Home >Backend Development >Python Tutorial >Perform example analysis using Python's parallelization
Perform example analysis using Python's parallelization
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-08 17:52:261667browse
Example: N-body problem
Physical premise:
Newton’s Law
Time Discrete equation of motion
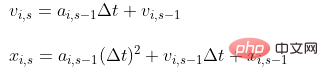
import numpy as np
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
Ns = [2**i for i in range(1,10)]
runtimes = []
def remove_i(x,i):
"从所有粒子中去除本粒子"
shape = (x.shape[0]-1,)+x.shape[1:]
y = np.empty(shape,dtype=float)
y[:i] = x[:i]
y[i:] = x[i+1:]
return y
def a(i,x,G,m):
"计算加速度"
x_i = x[i]
x_j = remove_i(x,i)
m_j = remove_i(m,i)
diff = x_j - x_i
mag3 = np.sum(diff**2,axis=1)**1.5
result = G * np.sum(diff * (m_j / mag3)[:,np.newaxis],axis=0)
return result
def timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt):
N = len(x0)
x1 = np.empty(x0.shape,dtype=float)
v1 = np.empty(v0.shape,dtype=float)
for i in range(N):
a_i0 = a(i,x0,G,m)
v1[i] = a_i0 * dt + v0[i]
x1[i] = a_i0 * dt**2 + v0[i] * dt + x0[i]
return x1,v1
def initial_cond(N,D):
x0 = np.array([[1,1,1],[10,10,10]])
v0 = np.array([[10,10,1],[0,0,0]])
m = np.array([10,10])
return x0,v0,m
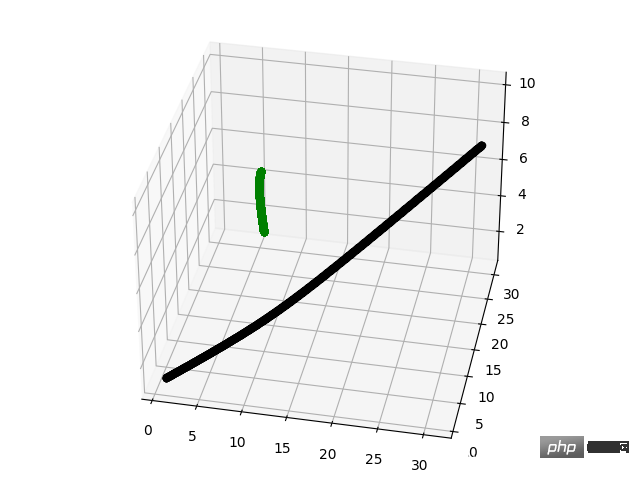
def stimulate(N,D,S,G,dt):
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
x0,v0,m = initial_cond(N,D)
for s in range(S):
x1,v1 = timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt)
x0,v0 = x1,v1
t = 0
for i in x0:
ax.scatter(i[0],i[1],i[2],label=str(s*dt),c=["black","green","red"][t])
t += 1
t = 0
plt.show()
start = time.time()
stimulate(2,3,3000,9.8,1e-3)
stop = time.time()
runtimes.append(stop - start)
Rendering
import datetime
import multiprocessing as mp
def accessional_fun():
f = open("accession.txt","r")
result = float(f.read())
f.close()
return result
def final_fun(name, param):
result = 0
for num in param:
result += num + accessional_fun() * 2
return {name: result}
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = datetime.datetime.now()
num_cores = int(mp.cpu_count())
print("你使用的计算机有: " + str(num_cores) + " 个核,当然了,Intel 7 以上的要除以2")
print("如果你使用的 Python 是 32 位的,注意数据量不要超过两个G")
print("请你再次检查你的程序是否已经改成了适合并行运算的样子")
pool = mp.Pool(num_cores)
param_dict = {'task1': list(range(10, 300)),
'task2': list(range(300, 600)),
'task3': list(range(600, 900)),
'task4': list(range(900, 1200)),
'task5': list(range(1200, 1500)),
'task6': list(range(1500, 1800)),
'task7': list(range(1800, 2100)),
'task8': list(range(2100, 2400)),
'task9': list(range(2400, 2700)),
'task10': list(range(2700, 3000))}
results = [pool.apply_async(final_fun, args=(name, param)) for name, param in param_dict.items()]
results = [p.get() for p in results]
end_time = datetime.datetime.now()
use_time = (end_time - start_time).total_seconds()
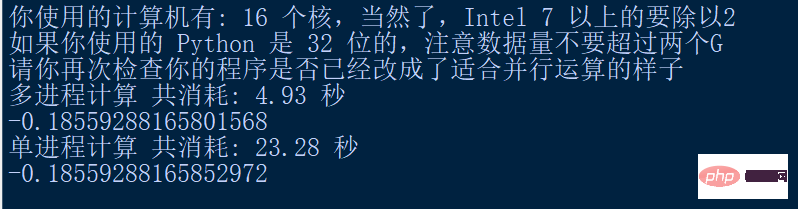
print("多进程计算 共消耗: " + "{:.2f}".format(use_time) + " 秒")
print(results)
The running results are as follows:

import math
import time
import multiprocessing as mp
def final_fun(name, param):
result = 0
for num in param:
result += math.cos(num) + math.sin(num)
return {name: result}
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time = time.time()
num_cores = int(mp.cpu_count())
print("你使用的计算机有: " + str(num_cores) + " 个核,当然了,Intel 7 以上的要除以2")
print("如果你使用的 Python 是 32 位的,注意数据量不要超过两个G")
print("请你再次检查你的程序是否已经改成了适合并行运算的样子")
pool = mp.Pool(num_cores)
param_dict = {'task1': list(range(10, 3000000)),
'task2': list(range(3000000, 6000000)),
'task3': list(range(6000000, 9000000)),
'task4': list(range(9000000, 12000000)),
'task5': list(range(12000000, 15000000)),
'task6': list(range(15000000, 18000000)),
'task7': list(range(18000000, 21000000)),
'task8': list(range(21000000, 24000000)),
'task9': list(range(24000000, 27000000)),
'task10': list(range(27000000, 30000000))}
results = [pool.apply_async(final_fun, args=(name, param)) for name, param in param_dict.items()]
results = [p.get() for p in results]
end_time = time.time()
use_time = end_time - start_time
print("多进程计算 共消耗: " + "{:.2f}".format(use_time) + " 秒")
result = 0
for i in range(0,10):
result += results[i].get("task"+str(i+1))
print(result)
start_time = time.time()
result = 0
for i in range(10,30000000):
result += math.cos(i) + math.sin(i)
end_time = time.time()
print("单进程计算 共消耗: " + "{:.2f}".format(end_time - start_time) + " 秒")
print(result)
The operation result:
Mechanics problem improvement:
import numpy as np
import time
from mpi4py import MPI
from mpi4py.MPI import COMM_WORLD
from types import FunctionType
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from multiprocessing import Pool
def remove_i(x,i):
shape = (x.shape[0]-1,) + x.shape[1:]
y = np.empty(shape,dtype=float)
y[:1] = x[:1]
y[i:] = x[i+1:]
return y
def a(i,x,G,m):
x_i = x[i]
x_j = remove_i(x,i)
m_j = remove_i(m,i)
diff = x_j - x_i
mag3 = np.sum(diff**2,axis=1)**1.5
result = G * np.sum(diff * (m_j/mag3)[:,np.newaxis],axis=0)
return result
def timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt,pool):
N = len(x0)
takes = [(i,x0,v0,G,m,dt) for i in range(N)]
results = pool.map(timestep_i,takes)
x1 = np.empty(x0.shape,dtype=float)
v1 = np.empty(v0.shape,dtype=float)
for i,x_i1,v_i1 in results:
x1[i] = x_i1
v1[i] = v_i1
return x1,v1
def timestep_i(args):
i,x0,v0,G,m,dt = args
a_i0 = a(i,x0,G,m)
v_i1 = a_i0 * dt + v0[i]
x_i1 = a_i0 * dt ** 2 +v0[i]*dt + x0[i]
return i,x_i1,v_i1
def initial_cond(N,D):
x0 = np.random.rand(N,D)
v0 = np.zeros((N,D),dtype=float)
m = np.ones(N,dtype=float)
return x0,v0,m
class Pool(object):
def __init__(self):
self.f = None
self.P = COMM_WORLD.Get_size()
self.rank = COMM_WORLD.Get_rank()
def wait(self):
if self.rank == 0:
raise RuntimeError("Proc 0 cannot wait!")
status = MPI.Status()
while True:
task = COMM_WORLD.recv(source=0,tag=MPI.ANY_TAG,status=status)
if not task:
break
if isinstance(task,FunctionType):
self.f = task
continue
result = self.f(task)
COMM_WORLD.isend(result,dest=0,tag=status.tag)
def map(self,f,tasks):
N = len(tasks)
P = self.P
Pless1 = P - 1
if self.rank != 0:
self.wait()
return
if f is not self.f:
self.f = f
requests = []
for p in range(1,self.P):
r = COMM_WORLD.isend(f,dest=p)
requests.append(r)
MPI.Request.waitall(requests)
results = []
for i in range(N):
result = COMM_WORLD.recv(source=(i%Pless1)+1,tag=i)
results.append(result)
return results
def __del__(self):
if self.rank == 0:
for p in range(1,self.p):
COMM_WORLD.isend(False,dest=p)
def simulate(N,D,S,G,dt):
x0,v0,m = initial_cond(N,D)
pool = Pool()
if COMM_WORLD.Get_rank()==0:
for s in range(S):
x1,v1 = timestep(x0,v0,G,m,dt,pool)
x0,v0 = x1,v1
else:
pool.wait()
if __name__ == '__main__':
simulate(128,3,300,1.0,0.001)
Ps = [1,2,4,8]
runtimes = []
for P in Ps:
start = time.time()
simulate(128,3,300,1.0,0.001)
stop = time.time()
runtimes.append(stop - start)
print(runtimes)The above is the detailed content of Perform example analysis using Python's parallelization. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:yisu.com. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete

