Home >Java >javaTutorial >What are the characteristics and usage of Java object-oriented
What are the characteristics and usage of Java object-oriented
- PHPzforward
- 2023-05-12 17:58:061268browse
The difference between process-oriented and object-oriented
Process-oriented: When the event is relatively simple, process-oriented is used to focus on the specific steps and processes of the event, and on the specific behaviors in the process. The function is the smallest unit, consider how to do it.
Object-oriented: Focus on finding "participants", encapsulate functions into objects, emphasize objects with functions, use classes/objects as the smallest unit, and consider who will do it.
Case: Xiao Ming takes something from the refrigerator
Process-oriented:
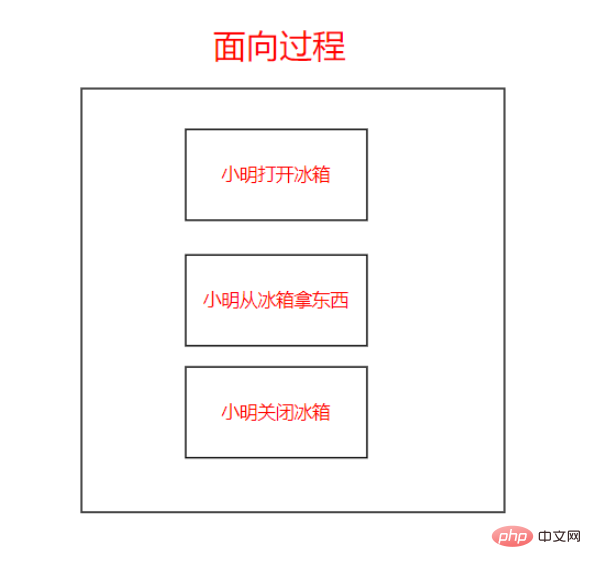
Object-oriented:

Process-oriented —> Object-oriented, in fact, it is a transition from the executor to the commander
The relationship between classes and objects
Everything is an object
Object: specific thing, specific entity, specific instance, specific product under the template
Class: extract the image part upwards from the object, publish the part, and form a class. The class is abstract Yes, it is a template. Generally, when writing code, you first write the class, and then create the corresponding object based on the class.
The class is the abstraction of the object, and the object is the instantiation of the class
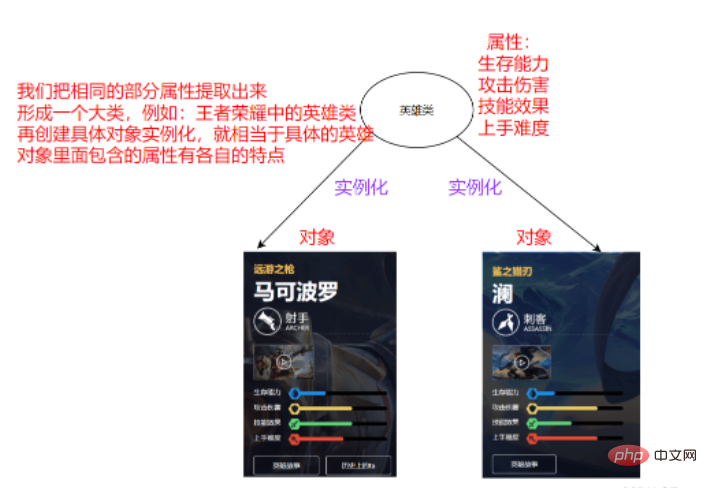
Creation of classes and objects
Creation of classes
1. Attributes (field member variables)
Attributes are used to define the class or the class The data or static characteristics contained in the object. The scope of attributes is the entire class body.
Attribute definition format:
[modifier] attribute type attribute name = [default value];
2. Method
Method is used to define the behavioral characteristics and functional implementation of this class or instance of this class. Methods are abstractions of the behavioral characteristics of classes and objects. Methods are very similar to functions in procedure-oriented programming. In process orientation, function is the most basic unit, and the entire program is composed of function calls. In object-oriented, the basic unit of the entire program is a class, and methods are subordinate to classes and objects.
Method definition format:
[modifier] method return type method name (formal parameter list) {
//Java statement
}
Let’s take the above creation of the King of Glory hero class as an example:
//创建英雄类
public class Hero {
//属性
String Name;//英雄姓名
int Survive;//生存能力
int Attack;//攻击伤害
int Skill;//技能效果
int Difficulty;//上手难度
//技能
public void Kill(int number){
//根据输入的数字释放几技能
System.out.println(Name+"释放"+number+"技能!!!");
}
//输出该英雄的属性
public void print(){
System.out.println("英雄:"+Name);
System.out.println("生存能力:"+Survive);
System.out.println("攻击伤害:"+Attack);
System.out.println("技能效果:"+Skill);
System.out.println("上手难度:"+Difficulty);
}
}Creation of objects
Next we create objects for the classes we created
public class TestCode01 {
//main方法,程序的入口
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个对象(英雄)-->马克波罗
Hero make = new Hero();
make.Name = "马克波罗";
make.Survive = 4;
make.Attack = 6;
make.Skill = 6;
make.Difficulty = 5;
//再创建一个英雄-->澜
Hero lan = new Hero();
lan.Name = "澜";
lan.Survive = 3;
lan.Attack = 5;
lan.Skill = 4;
lan.Difficulty = 6;
lan.Kill(1);
//输出两个英雄的属性
make.print();
System.out.println("-------------");
lan.print();
//释放技能
make.Kill(3);
System.out.println("-------------");
lan.Kill(2);
}
}Result: Each hero has the same attributes, and each attribute has different values. Through classes, we can create many objects, and each object has different attribute values.
For example: There are more than a hundred heroes in The King, each with different characteristics.
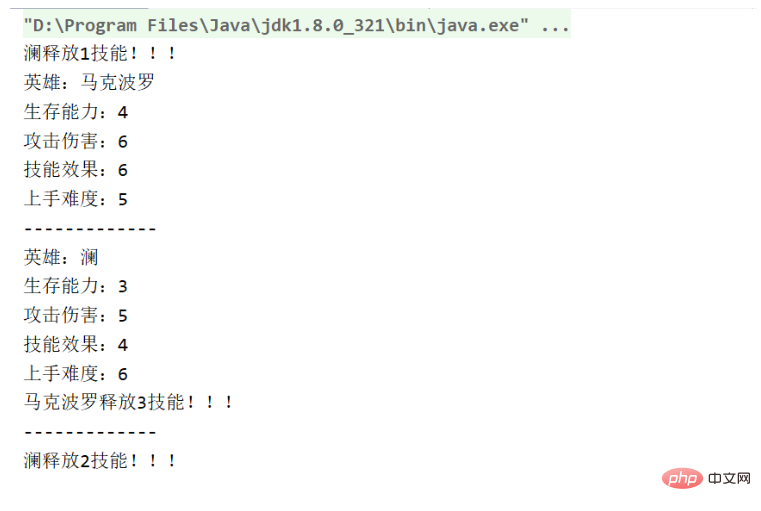
The process of creating an object:
(1) When encountering a class for the first time, the class must be loaded, and only loaded once .
(2) Create an object and open up space in the heap
(3) Initialize the object, and attribute assignments are all default initial values.
(4) The new keyword calls the constructor, executes the construction method, and reassigns the properties in the constructor
Constructor
Objects are all new. The new keyword is actually calling a method, which is called a constructor (constructor)
When calling the constructor, if there is no constructor written in your class, the system will assign a constructor to you by default Constructor (empty constructor)
Constructor method format:
[modifier] Constructor name () {
}
The difference between constructors and methods:
There is no return value of the method
There cannot be a return statement inside the method body
The name of the constructor is very special and must be consistent with the class name
The role of the constructor: not to create an object, because before the constructor is called, the object It has been created and the properties have default initialized values.
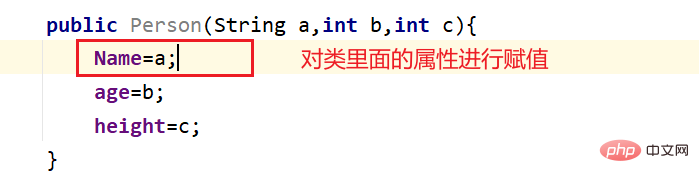
The purpose of calling the constructor is to assign values to properties.
Note: We generally do not initialize in an empty constructor, because then the properties of each object will be the same.
The following example:
class Hero{
//属性
String Name;//英雄姓名
int Survive;//生存能力
int Attack;//攻击伤害
int Skill;//技能效果
int Difficulty;//上手难度
public Hero(){
Survive=4;
Attack=5;
Skill=6;
Difficulty=7;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("英雄:"+Name);
System.out.println("生存能力:"+Survive);
System.out.println("攻击伤害:"+Attack);
System.out.println("技能效果:"+Skill);
System.out.println("上手难度:"+Difficulty);
}
}
public class TestCode01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建两个英雄对象
Hero make = new Hero();
make.Name="马克";
Hero lan=new Hero();
lan.Name="澜";
//输出两个属性
make.print();
lan.print();
}
}Because we assigned the value in the constructor, the properties will be the same when we create the object

In fact, we only need to ensure the existence of the empty constructor. There is no need to write the contents inside. If we want to use the constructor to assign values, we must overload the constructor
Constructor overloading
Generally, the existence of an empty constructor is guaranteed. In an empty constructor, attribute assignment operations are generally not performed.

