 Backend Development
Backend Development Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial The principles and implementation methods of radix sorting in various programming languages
The principles and implementation methods of radix sorting in various programming languagesThe principles and implementation methods of radix sorting in various programming languages
Description
RadixSort is a non-comparative integer sorting algorithm. Its principle is to cut integers into different numbers by digits. , and then compare each digit separately. Since integers can also represent strings (such as names or dates) and floating-point numbers in specific formats, radix sorting is not limited to integers. The invention of radix sort can be traced back to 1887 when Herman Hollery worked on the Tabulation Machine. The radix sort method can use LSD (Least significant digital) or MSD (Most significant digital). The sorting method of LSD starts from the rightmost of the key value, while the MSD sorting method starts from the leftmost of the key value. LSD uses counting sort or bucket sort, and MSD can use bucket sort. From low to high (LSD) is relatively simple, just rearrange bit by bit. If it is from high to low (MSD), it cannot be rearranged every time. It can be achieved by traversing layer by layer through recursion. Please see the source code of various versions for details.
There are many implementations of sorting algorithms on the Internet, but they often contain errors and lack comparisons in different languages. This series rearranges various sorting algorithms and implements them in different languages.
Implementation process
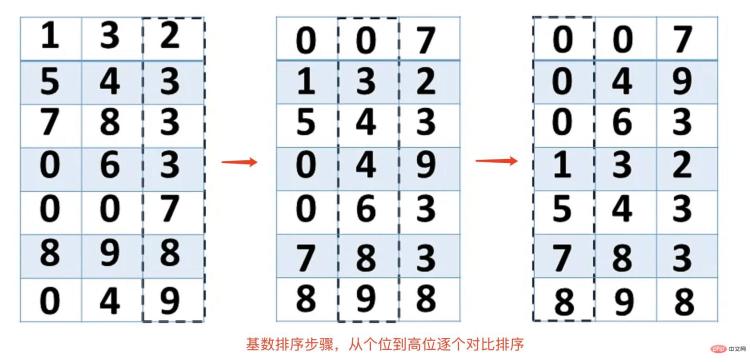
- Unify the sequence of numbers to be sorted (positive integers) into the same digit length, and pad the shorter digits with zeros.
- Each digit is sorted individually, from lowest to highest, or from highest to lowest.
- After sorting from lowest to high or from high to low, the sequence becomes an ordered sequence.
- Schematic diagram
##Performance analysis
class RadixSort {
// 基数排序,基于计数排序,按数位从低到高来排序
public static int[] countingSort(int arr[], int exponent) {
// 基数exponent按10进位,range为10
int range = 10;
int[] countList = new int[range];
int[] sortedList = new int[arr.length];
// 设定最小值以支持负数
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < min) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
// 根据基数求得当前项目对应位置的数值,并给对应计数数组位置加1
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int item = arr[i] - min;
// 根据exponent获得当前位置的数字是几,存入对应计数数组
int idx = (item / exponent) % range;
countList[idx] += 1;
}
// 根据位置计数,后面的位数为前面的累加之和
for (int i = 1; i < range; i++) {
countList[i] += countList[i - 1];
}
System.out.println("radixSort1 countingSort countList:" + Arrays.toString(countList));
// 根据计数数组按顺序取出排序内容
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int item = arr[i] - min;
int idx = (item / exponent) % range;
// 根据计数位置得到顺序
sortedList[countList[idx] - 1] = arr[i];
countList[idx] -= 1;
}
// 最后赋值给原数据
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = sortedList[i];
}
