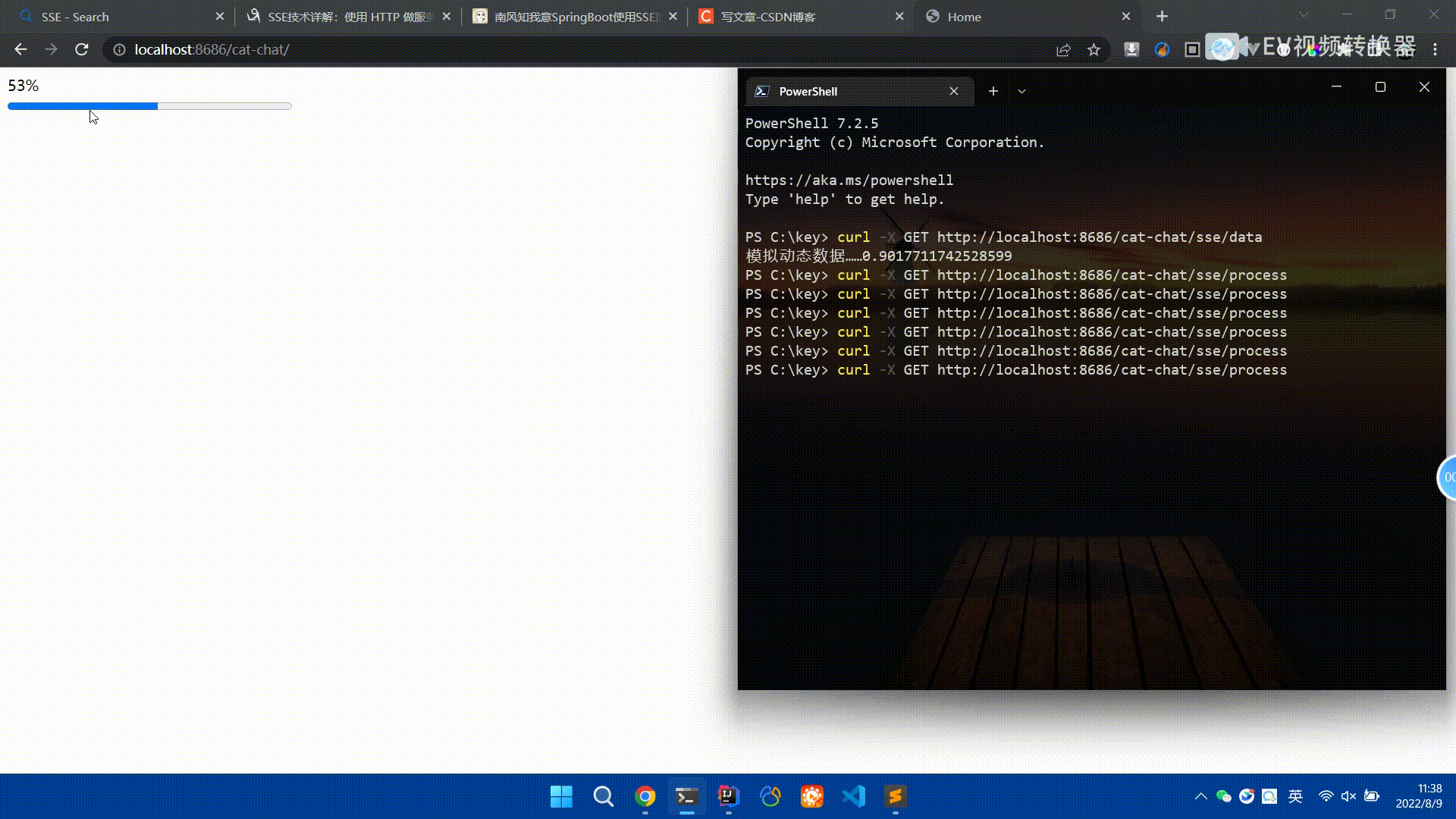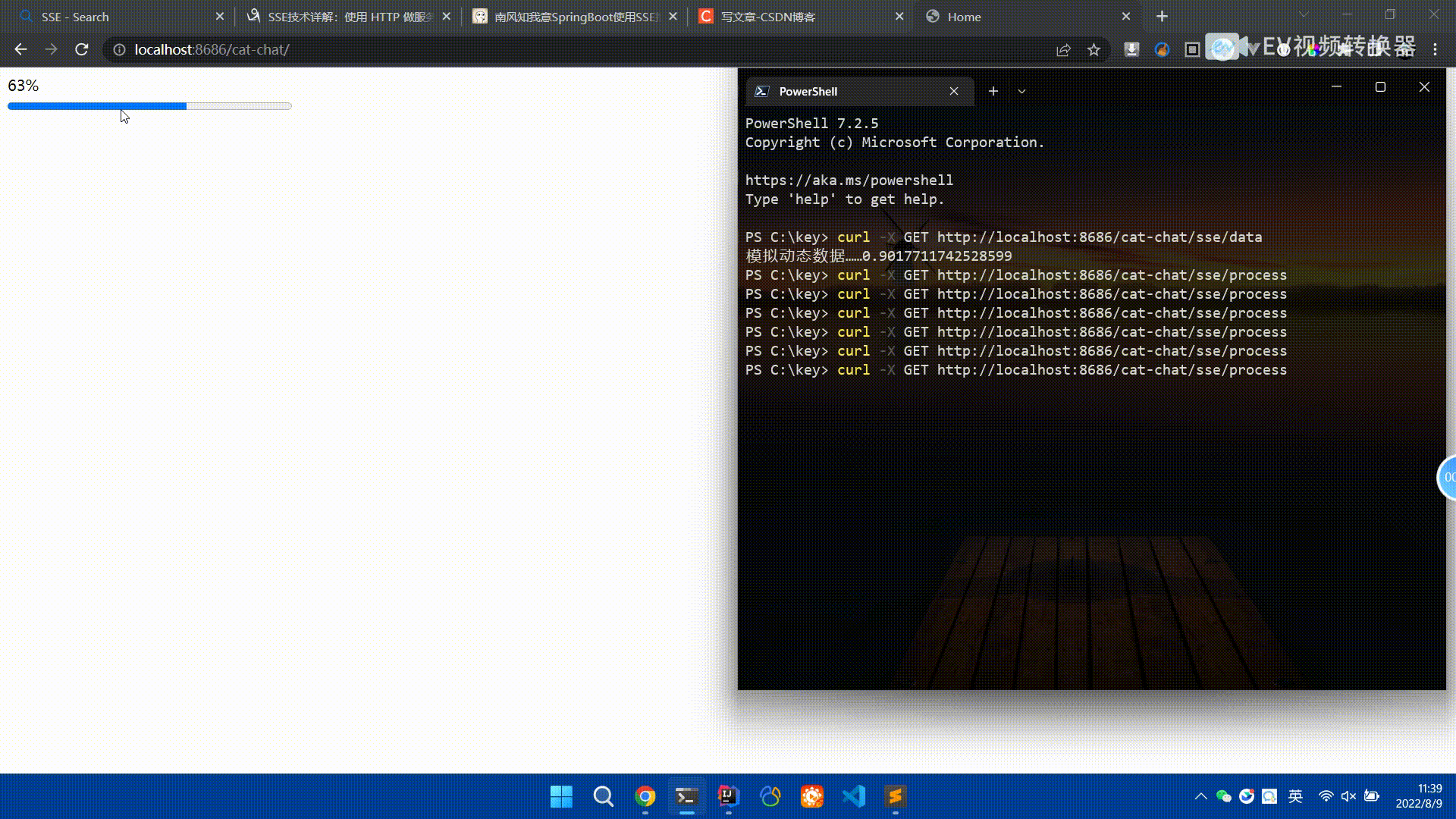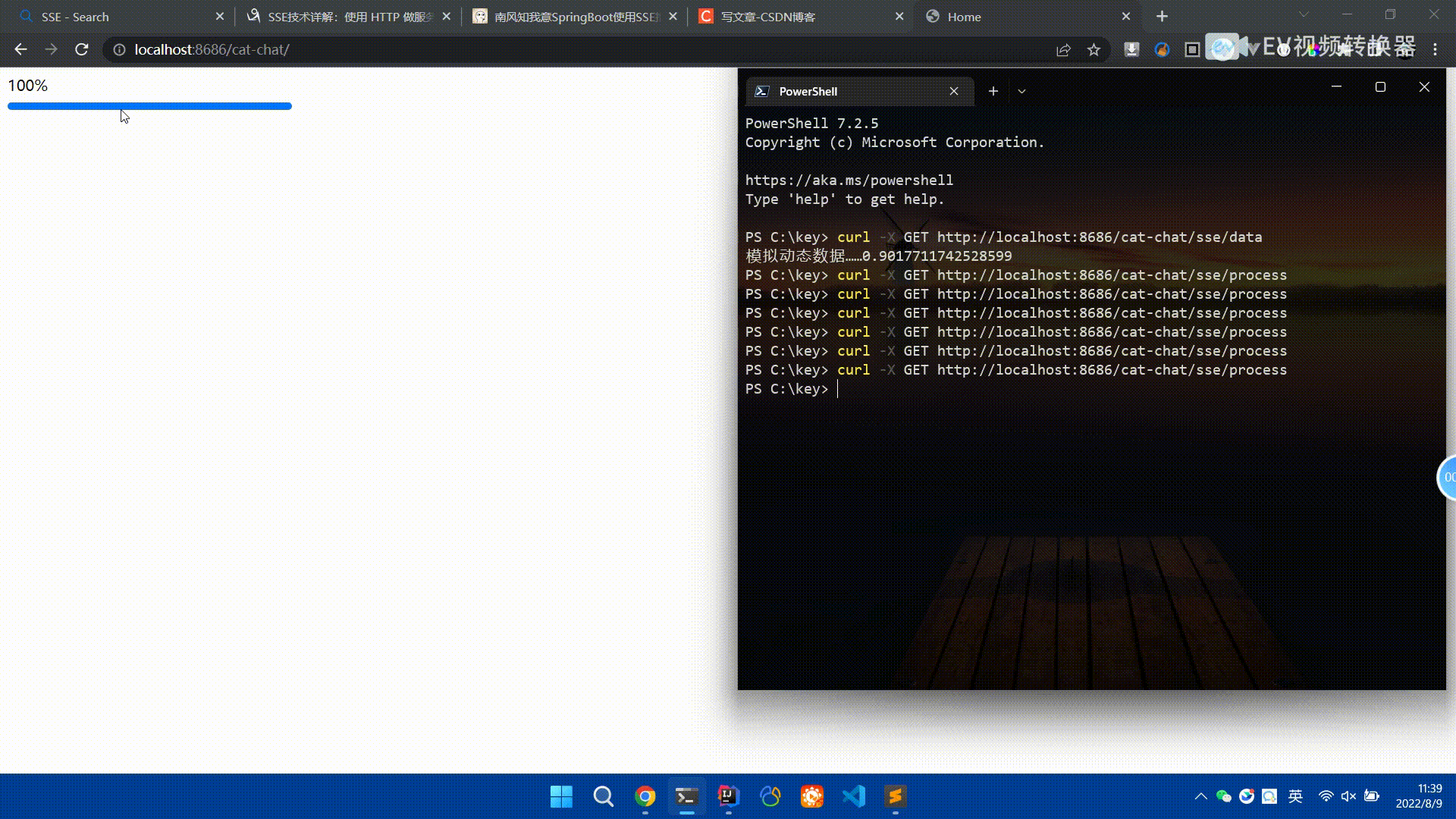 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
