Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to handle custom exceptions and return json in Springboot2.0
How to handle custom exceptions and return json in Springboot2.0
- 王林forward
- 2023-05-10 22:19:101460browse
1. Write a custom exception class
package cn.jfjb.crud.exception;
public class UserNotExistException extends RuntimeException {
public UserNotExistException() {
super("用户不存在");
}
}
2. Handle self-test exceptions
package cn.jfjb.crud.handler;
import cn.jfjb.crud.exception.UserNotExistException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public Map<string> handleException(Exception e) {
Map<string> map = new HashMap();
map.put("code", "user.notexist");
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}</string></string>
3. Configure the application.yml file (exceptions cannot be obtained without configuration)
server: error: include-exception: true
4. Write tests
package cn.jfjb.crud.controller;
import cn.jfjb.crud.exception.UserNotExistException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping({"/testException"})
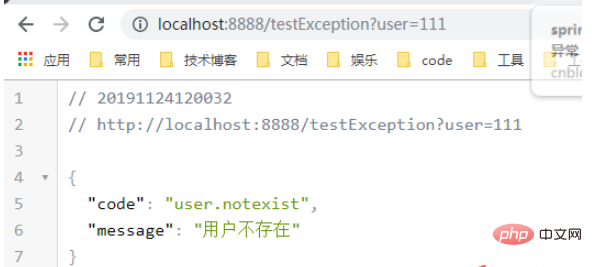
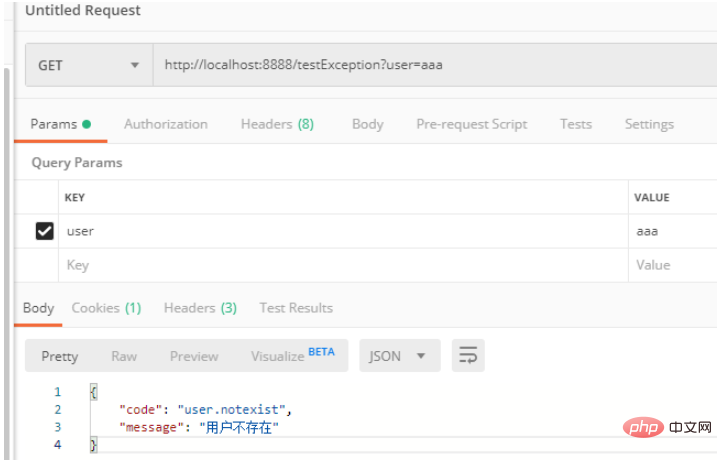
public String testException(@RequestParam("user") String user) {
if (user != "aaa") {
throw new UserNotExistException();
}
return "index";
}
}
The above is the detailed content of How to handle custom exceptions and return json in Springboot2.0. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:yisu.com. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete
Previous article:How to disable a certain health check in springbootNext article:How to disable a certain health check in springboot

