First summarize the difference between the two:
1. watch is executed lazily, but watchEffect is not. Regardless of the configuration of the third parameter of watch, watch is executed when the component is first executed. It will not be executed. It will only be executed when the dependencies change later. WatchEffect is executed immediately when the program is executed here, and then executed in response to its dependency changes.
2. The two are used in different ways. Watch generally passes in two parameters. The first parameter indicates what state should trigger the listener to rerun. The second parameter defines the listener callback function. And the callback function can also accept two parameters, pointing to the values before and after the state changes, so that we can see the changes before and after the state, but we cannot see it in watchEffect, and we cannot be more specific in the first parameter like watch. Define dependencies.
3. Watch can only monitor the values defined by reactive data and ref. If you want to monitor a single value, you need to pass the getter function of the corresponding value. However, watchEffect cannot monitor the values defined by reactive and ref. It can only monitor the values defined by reactive and ref. It can monitor its corresponding specific value (it feels a bit convoluted, see the code below).
The following are some small experiments based on the third point above:
watch:
1. Let watch and watchEffect monitor the value defined by reactive:
watch:
setup() {
const state = reactive({ count: 0, attr: { name: "" } });
watch(state, (post, pre) => {
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
console.log("watch 执行了");
});
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}When the clickEvent event is triggered to change the value of state.count, we can see the following results from the console, indicating that watch responded to the change in state.count, but did not do so initially. implement.

watchEffect:
setup() {
const state = reactive({ count: 0, attr: { name: "" } });
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("watchEffect 执行了");
console.log(state);
});
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}Click the button multiple times to trigger the clickEvent event. The console results are as follows, indicating that watchEffect executed the callback when the component was executed for the first time. , and then no longer responds to changes in state.count.

#Explanation watch can monitor the value defined by reactive, but watchEffect cannot.
2. Let watch and watchEffect monitor the value defined by ref.
watch:
setup(){
const count = ref(0);
watch(count, (post, pre) => {
console.log("watch 执行了");
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
});
const clickEvent = () => {
count.value++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}Result:

watchEffect:
setup(){
const count = ref(0);
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("watchEffect 执行了");
console.log(count);
});
const clickEvent = () => {
count.value++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}Result:

The results are the same as above, indicating that watch can respond to the value defined by ref, but watchEffect cannot.
2. Let watch and watchEffect respond to changes in a single value:
watch:
setup(){
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
watch(state.count, (post, pre) => {
console.log("watch 执行了");
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
});
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}The results show that no matter how the clickEvent event is triggered, the callback function in the watch will not be triggered. , nothing will be printed to the console.
watchEffect:
setup(){
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
watchEffect(() => {
console.log("watchEffect 执行了");
console.log(state.count);
});
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}Console result:
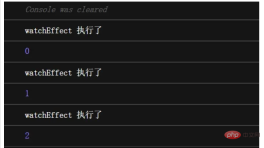
Explanation watchEffect can respond to a single value, but watch cannot. If you want watch In response to changes in count, you need to pass in the getter function as the first parameter, as follows:
setup(){
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
watch(
() => state.count,
(post, pre) => {
console.log("watch 执行了");
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
}
);
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}If the getter function returns the state reference value, the state reference will not be modified when changing state.count value, so it will not respond to changes in state.count. If you want to respond, you need to pass in the third parameter configuration {deep:true}. At the same time, the values of post and pre in the code are the same, as follows:
setup(){
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
//不会响应变化
watch(
() => state,
(post, pre) => {
console.log("watch 执行了");
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
}
);
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}setup(){
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
//加上了 {deep:true} 可以响应变化
watch(
() => state,
(post, pre) => {
console.log("watch 执行了");
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
},
{deep:true}
);
const clickEvent = () => {
state.count++;
};
return { clickEvent };
}If a reference value is returned, and you need to compare different values before and after the change, you need to pass in the getter function to return the value after a deep copy of the object. In the following example, an array is returned:
setup(){
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
const numbers = reactive([0, 1, 2, 3]);
watch(
() => [...numbers],
(post, pre) => {
console.log("watch 执行了");
console.log(post);
console.log(pre);
}
);
const clickEvent = () => {
numbers.push(1);
};
return { clickEvent };
}Control Taiwan’s result:

The above is the detailed content of How to use watch and watchEffect in vue3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 分享两个可以绘制 Flowable 流程图的Vue前端库Sep 07, 2022 pm 07:59 PM
分享两个可以绘制 Flowable 流程图的Vue前端库Sep 07, 2022 pm 07:59 PM前端有没有现成的库,可以直接用来绘制 Flowable 流程图的?下面本篇文章就跟小伙伴们介绍一下这两个可以绘制 Flowable 流程图的前端库。
 vue是前端css框架吗Aug 26, 2022 pm 07:37 PM
vue是前端css框架吗Aug 26, 2022 pm 07:37 PMvue不是前端css框架,而是前端JavaScript框架。Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式JS框架,是基于MVVM设计模式的前端框架,且专注于View层。Vue.js的优点:1、体积小;2、基于虚拟DOM,有更高的运行效率;3、双向数据绑定,让开发者不用再去操作DOM对象,把更多的精力投入到业务逻辑上;4、生态丰富、学习成本低。
 聊聊Vue3+qrcodejs如何生成二维码并添加文字描述Aug 02, 2022 pm 09:19 PM
聊聊Vue3+qrcodejs如何生成二维码并添加文字描述Aug 02, 2022 pm 09:19 PMVue3如何更好地使用qrcodejs生成二维码并添加文字描述?下面本篇文章给大家介绍一下Vue3+qrcodejs生成二维码并添加文字描述,希望对大家有所帮助。
 手把手带你了解VUE响应式原理Aug 26, 2022 pm 08:41 PM
手把手带你了解VUE响应式原理Aug 26, 2022 pm 08:41 PM本篇文章我们来了解 Vue2.X 响应式原理,然后我们来实现一个 vue 响应式原理(写的内容简单)实现步骤和注释写的很清晰,大家有兴趣可以耐心观看,希望对大家有所帮助!


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.