System.out.println("radixSort1 -> sortedList:" + Arrays.toString(sortedList));
return sortedList;
}
// 基数排序1,按数位大小,基于计数排序实现
public static int[] radixSort1(int arr[]) {
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
// 根据最大值,逐个按进位(基数)来应用排序,exponent即数位。
for (int exponent = 1; (max / exponent) > 0; exponent *= 10) {
countingSort(arr, exponent);
}
return arr;
}
}// 基数排序,从高到低逐位排序,递归方式,基于桶排序。具体步骤如下:
// 1. 找出数组中最大的数,确定其位数。
// 2. MSD是从高位开始,依次按照位数的值将数字放入到不同桶中。
// 3. 如果桶里的长度超过1,则通过递归继续按桶排序。当桶里的数据只有1位时添加到原列表对应位置。
// 重复步骤2和3,直到按照最高位排序完成。
class RadixSortMSD {
static int[] radixSort(int[] arr) {
int len = arr.length;
// 获取数组最大项
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
// 获取数组最小项
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (min > arr[i]) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
// 获取数字一共有几位,减去min得到最大值,以支持负数和减少最大值
int numberOfDigits = (int) (Math.log10(max - min) + 1);
int exponent = (int) (Math.pow(10, numberOfDigits - 1));
// 根据数组最大值,自后向前逐个按数位基数(exponent)比较排序。
return bucketSort(arr, len, exponent);
}
static int[] bucketSort(int[] arr, int len, int exponent) {
System.out.println("origin arr:" + Arrays.toString(arr) + " len=" + len + " exponent:" + exponent);
if (len <= 1 || exponent < 1) {
return arr;
}
// 获取数组最小项
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (min > arr[i]) {
min = arr[i];
}
}
// 位数按10递进
int range = 10;
// 定义桶二维数组,长度为10,放入0-9的数字
int[][] buckets = new int[range][len];
// 记录某个桶的最新长度,以便往桶内追加数据。
int[] bucketsCount = new int[range];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int item = arr[i] - min;
// 根据数位上的值,把数据追加到对应的桶里,减去min是支持负数
int bucketIdx = (item / exponent) % range;
// 把数据按下标插入到桶里
int numberIndex = bucketsCount[bucketIdx];
buckets[bucketIdx][numberIndex] = arr[i];
bucketsCount[bucketIdx] += 1;
}
// 将每个桶的数据按顺序逐个取出,重新赋值给原数组
int sortedIdx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++) {
int[] bucket = buckets[i];
int bucketLen = bucketsCount[i];
// 如果只有一个值,则直接更新到原数组
if (bucketsCount[i] == 1) {
arr[sortedIdx] = bucket[0];
sortedIdx += 1;
} else if (bucket.length > 0 && bucketLen > 0) {
// 如果是数组且记录大于1则继续递归调用,位数降低1位
// 递归调用传参时需要传入当前子序列、子序列长度、当前分解的位数基数
int[] sortedBucket = bucketSort(bucket, bucketLen, (int) (exponent / range));
// 依照已排序的子序列实际长度,把各个桶里的值按顺序赋给原数组
for (int j = 0; j < bucketLen; j++) {
int num = sortedBucket[j];
arr[sortedIdx] = num;
sortedIdx += 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println("exponent:" + exponent + " sorted arr:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
return arr;
}
Python"""
基数排序LSD版,本基于桶排序。
1. 找出数组中最大的数,确定其位数。
2. LSD是低位到高位,依次按照位数的值将数字放入到不同桶中。
3. 按照桶顺序重新给数组排序。
重复步骤2和3,直到排序完成。
"""
def radix_sort(arr):
max_value = max(arr) # 找出数组中最大的数
min_value = min(arr) #最小值,为了支持负数
digit = 1 # 从个位开始排序
# 每次排序一个数位,从低到高直到排序完成
while (max_value - min_value) // digit > 0:
# 创建10个桶,分别对应0-9的数位值
buckets = [[] for _ in range(10)]
for num in arr:
# 找出当前位数的值
digit_num = (num - min_value) // digit % 10
# 将数字添加到对应数位的桶中,相当于根据数位排序
buckets[digit_num].append(num)
print('buckets:', buckets)
# 通过exend展开数组,相当于逐层添加
arr = []
for bucket in buckets:
arr.extend(bucket)
# 或逐项添加
# for item in bucket:
# arr.append(item)
# 数位移动到下一位
digit *= 10
return arr"""
基数排序,从高到低逐位排序,递归方式,基于桶排序。具体步骤如下:
1. 找出数组中最大的数,确定其位数。
2. MSD是从高位开始,依次按照位数的值将数字放入到不同桶中。
3. 如果桶里的长度超过1,则通过递归继续按桶排序。当桶里的数据只有1位时添加到原列表对应位置。
重复步骤2和3,直到按照最高位排序完成。
"""
# 桶排序,根据数位递归调用
def bucket_sort(arr, exponent):
print('origin arr:', arr, 'exponent:', exponent)
if (len(arr) <= 1 or exponent <= 0):
return arr
min_value = min(arr)
radix = 10
amount = 10
print('prepared arr:', arr, 'exponent:', exponent)
# 构建排序的桶二维列表
buckets = [None] * radix
for i in range(len(arr)):
item = arr[i] - min_value
# 根据数位上的值,把数据追加到对应的桶里,减去min是支持负数
bucketIdx = int(item / exponent) % radix
# 填充空桶,或者提前填充为列表
if buckets[bucketIdx] is None:
buckets[bucketIdx] = []
buckets[bucketIdx].append(arr[i])
print('append to buckets:', buckets)
# 将每个桶的数据按顺序逐个取出,重新赋值给原数组
sortedIdx = 0
for i in range(radix):
bucket = buckets[i]
if bucket is None or len(bucket) < 1:
continue
# 如果是数组则继续递归调用,位数降低1位
sortedBucket = bucket_sort(bucket, exponent // amount)
# 把各个桶里的值按顺序赋给原数组
for num in sortedBucket:
print ('sortedIdx::', sortedIdx)
arr[sortedIdx] = num
print('bucket:', bucket, 'sortedBucket:', sortedBucket,
'sortedIdx:', sortedIdx, 'set arr:', arr)
sortedIdx += 1
print('exponent:', exponent, 'sorted arr:', arr)
return arr
# 基数排序,从高到低逐位排序MSD版,基于桶排序递归实现
def radix_sort_msd(arr):
# 根据最大值,逐个按进位(基数)来应用排序,从高位到低位。
# 获取数字的数位,这减去min_value是为了支持负数
# exponent是最大的数位,由高到低逐位计算
max_value = max(arr)
min_value = min(arr)
numberOfDigits = int(math.log10(max_value - min_value) + 1)
exponent = math.pow(10, numberOfDigits - 1)
return bucket_sort(arr, int(exponent))
Go// 2. 基数排序LSD版,计算最小值,基于计数排序实现
func radixSort2(arr []int) []int {
var arrLen = len(arr)
// 基数exponent按10进位,amount为10
var amount = 10
var sortedList = make([]int, arrLen)
var max = arr[0]
for i := 0; i < arrLen; i++ {
if arr[i] > max {
max = arr[i]
}
}
var min = arr[0]
for i := 0; i < arrLen; i++ {
if arr[i] < min {
min = arr[i]
}
}
// 根据基数求得当前项目对应位置的数值,并给对应计数数组位置加1
// 按最大值补齐数位,基数exponent按10进位
for exponent := 1; ((max - min) / exponent) > 0; exponent *= amount {
// 计数数组,长度为10,0-9一共10个数字
countList := make([]int, amount)
// 根据基数得到当前位数,并给计数数组对应位置加1
for i := 0; i < arrLen; i++ {
var item = arr[i] - min
var idx = (item / exponent) % amount
countList[idx] += 1
}
// 计数排序构建,自前往后,逐个将上一项的值存入当前项
for i := 1; i < amount; i++ {
countList[i] += countList[i-1]
}
fmt.Println("radixSort2 -> countList:", countList)
// 根据计数数组按顺序取出排序内容
for i := arrLen - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
item := arr[i] - min
var idx = (item / exponent) % amount
sortedList[countList[idx]-1] = arr[i]
countList[idx] -= 1
}
// 将新顺序赋值给原数组
for i := 0; i < arrLen; i++ {
arr[i] = sortedList[i]
}
}
return arr
}// 基数排序,从高到低逐位排序,递归方式,基于桶排序。具体步骤如下:
// 1. 找出数组中最大的数,确定其位数。
// 2. MSD是从高位开始,依次按照位数的值将数字放入到不同桶中。
// 3. 如果桶里的长度超过1,则通过递归继续按桶排序。当桶里的数据只有1位时添加到原列表对应位置。
// 重复步骤2和3,直到按照最高位排序完成。
func radixSortMSD(arr []int) []int {
var amount = 10
maxValue := max(arr)
exponent := pow(amount, getNumberOfDigits(maxValue)-1)
bucketSort(arr, exponent)
return arr
}
func bucketSort(arr []int, exponent int) []int {
fmt.Println("origin arr:", arr, "exponent: ", exponent)
if exponent < 1 || len(arr) <= 1 {
return arr
}
var amount = 10
fmt.Println("prepared arr:", arr, "exponent: ", exponent)
buckets := [][]int{}
// 按数位来获取最小值
minValue := getMinValue(arr, exponent)
// 增加偏移以便支持负数
offset := 0
if minValue < 0 {
offset = 0 - minValue
}
// 填充桶二维数组
for i := 0; i < (amount + offset); i++ {
buckets = append(buckets, []int{})
}
// 获取数组项指定数位的值,放入到对应桶中,桶的下标即顺序
for i, num := range arr {
bucketIdx := getDigit(arr, i, exponent) + offset
buckets[bucketIdx] = append(buckets[bucketIdx], num)
}
fmt.Println("append to buckets: ", buckets)
sortedIdx := 0
for _, bucket := range buckets {
if len(bucket) <= 0 {
continue
}
// 递归遍历所有的桶,由里而外逐个桶进行排序
sortedBucket := bucketSort(bucket, exponent/amount)
// 把各个桶里的值按顺序赋给原数组
for _, num := range sortedBucket {
arr[sortedIdx] = num
fmt.Println("bucket:", bucket, "sortedBucket: ", sortedBucket, "sortedIdx:", sortedIdx, "set arr: ", arr)
sortedIdx += 1
}
}
fmt.Println("exponent: ", exponent, "sorted arr: ", arr)
return arr
}
// 获取数字位数
func getNumberOfDigits(num int) int {
numberOfDigits := 0
for num > 0 {
numberOfDigits += 1
num /= 10
}
return numberOfDigits
}
// 获取绝对值
func abs(value int) int {
if value < 0 {
return -value
}
return value
}
// 获取数组最大值
func max(arr []int) int {
maxValue := arr[0]
for i := 1; i < len(arr); i++ {
if arr[i] > maxValue {
maxValue = arr[i]
}
}
return maxValue
}
// 计算数字次幂
func pow(a int, power int) int {
result := 1
for i := 0; i < power; i++ {
result *= a
}
return result
}
// 获取数组项指定数位的最小值
func getMinValue(arr []int, exponent int) int {
minValue := getDigit(arr, 0, exponent)
for i := 1; i < len(arr); i++ {
element := getDigit(arr, i, exponent)
if minValue > element {
minValue = element
}
}
return minValue
}
// 获取数字指定数位的值,超出数位补0,负数返回负数
// 如: 1024, 百位: 100 => 返回 0
// 如: -2048, 千位: 1000 => 返回 -2
func getDigit(arr []int, idx int, exponent int) int {
element := arr[idx]
digit := abs(element) / exponent % 10
if element < 0 {
return -digit
}
return digit
}
JS// 基数排序2,从低到高逐个数位对比排序,基于桶排序,利用JS数组展开来还原数组
function radixSort2(arr) {
// 倒数获取数字指定位置的数
function getDigit(num, position) {
const digit = Math.floor(num / Math.pow(10, position - 1)) % 10
return digit
}
// 获取数组最大数字的位数
function getNumberLength(num) {
let maxLength = 0
while (num > 0) {
maxLength++
num /= 10
}
return maxLength
}
const max = Math.max.apply(null, arr)
const min = Math.min.apply(null, arr)
const maxLength = getNumberLength(max - min)
for (let i = 0; i < maxLength; i++) {
// 每个数位准备10个空数组,用于放数字0-9
const buckets = Array.from({
length: 10
}, () => [])
// 遍历数组将数位上的数放入对应桶里
for (let j = 0, l = arr.length; j < l; j++) {
const item = (arr[j] - min)
// 从后往前获取第x位置的数,通过计算的方式
const num = getDigit(item, i + 1)
// 当前位数如果不为空则添加到基数桶中
if (num !== isNaN) {
buckets[num].push((arr[j]))
}
}
// 将桶逐级展开取出数字,如果支持flat则直接使用数组的flat()
if (buckets.flat) {
arr = buckets.flat()
} else {
// 定定义数组展开函数
// arr = flat(buckets)
}
}
return arr
}// 基数排序,从高到低逐位排序,递归方式,基于桶排序。具体步骤如下:
// 1. 找出数组中最大的数,确定其位数。
// 2. MSD是从高位开始,依次按照位数的值将数字放入到不同桶中。
// 3. 如果桶里的长度超过1,则通过递归继续按桶排序。当桶里的数据只有1位时添加到原列表对应位置。
// 重复步骤2和3,直到按照最高位排序完成。
function radixSortMSD(arr) {
function bucketSort(arr, exponent) {
console.log('origin arr:', arr, 'exponent:', exponent)
if (!arr || arr.length <= 1 || exponent < 1) {
return arr
}
const min = Math.min.apply(null, arr)
const range = 10
// 定义桶二维数组,长度为10,放入0-9的数字
const buckets = []
for (let i = 0; i < range; i++) {
buckets[i] = []
}
for (let i = 0, l = arr.length; i < l; i++) {
const item = arr[i] - min
// 根据数位上的值,把数据追加到对应的桶里,减去min是支持负数
const bucketIdx = Math.floor(item / exponent % range)
// 提前填充空桶或使用时再填充
if (!buckets[bucketIdx]) {
buckets[bucketIdx] = []
}
buckets[bucketIdx].push(arr[i])
}
// 将每个桶的数据按顺序逐个取出,重新赋值给原数组
let sortedIdx = 0
for (let i = 0; i < range; i++) {
const bucket = buckets[i]
if (bucket && bucket.length > 0) {
// 如果是数组则继续递归调用,位数降低1位
const sortedBucket = bucketSort(bucket, Math.floor(exponent / range))
// 把各个桶里的值按顺序赋给原数组
sortedBucket.forEach(num => {
arr[sortedIdx] = num
sortedIdx += 1
})
}
}
return arr
}
const max = Math.max.apply(null, arr)
const min = Math.min.apply(null, arr)
// 获取数字一共有几位,减去min得到最大值,以支持负数和减少最大值
const numberOfDigits = Math.floor(Math.log10(max - min) + 1)
const exponent = Math.pow(10, numberOfDigits - 1)
// 根据数组最大值,自后向前逐个按数位基数(exponent)比较排序。
return bucketSort(arr, exponent)
}
TSclass RadixSort {
// 基数排序,基于计数排序的基础上,按数字的每个位置来排序
countingSort(arr: Array<number>, exponent: number) {
const countList = Array<number>()
const range = 10
countList.length = range
countList.fill(0)
const min = Math.min.apply(null, arr)
for (let i = 0, l = arr.length; i < l; i++) {
const item = arr[i] - min
// 取得数字的最后一位,并给对应计数数组加1
const idx = Math.floor((item / exponent) % range)
countList[idx] += 1
}
console.log('countingSort countList:', countList)
// 根据位置计数,后面的位数为前面的累加之和
for (let i = 1; i < range; i++) {
countList[i] += countList[i - 1]
}
const sortedList = Array<number>()
// 根据计数数组按顺序取出排序内容
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const item = arr[i] - min
const idx = Math.floor((item / exponent) % range)
sortedList[countList[idx] - 1] = arr[i]
countList[idx] -= 1
}
// 最后赋值给原数据
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = sortedList[i]
}
return sortedList
}
// 基数排序LSD版,基于计数排序的基础,支持负数,按数字的每个位置来排序
radixSort(arr: Array<number>) {
let sortedList = Array<number>()
const max = Math.max.apply(null, arr)
const min = Math.min.apply(null, arr)
for (
let exponent = 1;
Math.floor((max - min) / exponent) > 0;
exponent *= 10
) {
sortedList = this.countingSort(arr, exponent)
}
return sortedList
}
}
C// 计数排序,根据基数按位进行计数
void counting_sort(int arr[], int len, int exponent)
{
int sorted_list[len];
int range = 10;
int count_list[range];
// 找出最小值
int min_value = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < min_value)
min_value = arr[i];
}
memset(count_list, 0, range * sizeof(int));
// 根据数字所在位置进行计数
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
int item = arr[i] - min_value;
int idx = (item / exponent) % range;
count_list[idx]++;
}
// 构建计数排序,当前位置加上左侧位置,后面的位数为前面的累加之和
for (int i = 1; i < range; i++)
{
count_list[i] += count_list[i - 1];
}
// 构建输出数组,根据计数数组按顺序取得排序内容
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
int item = arr[i] - min_value;
int idx = (item / exponent) % range;
// 根据位置重排结果,减去min值还原数据
sorted_list[count_list[idx] - 1] = arr[i];
count_list[idx]--;
}
// 复制到数组重排原始数组
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
arr[i] = sorted_list[i];
}
}
// 基数排序,从低位到高位LSD版,基于计数排序
int *radix_sort(int arr[], int len)
{
int max_value = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > max_value)
max_value = arr[i];
}
int min_value = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < min_value)
min_value = arr[i];
}
// 根据最大值,逐个按进位(基数)来应用排序,exponent即数位基数,按个十百千递增。
for (int exponent = 1; (max_value - min_value) / exponent > 0; exponent *= 10)
{
counting_sort(arr, len, exponent);
}
return arr;
}// 根据最大长度来获取数字第n位的值,从前往后开始,前面不足最大长度时补零
int get_digit_by_position(int num, int position, int max_length)
{
if (num == 0)
{
return 0;
}
int number_length = (int)log10(num) + 1;
// 查询的位置加上自身长度不足最大长度则返回0
if ((position + number_length) < max_length)
{
return 0;
}
int exponent = (int)pow(10, number_length - position);
int digit = 0;
if (exponent > 0)
{
digit = (num / exponent) % 10;
}
return digit;
}
// 基数排序,从高位到逐个对比排序,通过桶排序递归调用
// arr是数组,len是当前数组长度,position为自前往后的位置,max_length是最大值的数位
int *bucket_sort(int arr[], int len, int position, int max_length)
{
printf("\r\nlen=%d position=%d max_length=%d ", len, position, max_length);
if (len <= 1 || position > max_length)
{
return arr;
}
// 找出最小值
int min_value = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < min_value)
min_value = arr[i];
}
int range = 10;
// 桶一共从0-9十个数字
int buckets[range][len];
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++)
{
// 此处未提前使用,也可以不设置默认值
memset(buckets[i], 0, len * sizeof(int));
// print_array(buckets[i], len);
}
// 默认填充内容为0
int bucket_count_list[range];
memset(bucket_count_list, 0, range * sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
int item = arr[i] - min_value;
// 根据数位上的值,减去最小值,分配到对应的桶里
int bucket_idx = get_digit_by_position(item, position, max_length);
// 把数据按下标插入到桶里
int number_idx = bucket_count_list[bucket_idx];
buckets[bucket_idx][number_idx] = arr[i];
bucket_count_list[bucket_idx] += 1;
}
// 将每个桶的数据按顺序逐个取出,重新赋值给原数组
int sorted_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++)
{
int *bucket = buckets[i];
int bucket_len = bucket_count_list[i];
int bucket_size = sizeof(*bucket) / sizeof(bucket[0]);
// 如果只有一个值,则直接更新到原数组
if (bucket_count_list[i] == 1)
{
arr[sorted_idx] = bucket[0];
sorted_idx += 1;
}
else if (bucket_size > 0 && bucket_len > 0)
{
// 如果是数组且记录追加大于1则继续递归调用,位置增加1位
// 递归调用传参时需要传入当前子序列、子序列长度、当前分解的位数基数
int *sorted_bucket = bucket_sort(bucket, bucket_len, position + 1, max_length);
// 依照已排序的子序列实际长度,把各个桶里的值按顺序赋给原数组
for (int j = 0; j < bucket_len; j++)
{
int num = sorted_bucket[j];
arr[sorted_idx] = num;
sorted_idx += 1;
}
}
}
printf("\r\n position:%d", position);
print_array(arr, len);
return arr;
}
// 计数排序,根据数字的位置逐个对比排序,从高到低MSD,递归方式
int *radix_sort_msd(int arr[], int len)
{
// 找出最大值
int max_value = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > max_value)
max_value = arr[i];
}
// 获取最小项
int min_value = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (min_value > arr[i])
{
min_value = arr[i];
}
}
// 获取数字一共有几位,减去min得到最大值,以支持负数和减少最大值
int max_length = (int)(log10(max_value - min_value) + 1);
// 根据数组最大值的长度,从前往后逐个对比排序。
return bucket_sort(arr, len, 1, max_length);
}
C // 基数排序,从个位到高位LSD版,基于计数排序实现
int *radixSort(int *arr, int len)
{
// 以10倍递进
int range = 10;
int sortedList[len];
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > max)
{
max = arr[i];
}
}
int min = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < min)
{
min = arr[i];
}
}
// 根据最大值,逐个按进位(基数)来应用排序,exponent即基数。
for (int exponent = 1; ((max - min) / exponent) > 0; exponent *= range)
{
// 计数数组,长度为10,0-9一共10个数字
int countList[range];
memset(countList, 0, range * sizeof(int));
// 根据基数得到当前位数,并给计数数组对应位置加1
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
int item = arr[i] - min;
int idx = (item / exponent) % range;
countList[idx] += 1;
}
// 计数排序构建,自前往后,逐个将上一项的值存入当前项
for (int i = 1; i < range; i++)
{
countList[i] += countList[i - 1];
}
// 根据计数数组按顺序取出排序内容
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
int item = arr[i] - min;
int idx = (item / exponent) % range;
sortedList[countList[idx] - 1] = arr[i];
countList[idx] -= 1;
}
// 复制输出数组到原始数组
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
arr[i] = sortedList[i];
}
}
return arr;
}
LinkThe difference between radix sort, counting sort, and bucket sortThe concepts of radix sort, counting sort, and bucket sort are very similar, but there are also differences. The main differences are as follows: Counting Sorting: Set several buckets according to the array value, each bucket corresponds to a value, store the values of these buckets in the next bucket for sorting, and finally take out the values in the corresponding buckets in order. Bucket sorting: It is divided into several buckets according to the situation. Each bucket stores a certain range of values. Each bucket is sorted separately, and finally all data is taken out in the order of the buckets. Radix sorting: Allocate buckets according to the number of digits in the data. Each bit corresponds to a bucket. First, align the digits of all data according to the maximum number of digits, and then arrange them according to the value of the digits. Radix sort is based on counting sort or bucket sort. The above is the detailed content of The principles and implementation methods of radix sorting in various programming languages. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What are the alternatives to concatenate two lists in Python?May 09, 2025 am 12:16 AM
What are the alternatives to concatenate two lists in Python?May 09, 2025 am 12:16 AMThere are many methods to connect two lists in Python: 1. Use operators, which are simple but inefficient in large lists; 2. Use extend method, which is efficient but will modify the original list; 3. Use the = operator, which is both efficient and readable; 4. Use itertools.chain function, which is memory efficient but requires additional import; 5. Use list parsing, which is elegant but may be too complex. The selection method should be based on the code context and requirements.
