Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >What are the ways to use Python queues?
What are the ways to use Python queues?
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-12 14:19:191638browse
There are roughly three queue modules used in python:
1. from queue import Queue
This module is suitable for inter-thread communication, but cannot be used for inter-process communication.
Sample code 1: [Note: There is an error in the code at this time! ! ! 】
import time
import threading
from queue import Queue
def task_func():
global queue
while queue.qsize() > 0:
x = queue.get()
print(f"num: {x}")
time.sleep(0.1)
def producer_data():
global queue
for i in range(100):
queue.put(i)
time.sleep(0.1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = Queue()
producer_thread = threading.Thread(target=producer_data)
producer_thread.start()
thread_list = []
for i in range(5):
thread = threading.Thread(target=task_func)
thread.start()
thread_list.append(thread)
for thread in thread_list:
thread.join()
print("主程序执行结束!")Note: How to write the above:
while queue.qsize() > 0:
x = queue.get()When the producer speed is not as fast as the consumer speed, the above consumer code will end early, resulting in the producer speed Cannot be consumed.
while True:
x = queue.get()There are also problems with this way of writing. At this time, the consumer queue will always monitor whether the producer queue has data, causing the thread to be blocked all the time, and the program will be blocked and will not stop, which is a serious waste of system resources. If you use a scheduled task library such as apscheduler, the scheduled task will not be started.
In fact, the timeout parameter is provided in the put() or get() method in the queue queue. Using this parameter can effectively solve the above-mentioned problems of inability to consume and thread blocking.
Sample code 2:
import time
import threading
from queue import Queue
def task_func():
global queue
while True:
x = queue.get(timeout=10)
print(f"num: {x}")
def producer_data():
global queue
for i in range(100):
queue.put(i)
time.sleep(0.1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
queue = Queue()
producer_thread = threading.Thread(target=producer_data)
producer_thread.start()
thread_list = []
for i in range(5):
thread = threading.Thread(target=task_func)
thread.start()
thread_list.append(thread)
for thread in thread_list:
thread.join()
print("主程序执行结束!")Running result:

According to different situations, the value of timeout can be set according to the actual situation. If you use a scheduled task, it is okay to use timeout, and the program will not stop throwing an exception.
2. from multiprocessing import Queue
This module is used for processes, but cannot be used for process pools
Sample code:
import time
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import queue
def producer(queue):
queue.put("a")
time.sleep(2)
def consumer(queue):
time.sleep(2)
data = queue.get()
print(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# queue = queue.Queue()
queue = Queue()
my_producer = Process(target=producer, args=(queue, ))
my_consumer = Process(target=consumer, args=(queue, ))
my_producer.start()
my_consumer.start()
my_producer.join()
my_consumer.join()
# 使用queue模块的Queue()会报错
# 使用multiprocessing中的Queue(),正确输出aRunning results:
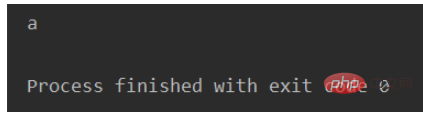
3. from multiprocessing import Manager
Sample code:
import time
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue, Pool, Manager
def producer(queue):
queue.put("a")
time.sleep(2)
def consumer(queue):
time.sleep(2)
data = queue.get()
print(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# queue = Queue()
queue = Manager().Queue()
pool = Pool()
# pool中的进程间通信需要使用Manager
pool.apply_async(producer, args=(queue, ))
pool.apply_async(consumer, args=(queue, ))
pool.close()
pool.join()Running results:
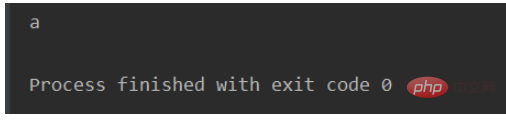
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to use Python queues?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

