Introduction
There is another algorithm for constructing a minimum spanning tree, namely the Kruskal algorithm: Let the graph G=(V, E) be an undirected connected weighted graph, V={1,2,... n}; Suppose the minimum spanning tree T=(V, TE). The initial state of the tree has only n nodes and a non-connected graph with no edges T=(V, {}). Kruskal's algorithm treats these n nodes as n Isolated connected branches. It first sorts all the edges according to their weights from small to large, and then if the number of edges to be selected in T is less than n-1, it makes a greedy selection like this: select the edge (i,j) with the smallest weight in the edge set E ), if adding edge (i, j) to the set TE does not produce a cycle, then add edge (i, j) to the edge set TE, that is, use edge (i, j) to merge the two branches into a connected branch ; Otherwise, continue to select the next shortest edge. Delete the edge (i, j) from the set E and continue the greedy selection above until all nodes in T are on the same connected branch. At this time, the selected n-1 edges exactly constitute a minimum spanning tree T of the graph G.
Kruskal's algorithm uses a very smart method, which is to use sets to avoid circles; if the starting point and end point of the selected edge to join are both in the T set, it can be concluded that a loop will be formed, and the two changed nodes cannot Belong to the same collection.
Algorithm steps
1 Initialization. Sort all edges in ascending order of weight, and initialize each node set number to its own number.
2 Select the edge (u, v) with the smallest weight in the sorted order.
3 If nodes u and v belong to two different connected branches, add edge (u, v) to the edge set TE and merge the two connected branches.
4 If the number of selected edges is less than n-1, go to step 2, otherwise the algorithm ends.
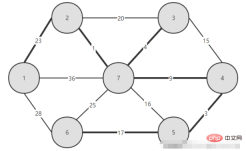
1. Picture after construction
2. Code
package graph.kruskal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Kruskal {
static final int N = 100;
static int fa[] = new int[N];
static int n;
static int m;
static Edge e[] = new Edge[N * N];
static List<Edge> edgeList = new ArrayList();
static {
for (int i = 0; i < e.length; i++) {
e[i] = new Edge();
}
}
// 初始化集合号为自身
static void Init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fa[i] = i;
}
// 合并
static int Merge(int a, int b) {
int p = fa[a];
int q = fa[b];
if (p == q) return 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 检查所有结点,把集合号是 q 的改为 p
if (fa[i] == q)
fa[i] = p; // a 的集合号赋值给 b 集合号
}
return 1;
}
// 求最小生成树
static int Kruskal(int n) {
int ans = 0;
Collections.sort(edgeList);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
if (Merge(edgeList.get(i).u, edgeList.get(i).v) == 1) {
ans += edgeList.get(i).w;
n--;
if (n == 1)//n-1次合并算法结束
return ans;
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
m = scanner.nextInt();
Init(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
e[i].u = scanner.nextInt();
e[i].v = scanner.nextInt();
e[i].w = scanner.nextInt();
edgeList.add(e[i]);
}
System.out.println("最小的花费是:" + Kruskal(n));
}
}
class Edge implements Comparable {
int u;
int w;
int v;
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (this.w > ((Edge) o).w) {
return 1;
} else if (this.w == ((Edge) o).w) {
return 0;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}3. Test
Green is input, White is the output.

The above is the detailed content of How to implement Kruskal algorithm in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PMThe article discusses using Maven and Gradle for Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution, comparing their approaches and optimization strategies.
 How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PMThe article discusses creating and using custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management, using tools like Maven and Gradle.
 How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PMThe article discusses implementing multi-level caching in Java using Caffeine and Guava Cache to enhance application performance. It covers setup, integration, and performance benefits, along with configuration and eviction policy management best pra
 How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PMThe article discusses using JPA for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading. It covers setup, entity mapping, and best practices for optimizing performance while highlighting potential pitfalls.[159 characters]
 How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PMJava's classloading involves loading, linking, and initializing classes using a hierarchical system with Bootstrap, Extension, and Application classloaders. The parent delegation model ensures core classes are loaded first, affecting custom class loa


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function