 Python: Efficient Ways to Merge Two ListsMay 09, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python: Efficient Ways to Merge Two ListsMay 09, 2025 am 12:15 AMThere are many ways to merge Python lists: 1. Use operators, which are simple but not memory efficient for large lists; 2. Use extend method, which is efficient but will modify the original list; 3. Use itertools.chain, which is suitable for large data sets; 4. Use * operator, merge small to medium-sized lists in one line of code; 5. Use numpy.concatenate, which is suitable for large data sets and scenarios with high performance requirements; 6. Use append method, which is suitable for small lists but is inefficient. When selecting a method, you need to consider the list size and application scenarios.
 Compiled vs Interpreted Languages: pros and consMay 09, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Compiled vs Interpreted Languages: pros and consMay 09, 2025 am 12:06 AMCompiledlanguagesofferspeedandsecurity,whileinterpretedlanguagesprovideeaseofuseandportability.1)CompiledlanguageslikeC arefasterandsecurebuthavelongerdevelopmentcyclesandplatformdependency.2)InterpretedlanguageslikePythonareeasiertouseandmoreportab
 Python: For and While Loops, the most complete guideMay 09, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Python: For and While Loops, the most complete guideMay 09, 2025 am 12:05 AMIn Python, a for loop is used to traverse iterable objects, and a while loop is used to perform operations repeatedly when the condition is satisfied. 1) For loop example: traverse the list and print the elements. 2) While loop example: guess the number game until you guess it right. Mastering cycle principles and optimization techniques can improve code efficiency and reliability.
 Python concatenate lists into a stringMay 09, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python concatenate lists into a stringMay 09, 2025 am 12:02 AMTo concatenate a list into a string, using the join() method in Python is the best choice. 1) Use the join() method to concatenate the list elements into a string, such as ''.join(my_list). 2) For a list containing numbers, convert map(str, numbers) into a string before concatenating. 3) You can use generator expressions for complex formatting, such as ','.join(f'({fruit})'forfruitinfruits). 4) When processing mixed data types, use map(str, mixed_list) to ensure that all elements can be converted into strings. 5) For large lists, use ''.join(large_li
 Python's Hybrid Approach: Compilation and Interpretation CombinedMay 08, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python's Hybrid Approach: Compilation and Interpretation CombinedMay 08, 2025 am 12:16 AMPythonusesahybridapproach,combiningcompilationtobytecodeandinterpretation.1)Codeiscompiledtoplatform-independentbytecode.2)BytecodeisinterpretedbythePythonVirtualMachine,enhancingefficiencyandportability.
 Learn the Differences Between Python's 'for' and 'while' LoopsMay 08, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Learn the Differences Between Python's 'for' and 'while' LoopsMay 08, 2025 am 12:11 AMThekeydifferencesbetweenPython's"for"and"while"loopsare:1)"For"loopsareidealforiteratingoversequencesorknowniterations,while2)"while"loopsarebetterforcontinuinguntilaconditionismetwithoutpredefinediterations.Un
 Python concatenate lists with duplicatesMay 08, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python concatenate lists with duplicatesMay 08, 2025 am 12:09 AMIn Python, you can connect lists and manage duplicate elements through a variety of methods: 1) Use operators or extend() to retain all duplicate elements; 2) Convert to sets and then return to lists to remove all duplicate elements, but the original order will be lost; 3) Use loops or list comprehensions to combine sets to remove duplicate elements and maintain the original order.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.






