Preface
In development, when we query the date type in the database, it is often not in the time format we want, such as the following situation:
These dates are related in my database The fields are all set to datatime format:

The data types are as follows:

The entity is configured like this:

Then the default query result is like this:

Help, what kind of format is this, it’s not me at all The desired year, month, day, hour, minute and second.
In fact, it is very simple to solve this problem. It is just that the time format is wrong. Let’s solve this problem through global settings and local settings.
Solve the problem
1 Global settings (recommended)
Generally speaking, for convenience and uniformity, we can set global processing date formatting and configure it in the configuration file
Think of the application configuration file as having properties and There are two formats of yaml. I have prepared the codes required for different formats respectively.
properties format
# 设置全局的日期格式为年月日时分秒 spring.jackson.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss # 世界标准时间,为了方式时差,需要+8小时 spring.jackson.time-zone=GMT+8

yaml format
Of course, the above is the properties format, if you are using the yaml format, then you can Use the following configuration:
spring
jackson:
date-format: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss #设置全局的日期格式为年月日时分秒
time-zone: GMT+8 #世界标准时间,为了方式时差,需要+8小时After adding this configuration item, you can restart the service and access the interface again:
You can find that it is the time format we want, but the time is found It is 8 hours longer than the database.
This is caused by adding the time zone. If the time zone configuration item is added, it will be 8 hours longer than the original time. Therefore, this time zone configuration item depends on personal needs and can be configured. You don’t need to configure it

2 Local settings (not recommended)
Although global configuration is very popular, sometimes we cannot force the global to maintain a unified format , only perform time processing on individual ones
At this time, the role of local settings is reflected. For the convenience of demonstration, I comment out the global settings:

Introducing pom
Local settings require the use of fastjson dependencies, so you need to download the dependencies
<!--fastjson-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.58</version>
</dependency>Add annotations
Add annotations to the fields that require time formatting :
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+8")
It has two parameters:
1: pattern: time format
2: timezone: time zone
The principle is the same as the two parameters of global settings
Here I estimate that I will take out one annotated and one unannotated time attribute for comparison:

Restart the project, test the interface, and compare the two Date format

Of course, like the global configuration, the parameters in the annotation can also be flexibly selected according to your own needs:
For example, I don’t want the time zone here and if you want the format of year, month and day, then just change it directly:

The result will of course be how you configure it:

The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot implements setting global and local time formatting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
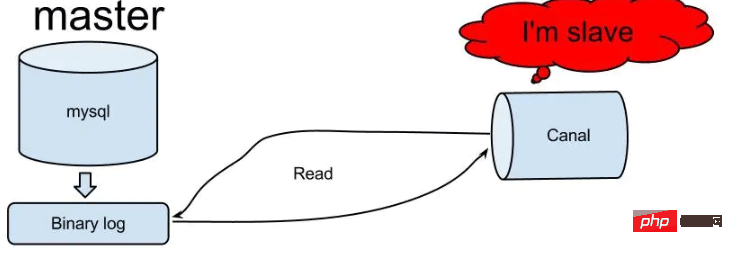 怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PM
怎么使用SpringBoot+Canal实现数据库实时监控May 10, 2023 pm 06:25 PMCanal工作原理Canal模拟MySQLslave的交互协议,伪装自己为MySQLslave,向MySQLmaster发送dump协议MySQLmaster收到dump请求,开始推送binarylog给slave(也就是Canal)Canal解析binarylog对象(原始为byte流)MySQL打开binlog模式在MySQL配置文件my.cnf设置如下信息:[mysqld]#打开binloglog-bin=mysql-bin#选择ROW(行)模式binlog-format=ROW#配置My
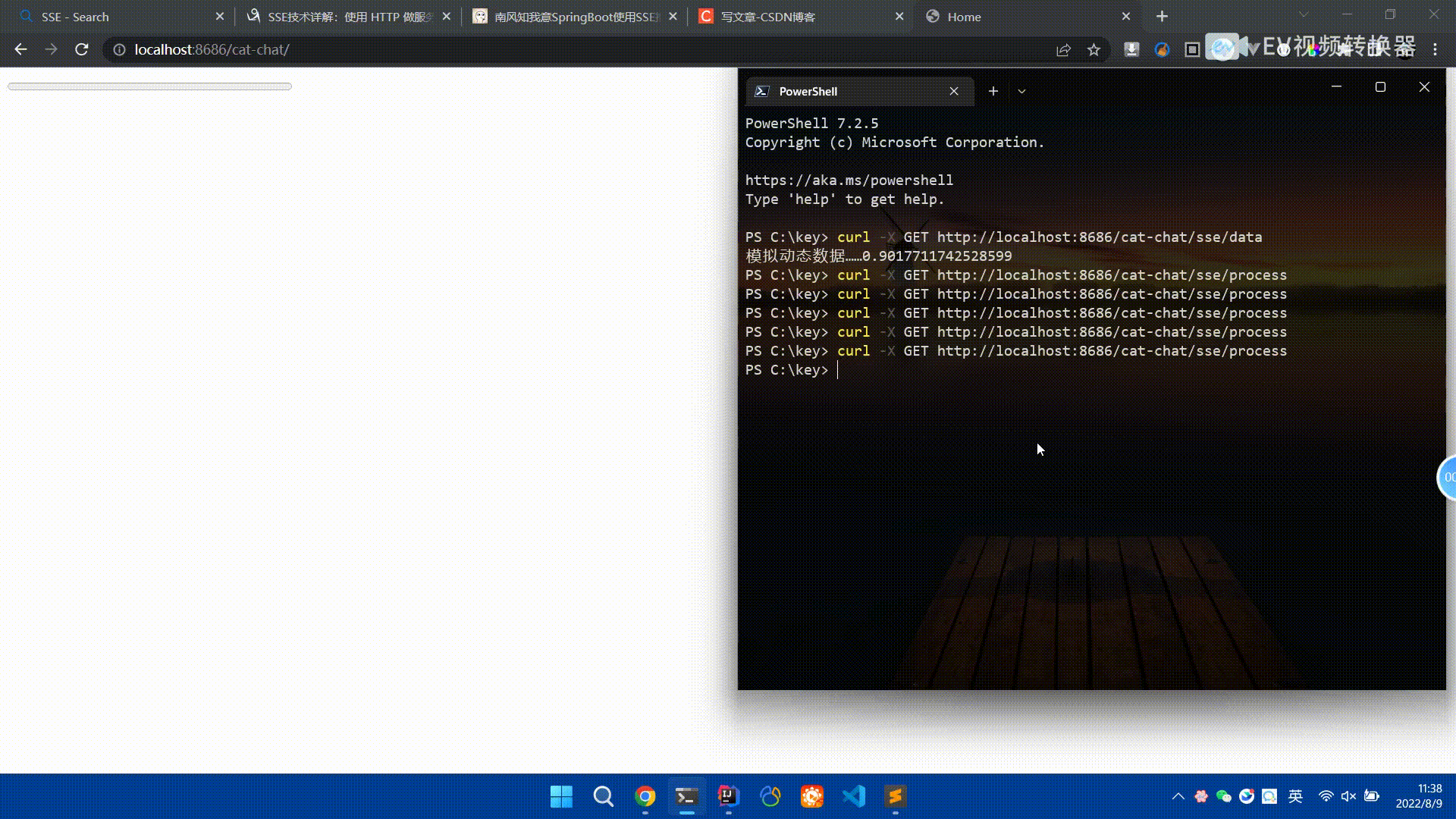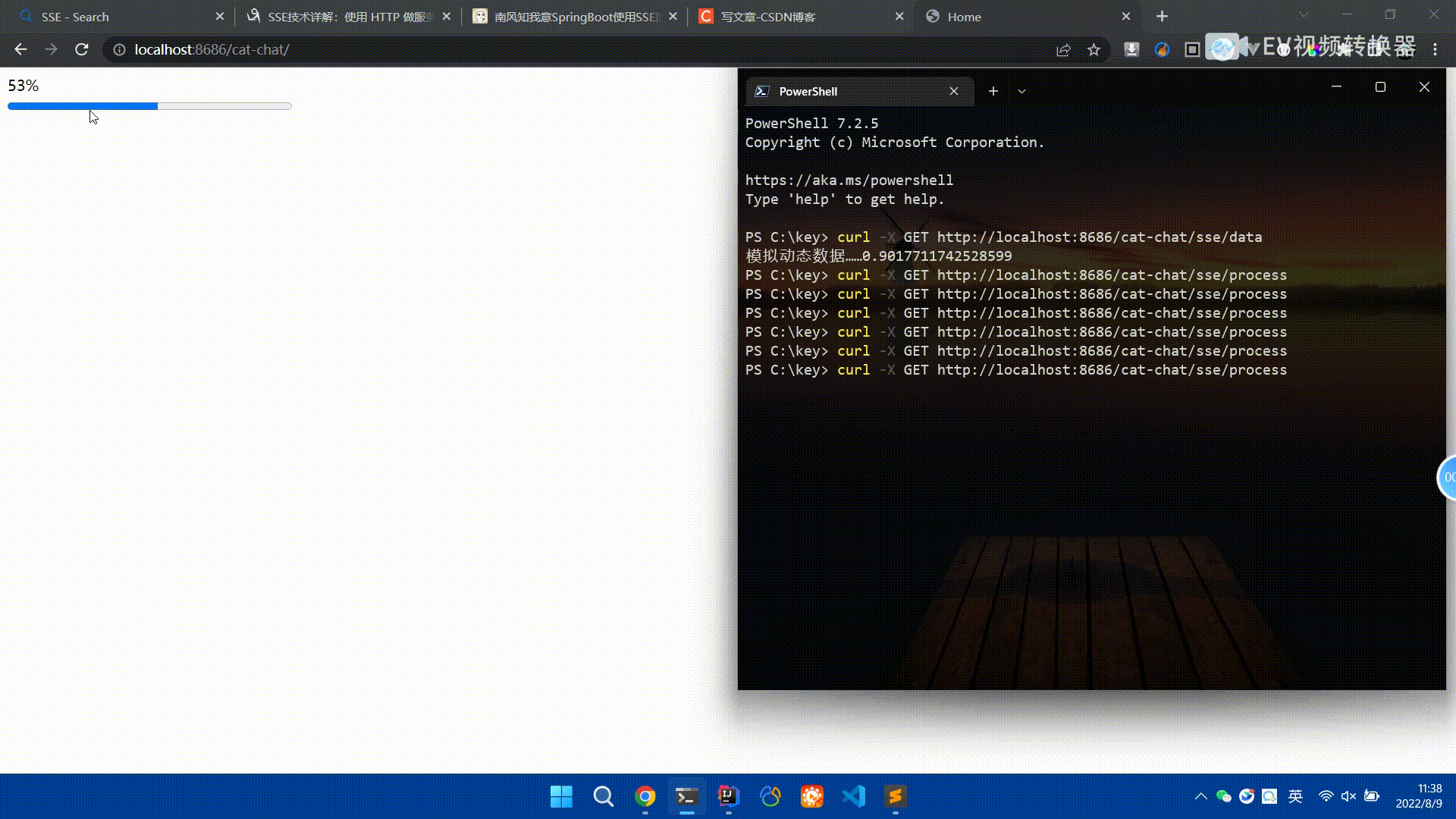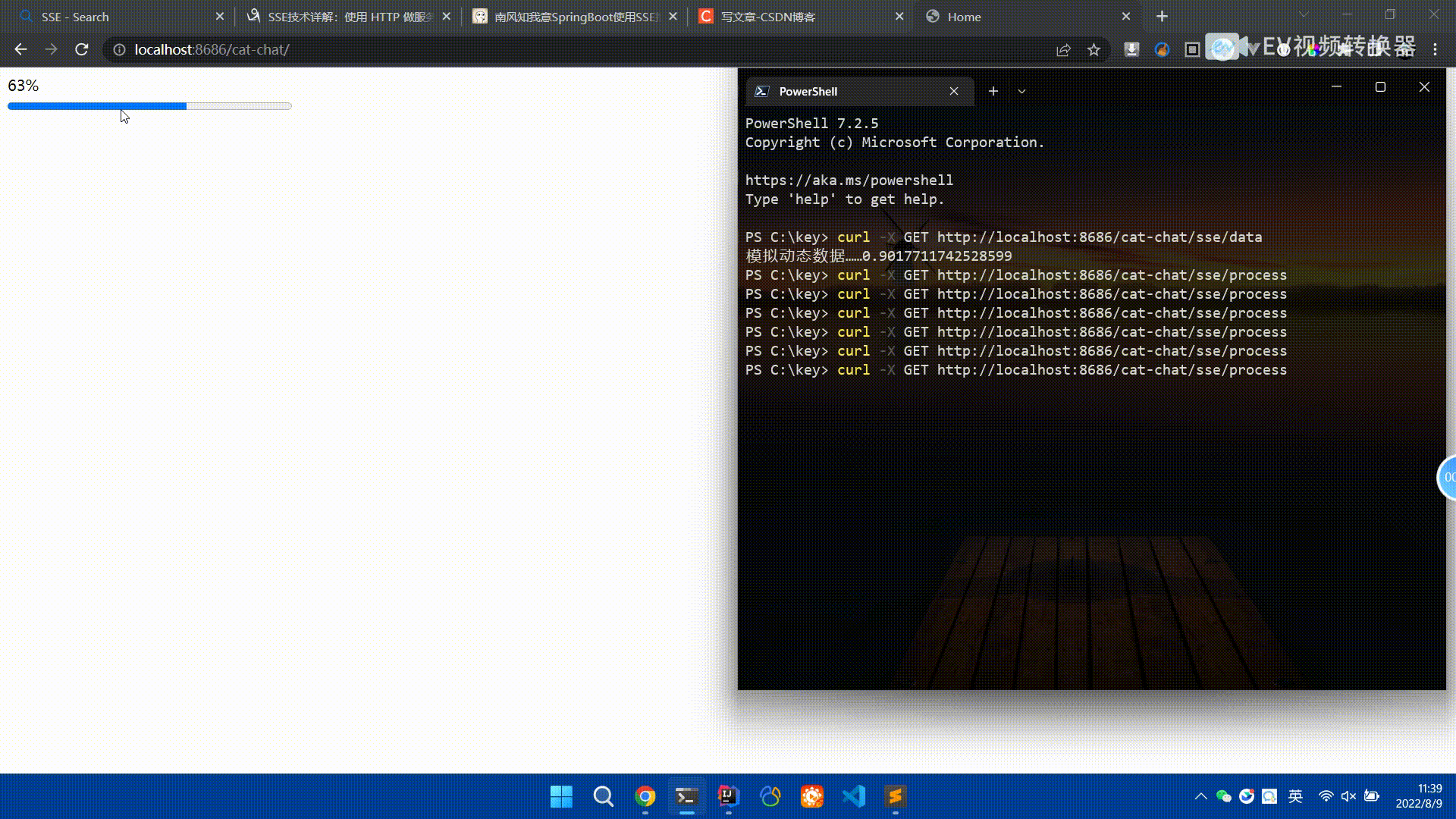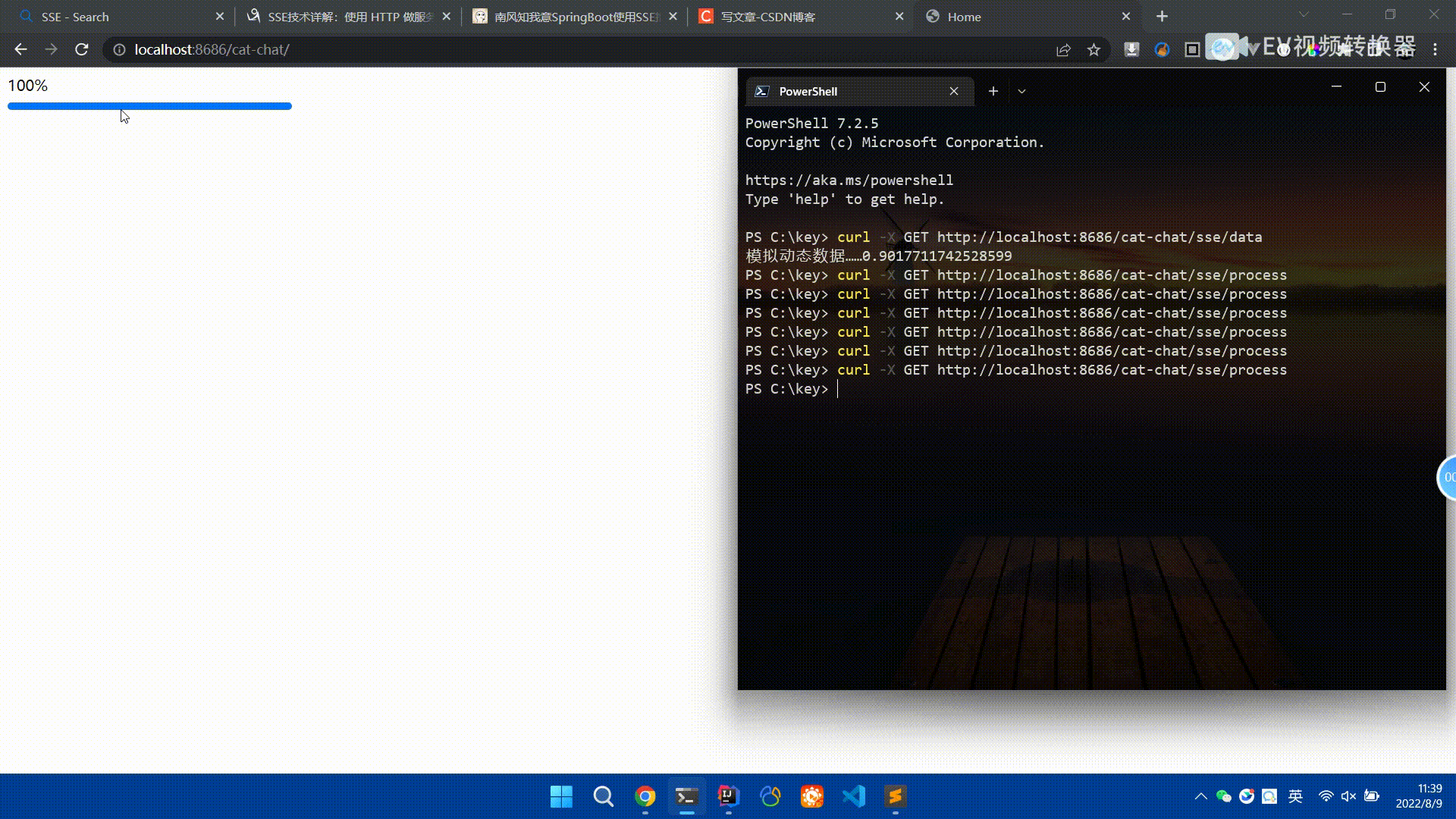 Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM
Spring Boot怎么使用SSE方式向前端推送数据May 10, 2023 pm 05:31 PM前言SSE简单的来说就是服务器主动向前端推送数据的一种技术,它是单向的,也就是说前端是不能向服务器发送数据的。SSE适用于消息推送,监控等只需要服务器推送数据的场景中,下面是使用SpringBoot来实现一个简单的模拟向前端推动进度数据,前端页面接受后展示进度条。服务端在SpringBoot中使用时需要注意,最好使用SpringWeb提供的SseEmitter这个类来进行操作,我在刚开始时使用网上说的将Content-Type设置为text-stream这种方式发现每次前端每次都会重新创建接。最
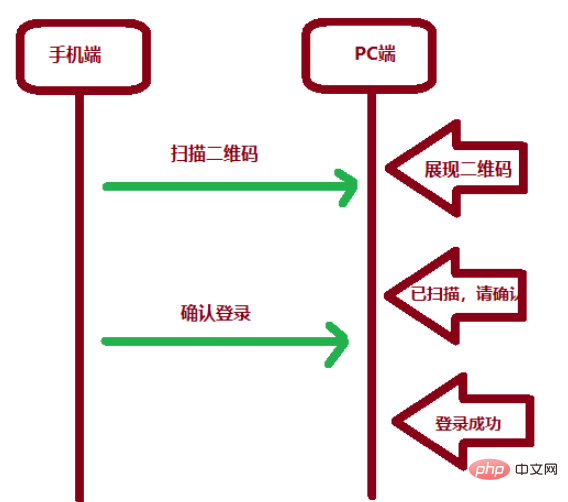 SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM
SpringBoot怎么实现二维码扫码登录May 10, 2023 pm 08:25 PM一、手机扫二维码登录的原理二维码扫码登录是一种基于OAuth3.0协议的授权登录方式。在这种方式下,应用程序不需要获取用户的用户名和密码,只需要获取用户的授权即可。二维码扫码登录主要有以下几个步骤:应用程序生成一个二维码,并将该二维码展示给用户。用户使用扫码工具扫描该二维码,并在授权页面中授权。用户授权后,应用程序会获取一个授权码。应用程序使用该授权码向授权服务器请求访问令牌。授权服务器返回一个访问令牌给应用程序。应用程序使用该访问令牌访问资源服务器。通过以上步骤,二维码扫码登录可以实现用户的快
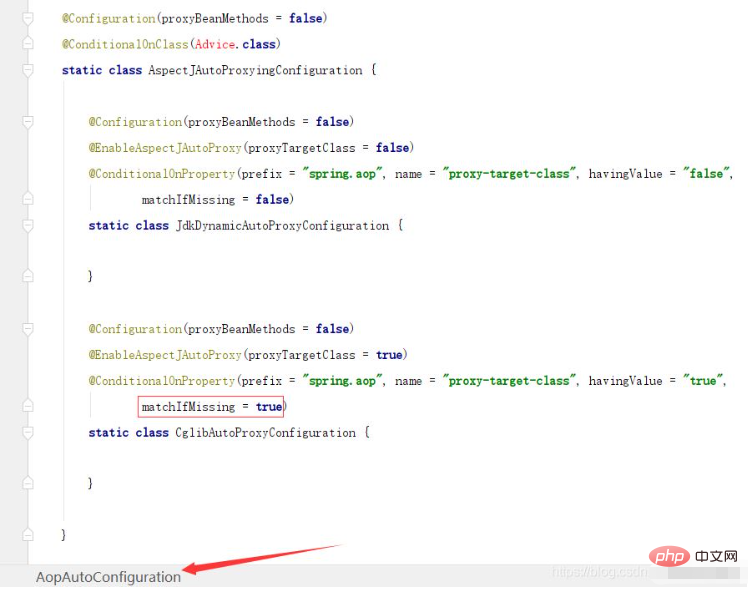 SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
SpringBoot/Spring AOP默认动态代理方式是什么May 10, 2023 pm 03:52 PM1.springboot2.x及以上版本在SpringBoot2.xAOP中会默认使用Cglib来实现,但是Spring5中默认还是使用jdk动态代理。SpringAOP默认使用JDK动态代理,如果对象没有实现接口,则使用CGLIB代理。当然,也可以强制使用CGLIB代理。在SpringBoot中,通过AopAutoConfiguration来自动装配AOP.2.Springboot1.xSpringboot1.xAOP默认还是使用JDK动态代理的3.SpringBoot2.x为何默认使用Cgl
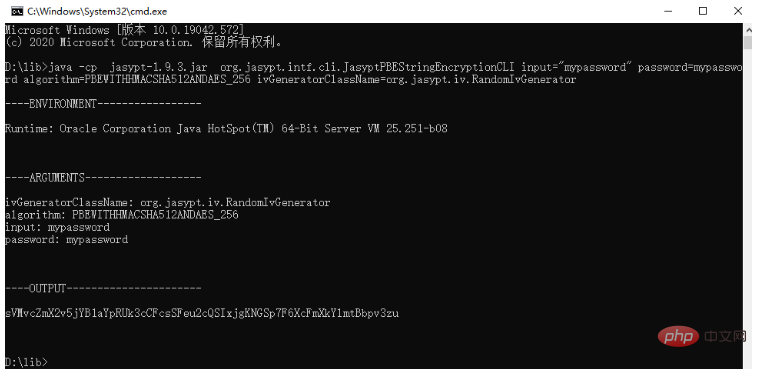 spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM
spring boot怎么对敏感信息进行加解密May 10, 2023 pm 02:46 PM我们使用jasypt最新版本对敏感信息进行加解密。1.在项目pom文件中加入如下依赖:com.github.ulisesbocchiojasypt-spring-boot-starter3.0.32.创建加解密公用类:packagecom.myproject.common.utils;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.PooledPBEStringEncryptor;importorg.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.SimpleStrin
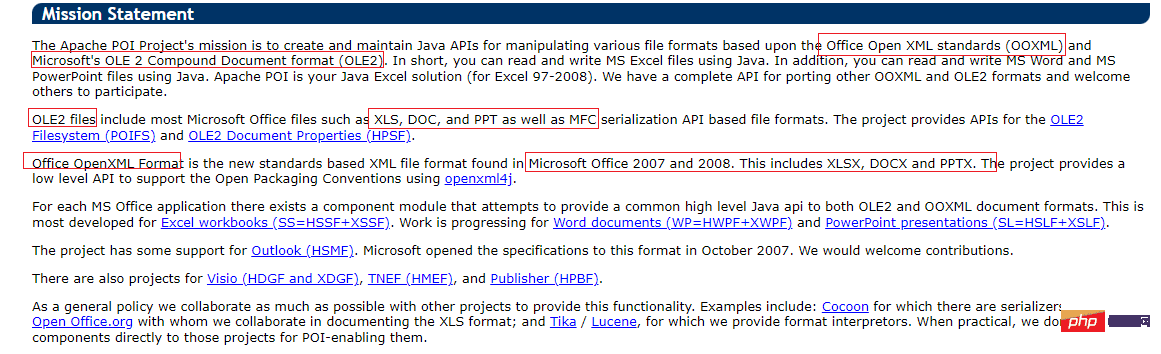 使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM
使用Java SpringBoot集成POI实现Word文档导出Apr 21, 2023 pm 12:19 PM知识准备需要理解ApachePOI遵循的标准(OfficeOpenXML(OOXML)标准和微软的OLE2复合文档格式(OLE2)),这将对应着API的依赖包。什么是POIApachePOI是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的JavaAPI,ApachePOI提供API给Java程序对MicrosoftOffice格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“PoorObfuscationImplementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。ApachePOI是创建和维护操作各种符合Offic
 springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM
springboot怎么整合shiro实现多验证登录功能May 10, 2023 pm 04:19 PM1.首先新建一个shiroConfigshiro的配置类,代码如下:@ConfigurationpublicclassSpringShiroConfig{/***@paramrealms这儿使用接口集合是为了实现多验证登录时使用的*@return*/@BeanpublicSecurityManagersecurityManager(Collectionrealms){DefaultWebSecurityManagersManager=newDefaultWebSecurityManager();
 SpringBoot项目打包发布到外部tomcat遇到的问题怎么解决May 10, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
SpringBoot项目打包发布到外部tomcat遇到的问题怎么解决May 10, 2023 pm 05:49 PM先说遇到问题的情景:初次尝试使用springboot框架写了个小web项目,在IntellijIDEA中能正常启动运行。使用maven运行install,生成war包,发布到本机的tomcat下,出现异常,主要的异常信息是.......LifeCycleException。经各种搜索,找到答案。springboot因为内嵌tomcat容器,所以可以通过打包为jar包的方法将项目发布,但是如何将springboot项目打包成可发布到tomcat中的war包项目呢?1.既然需要打包成war包项目,首


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.