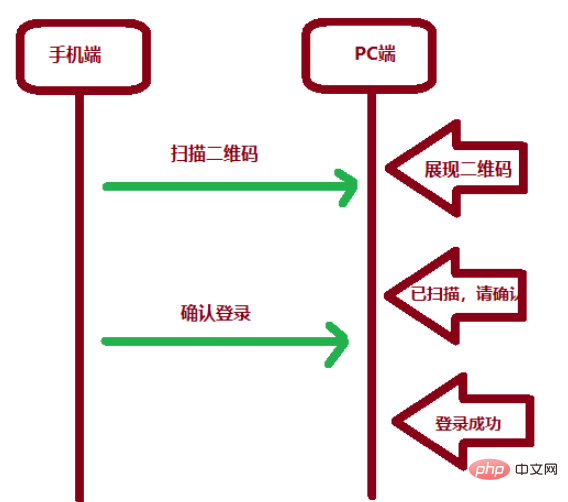 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
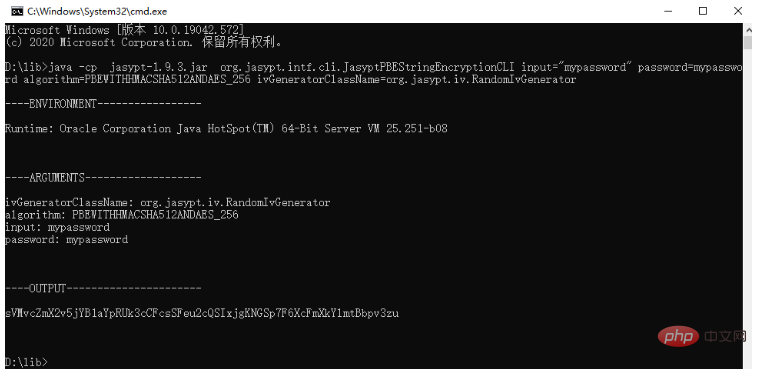 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
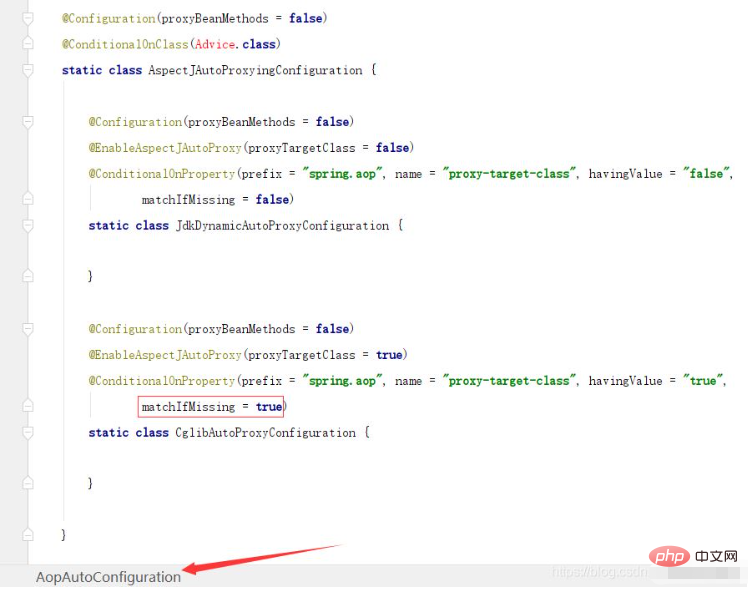 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM
Springboot如何实现视频上传及压缩功能May 10, 2023 pm 05:16 PM一、定义视频上传请求接口publicAjaxResultvideoUploadFile(MultipartFilefile){try{if(null==file||file.isEmpty()){returnAjaxResult.error("文件为空");}StringossFilePrefix=StringUtils.genUUID();StringfileName=ossFilePrefix+"-"+file.getOriginalFilename(


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.