Generally, we will overload the constructor. In the overloaded constructor Perform attribute assignment operations
在重载构造器以后,假如空构造器忘写了,系统也不会给你分配默认的空构造器了,那么你要调用的话就会出错了。所以我们重载构造器时,一般要保留默认构造器
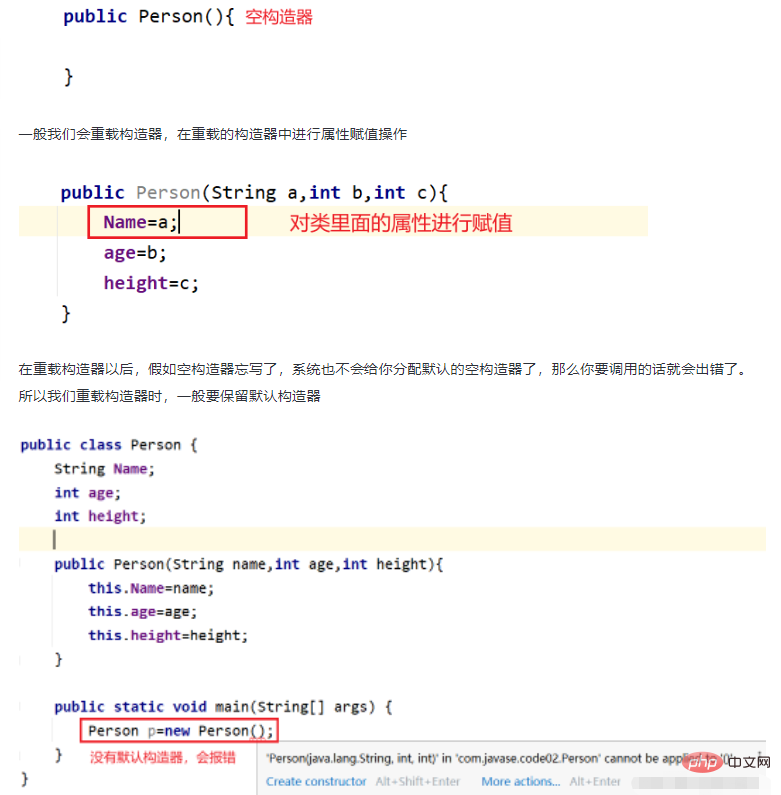
当形参名字和属性名字重名的时候,会出现就近原则:在要表示对象的属性前加上this.来修饰 ,因为this代表的就是你创建的那个对象
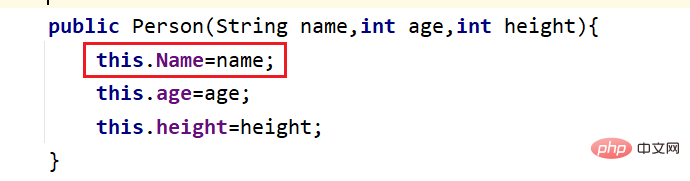
this的使用
this就是指当前的对象
this可以修饰属性
当属性名字和形参发生重名的时候,或者 属性名字 和局部变量重名的时候,都会发生就近原则,所以如果我要是直接使用变量名字的话就指的是离的近的那个形参或者局部变量,这时候如果我想要表示属性的话,在前面要加上:this.修饰(如果不发生重名问题的话,实际上你要是访问属性也可以省略this.)

this修饰方法
在同一个类中,方法可以互相调用,this.可以省略不写。

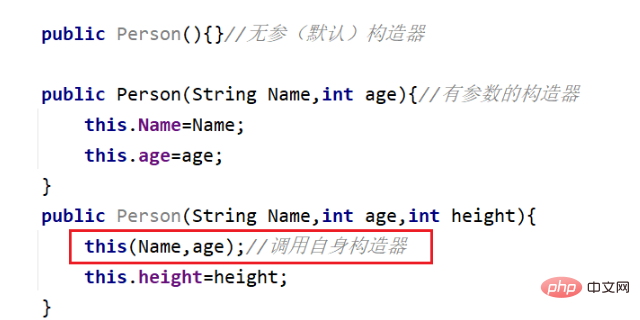
this可以修饰构造器
同一个类中的构造器可以相互用this调用,注意:this修饰构造器必须放在第一行
static修饰
static可以修饰:属性、方法、代码块、内部类
static修饰属性
在类加载的时候,会将静态内容也加载到方法区的静态域中,静态的内容先于对象存在,并且这个静态内容被所有该类的对象共享。
在类加载的时候一起加载入方法区中的静态域中
先于对象存在
访问方式: 对象名.属性名 类名.属性名(推荐)

static修饰属性的应用场景:某些特定的数据想要在内存中共享,只有一块 -->这个情况下,就可以用static修饰的属性。
static修饰方法:
static和public都是修饰符,并列的没有先后顺序,先写谁后写谁都行
在静态方法中不能使用this关键字
在静态方法中不能访问非静态的方法
在静态方法中不能访问非静态的属性
静态的方法可以用 对象名.方法名去调用 也可以 用 类名.方法名 (推荐)
在同一个类中可以直接调用静态方法
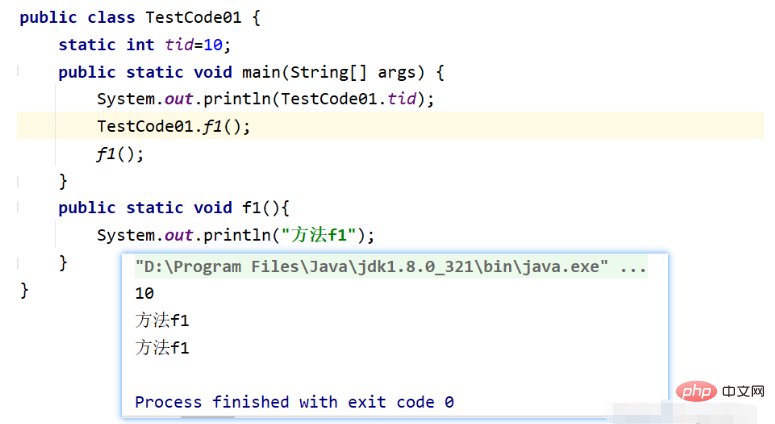
代码块
代码块的分类: 普通块、构造块、静态块、同步块(多线程)
代码块执行顺序: 最先执行静态块–>再执行构造块,(不常用)–>再执行构造器–>再执行方法中的普通块
public class Test {
//属性
int a;
static int sa;
//方法
public void a(){
System.out.println("-----a");
{
//普通块限制了局部变量的作用范围
System.out.println("这是普通块");
System.out.println("----000000");
int num = 10;
System.out.println(num);
}
}
public static void b(){
System.out.println("------b");
}
//构造块
{
System.out.println("------这是构造块");
}
//静态块
static{
System.out.println("-----这是静态块");
//在静态块中只能方法:静态属性,静态方法
System.out.println(sa);
b();
}
//构造器
public Test(){
System.out.println("这是空构造器");
}
public Test(int a){
this.a = a;
}
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test t = new Test();
t.a();
Test t2 = new Test();
t2.a();
}
}包(import)
包的作用: 为了解决重名的作用,解决权限问题
包名的定义:
名字全部小写
中间用.隔开
一般都是公司域名倒着写:com.jd 、com.taobao
加上模块名字 :com.taobao.login
不能使用系统中的关键字:null
包声明的位置一般都在非注释代码的第一行
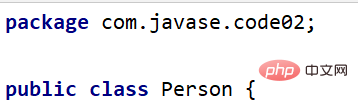
导包:
(1)使用不同包下的类要需要导包, 例如:import java.util.Date;
(2)在导包以后,还想用其他包下同名的类,就必须要手动自己写所在的包。
(3)同一个包下的类想使用不需要导包,可以直接使用。
(4)在java.lang包下的类,可以直接使用无需导包
(5)可以直接导入*:
静态导入:
//静态导入:
import static java.lang.Math.*;
//导入:java.lang下的Math类中的所有静态的内容
public class Test {
//这是一个main方法,是程序的入口:
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(random());
System.out.println(PI);
System.out.println(round(5.6));
}
//在静态导入后,同一个类中有相同的方法的时候,会优先走自己定义的方法。
public static int round(double a){
return 1000;
}
}The above is the detailed content of What are the characteristics and usage of Java object-oriented. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Can Reflection Reveal Generic Parameter Types in Java?
- How Can I Efficiently Remove Whitespace from a String in Java?
- How Do Ellipses (...) Function in Java Method Signatures (e.g., Varargs)?
- How Can I Generate and Handle RepaintManager Exceptions in Java Swing?
- Why are Key Bindings a Superior Alternative to KeyListeners for User Input?

