Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to solve maze path problem in Java using depth-first and breadth-first algorithms
How to solve maze path problem in Java using depth-first and breadth-first algorithms
- PHPzforward
- 2023-05-09 19:58:07674browse
深度优先
实现效果
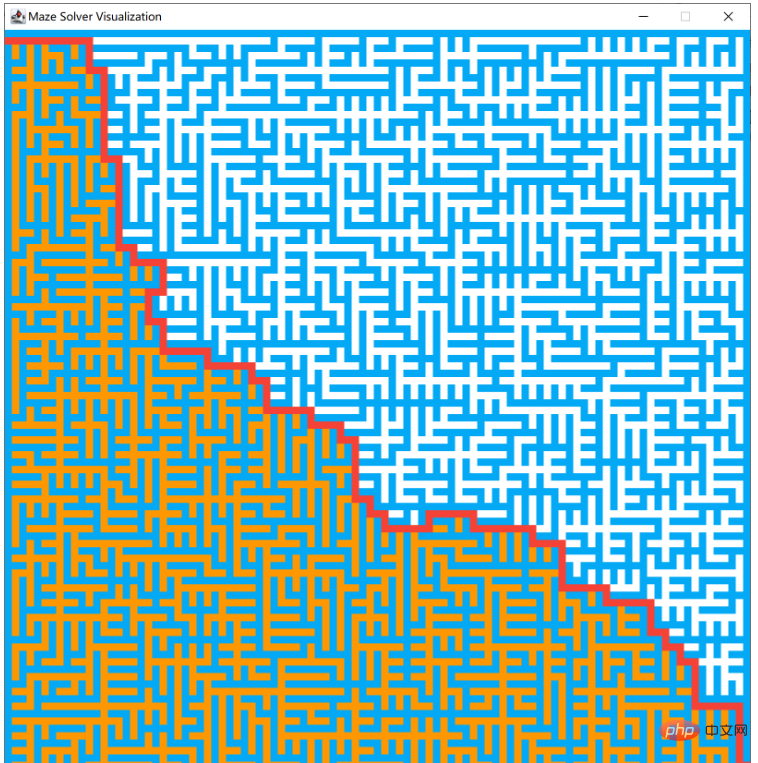
示例代码
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class AlgoFrame extends JFrame{
private int canvasWidth;
private int canvasHeight;
public AlgoFrame(String title, int canvasWidth, int canvasHeight){
super(title);
this.canvasWidth = canvasWidth;
this.canvasHeight = canvasHeight;
AlgoCanvas canvas = new AlgoCanvas();
setContentPane(canvas);
pack();
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setResizable(false);
setVisible(true);
}
public AlgoFrame(String title){
this(title, 1024, 768);
}
public int getCanvasWidth(){return canvasWidth;}
public int getCanvasHeight(){return canvasHeight;}
// data
private MazeData data;
public void render(MazeData data){
this.data = data;
repaint();
}
private class AlgoCanvas extends JPanel{
public AlgoCanvas(){
// 双缓存
super(true);
}
@Override
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
// 抗锯齿
// RenderingHints hints = new RenderingHints(
// RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
// RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
// hints.put(RenderingHints.KEY_RENDERING, RenderingHints.VALUE_RENDER_QUALITY);
// g2d.addRenderingHints(hints);
// 具体绘制
int w = canvasWidth/data.M();
int h = canvasHeight/data.N();
for(int i = 0 ; i < data.N() ; i ++ )
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < data.M() ; j ++){
if (data.getMaze(i, j) == MazeData.WALL)
AlgoVisHelper.setColor(g2d, AlgoVisHelper.LightBlue);
else
AlgoVisHelper.setColor(g2d, AlgoVisHelper.White);
if(data.path[i][j])
AlgoVisHelper.setColor(g2d, AlgoVisHelper.Orange);
if(data.result[i][j])
AlgoVisHelper.setColor(g2d, AlgoVisHelper.Red);
AlgoVisHelper.fillRectangle(g2d, j * w, i * h, w, h);
}
}
}
@Override
public Dimension getPreferredSize(){
return new Dimension(canvasWidth, canvasHeight);
}
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.Ellipse2D;
import java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D;
import java.lang.InterruptedException;
public class AlgoVisHelper {
private AlgoVisHelper(){}
public static final Color Red = new Color(0xF44336);
public static final Color Pink = new Color(0xE91E63);
public static final Color Purple = new Color(0x9C27B0);
public static final Color DeepPurple = new Color(0x673AB7);
public static final Color Indigo = new Color(0x3F51B5);
public static final Color Blue = new Color(0x2196F3);
public static final Color LightBlue = new Color(0x03A9F4);
public static final Color Cyan = new Color(0x00BCD4);
public static final Color Teal = new Color(0x009688);
public static final Color Green = new Color(0x4CAF50);
public static final Color LightGreen = new Color(0x8BC34A);
public static final Color Lime = new Color(0xCDDC39);
public static final Color Yellow = new Color(0xFFEB3B);
public static final Color Amber = new Color(0xFFC107);
public static final Color Orange = new Color(0xFF9800);
public static final Color DeepOrange = new Color(0xFF5722);
public static final Color Brown = new Color(0x795548);
public static final Color Grey = new Color(0x9E9E9E);
public static final Color BlueGrey = new Color(0x607D8B);
public static final Color Black = new Color(0x000000);
public static final Color White = new Color(0xFFFFFF);
public static void strokeCircle(Graphics2D g, int x, int y, int r){
Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D.Double(x-r, y-r, 2*r, 2*r);
g.draw(circle);
}
public static void fillCircle(Graphics2D g, int x, int y, int r){
Ellipse2D circle = new Ellipse2D.Double(x-r, y-r, 2*r, 2*r);
g.fill(circle);
}
public static void strokeRectangle(Graphics2D g, int x, int y, int w, int h){
Rectangle2D rectangle = new Rectangle2D.Double(x, y, w, h);
g.draw(rectangle);
}
public static void fillRectangle(Graphics2D g, int x, int y, int w, int h){
Rectangle2D rectangle = new Rectangle2D.Double(x, y, w, h);
g.fill(rectangle);
}
public static void setColor(Graphics2D g, Color color){
g.setColor(color);
}
public static void setStrokeWidth(Graphics2D g, int w){
int strokeWidth = w;
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(strokeWidth, BasicStroke.CAP_ROUND, BasicStroke.JOIN_ROUND));
}
public static void pause(int t) {
try {
Thread.sleep(t);
// System.out.println("Dely");
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Error sleeping");
}
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Stack;
public class AlgoVisualizer {
private static int DELAY = 10;
private static int blockSide = 8;
private MazeData data;
private AlgoFrame frame;
private static final int d[][] = {{-1,0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; //左下右上
public AlgoVisualizer(String mazeFile){
// 初始化数据
data = new MazeData(mazeFile);
int sceneHeight = data.N() * blockSide;
int sceneWidth = data.M() * blockSide;
// 初始化视图
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
frame = new AlgoFrame("Maze Solver Visualization", sceneWidth, sceneHeight);
new Thread(() -> {
run();
}).start();
});
}
public void run(){
setData(-1, -1, false);
Stack<Position> stack = new Stack<Position>();
Position entrance = new Position(data.getEntranceX(), data.getEntranceY());
stack.push(entrance);
data.visited[entrance.getX()][entrance.getY()] = true;
boolean isSolved = false;
while (!stack.empty()) {
Position curPos = stack.pop();
setData(curPos.getX(), curPos.getY(), true);
if (curPos.getX() == data.getExitX() && curPos.getY() == data.getExitY()) {
isSolved = true;
findPath(curPos); //find the path from the final position
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = curPos.getX() + d[i][0];
int newY = curPos.getY() + d[i][1];
if (data.inArea(newX, newY) && !data.visited[newX][newY] &&
data.getMaze(newX, newY) == MazeData.ROAD) {
stack.push(new Position(newX, newY, curPos));
data.visited[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
if (!isSolved) {
System.out.println("the maze has no solution");
}
setData(-1, -1, false);
}
public void findPath(Position des) {
Position cur = des;
while (cur != null) {
data.result[cur.getX()][cur.getY()] = true;
cur = cur.getPrev();
}
}
private void setData(int x, int y, boolean isPath){
if (data.inArea(x, y)) {
data.path[x][y] = isPath;
}
frame.render(data);
AlgoVisHelper.pause(DELAY);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String mazeFile = "maze_101_101.txt";
AlgoVisualizer vis = new AlgoVisualizer(mazeFile);
}
}
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MazeData {
public static final char ROAD = ' ';
public static final char WALL = '#';
private int N, M;
private char[][] maze;
private int entranceX, entranceY;
private int exitX, exitY;
public boolean[][] visited;
public boolean[][] path;
public boolean[][] result;
public MazeData(String filename){
if(filename == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Filename can not be null!");
Scanner scanner = null;
try{
File file = new File(filename);
if(!file.exists())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File " + filename + " doesn't exist");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
scanner = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(fis), "UTF-8");
// 读取第一行
String nmline = scanner.nextLine();
String[] nm = nmline.trim().split("\\s+");
//System.out.print(nm[0] + ' ' + nm[1]);
N = Integer.parseInt(nm[0]);
// System.out.println("N = " + N);
M = Integer.parseInt(nm[1]);
// System.out.println("M = " + M);
// 读取后续的N行
maze = new char[N][M];
visited = new boolean[N][M];
path = new boolean[N][M];
result = new boolean[N][M];
for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++){
