Home >Java >javaTutorial >How SpringBoot2.0 implements remote invocation of RPC services
How SpringBoot2.0 implements remote invocation of RPC services
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-11 20:22:041402browse
1. Introduction to Dubbo framework
1.Framework dependencies
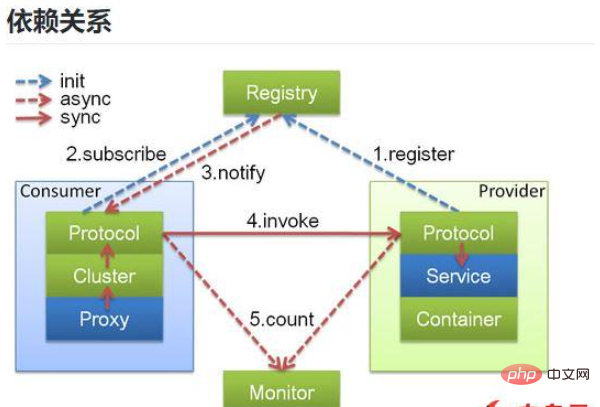
Legend description:
1) The small boxes in the figure, Protocol, Cluster, Proxy, Service, Container, Registry, and Monitor, represent layers or modules. The blue ones indicate interactions with the business, and the green ones only interact within Dubbo.
2) The background squares Consumer, Provider, Registry, and Monitor in the figure represent the deployment logical topology nodes.
3) The blue dotted line in the figure is called during initialization, the red dotted line is asynchronous call during runtime, and the red solid line is synchronously called at runtime.
4) The figure only contains the RPC layer, not the Remoting layer. Remoting as a whole is implicit in the Protocol.
2. Core role description
1) Provider is the service provider that exposes the service
2) Consumer calls the service consumer (load) of the remote service Balance)
3) Registry service registration and discovery registration center (monitoring, heartbeat, kick-out, re-entry)
4) Monitor service consumer and provider cumulative call times in memory and calling time, proactively sending statistical data to the monitoring center every minute.
5) Container service running container: remote calling, serialization
2. Integration with SpringBoot2.0
1. Core dependencies
<!-- 这里包含了Zookeeper依赖和Dubbo依赖 --> <dependency> <groupid>com.alibaba.boot</groupid> <artifactid>dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactid> <version>0.2.0</version> </dependency>
2. Project structure description
Structural description
dubbo-consume:服务消费方 dubbo-provider:服务提供方 dubbo-common:公共代码块,Dubbo接口,实体类
3. Core configuration
1 ) Provider configuration
server: tomcat: uri-encoding: UTF-8 max-threads: 1000 min-spare-threads: 30 port: 7007 connection-timeout: 5000ms spring: application: name: block-dubbo-provider # Dubbo 配置文件 dubbo: application: name: block-dubbo-provider registry: address: 127.0.0.1:2181 protocol: zookeeper protocol: name: dubbo port: 20880 scan: base-packages: com.boot.consume
2) Consumer configuration
server: tomcat: uri-encoding: UTF-8 max-threads: 1000 min-spare-threads: 30 port: 7008 connection-timeout: 5000ms spring: application: name: block-dubbo-consume # Dubbo 配置文件 dubbo: application: name: block-dubbo-consume registry: address: 127.0.0.1:2181 protocol: zookeeper
3. Demonstration case
1. Service remote invocation
1) Provider service interface
Note the annotation here com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service
@Service
@Component
public class DubboServiceImpl implements DubboService {
private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DubboServiceImpl.class) ;
@Override
public String getInfo(String param) {
LOGGER.info("字符参数:{}",param);
return "[Hello,Cicada]";
}
@Override
public UserEntity getUserInfo(UserEntity userEntity) {
LOGGER.info("实体类参数:{}",userEntity);
return userEntity;
}
}
2) Consumer interface
Note the annotations here
com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Referenceorg.springframework.stereotype.Service
@Service
public class ConsumeService implements DubboService {
@Reference
private DubboService dubboService ;
@Override
public String getInfo(String param) {
return dubboService.getInfo(param);
}
@Override
public UserEntity getUserInfo(UserEntity userEntity) {
return dubboService.getUserInfo(userEntity);
}
}
2 , Interface timeout configuration
This configuration can be configured on the service provider or the service consumer. Here is a demonstration of the configuration on the provider. Note: timeout 1) Service interface annotation
@Service(timeout = 2000)
@Component
public class DubboServiceImpl implements DubboService {
}
2) Consumer call
@Override
public String timeOut(Integer time) {
return dubboService.timeOut(time);
}
3) Test interface
Service timeout throws exception
com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.TimeoutException
3. Interface multi-version configuration
1) Service provider
Provides two versions of the same interface. Note: version.
Version one:
@Service(version = "1.0.0")
@Component
public class VersionOneImpl implements VersionService {
@Override
public String getVersion() {
return "{当前版本:1.0.0}";
}
}
Version two:
@Service(version = "2.0.0")
@Component
public class VersionTwoImpl implements VersionService {
@Override
public String getVersion() {
return "{当前版本:2.0.0}";
}
}
2) The consumer calls
through the @Reference(version) annotation, which will point to different versions. Interface implementation.
@Service
public class VersionServiceImpl implements VersionService {
@Reference(version = "1.0.0")
private VersionService versionService1 ;
@Reference(version = "2.0.0")
private VersionService versionService2 ;
@Override
public String getVersion() {
return versionService1.getVersion();
}
public String version2 (){
return versionService2.getVersion() ;
}
}The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot2.0 implements remote invocation of RPC services. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Why is my Android App Throwing \'java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver\' When Connecting to MySQL?
- What is the difference between Java System Properties and Environment Variables?
- What\'s the Key Difference Between Stream.map() and Stream.flatMap() in Java 8?
- Why Did Java and C# Choose to Avoid Multiple Inheritance?
- How to Communicate Between a Fragment and its Adapter Using an Interface?