String line = scanner.nextLine();
// 每行保证有M个字符
if(line.length() != M)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Maze file " + filename + " is invalid");
for(int j = 0 ; j < M ; j ++)
{
maze[i][j] = line.charAt(j);
visited[i][j] = false;
path[i][j] = false;
result[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(scanner != null)
scanner.close();
}
entranceX = 1;
entranceY = 0;
exitX = N - 2 ;
exitY = M - 1;
}
public int N(){ return N; }
public int M(){ return M; }
public int getEntranceX() {return entranceX;}
public int getEntranceY() {return entranceY;}
public int getExitX() { return exitX;}
public int getExitY() { return exitY;}
public char getMaze(int i, int j){
if(!inArea(i,j))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("i or j is out of index in getMaze!");
return maze[i][j];
}
public boolean inArea(int x, int y){
return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < M;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println(N + " " + M);
for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < M ; j ++)
System.out.print(maze[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
return;
}
}
public class Position {
private int x, y;
private Position prev;
public Position(int x, int y, Position prev ) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.prev = prev;
}
public Position(int x, int y) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this(x, y, null);
}
public int getX() { return x;}
public int getY() { return y;}
public Position getPrev() {return prev;}
}上面是深度优先的非递归遍历方法
下面是广度优先的遍历方法
广度优先
实现效果
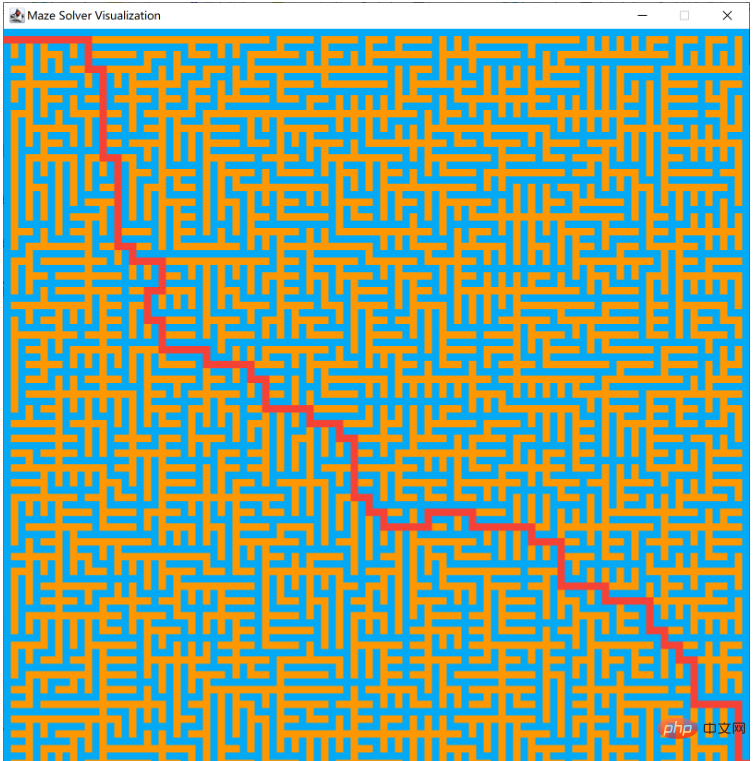
示例代码
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class AlgoVisualizer {
private static int DELAY = 10;
private static int blockSide = 8;
private MazeData data;
private AlgoFrame frame;
private static final int d[][] = {{-1,0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}}; //左下右上
public AlgoVisualizer(String mazeFile){
// 初始化数据
data = new MazeData(mazeFile);
int sceneHeight = data.N() * blockSide;
int sceneWidth = data.M() * blockSide;
// 初始化视图
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
frame = new AlgoFrame("Maze Solver Visualization", sceneWidth, sceneHeight);
new Thread(() -> {
run();
}).start();
});
}
public void run(){
setData(-1, -1, false);
LinkedList<Position> queue = new LinkedList<Position>();
Position entrance = new Position(data.getEntranceX(), data.getEntranceY());
queue.addLast(entrance);
data.visited[entrance.getX()][entrance.getY()] = true;
boolean isSolved = false;
while ( queue.size() != 0) {
Position curPos = queue.pop();
setData(curPos.getX(), curPos.getY(), true);
if (curPos.getX() == data.getExitX() && curPos.getY() == data.getExitY()) {
isSolved = true;
findPath(curPos); //find the path from the final position
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newX = curPos.getX() + d[i][0];
int newY = curPos.getY() + d[i][1];
if (data.inArea(newX, newY) && !data.visited[newX][newY] &&
data.getMaze(newX, newY) == MazeData.ROAD) {
queue.addLast(new Position(newX, newY, curPos));
data.visited[newX][newY] = true;
}
}
}
if (!isSolved) {
System.out.println("the maze has no solution");
}
setData(-1, -1, false);
}
public void findPath(Position des) {
Position cur = des;
while (cur != null) {
data.result[cur.getX()][cur.getY()] = true;
cur = cur.getPrev();
}
}
private void setData(int x, int y, boolean isPath){
if (data.inArea(x, y)) {
data.path[x][y] = isPath;
}
frame.render(data);
AlgoVisHelper.pause(DELAY);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String mazeFile = "maze_101_101.txt";
AlgoVisualizer vis = new AlgoVisualizer(mazeFile);
}
}知识点总结


q为抽象的队列


The above is the detailed content of How to solve maze path problem in Java using depth-first and breadth-first algorithms. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:yisu.com. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete

