Home >Java >javaTutorial >What is the role of Java load balancing algorithm?
What is the role of Java load balancing algorithm?
- PHPzforward
- 2023-05-07 14:37:18893browse
Preface
Load balancing has extensive and in-depth applications in the Java field. Whether it is the famous nginx or microservice governance components such as dubbo, feign, etc., load balancing algorithms are actually used in them.
The core idea of load balancing lies in its underlying algorithm idea. For example, the well-known algorithms include polling, random, minimum connection, weighted polling, etc. In reality, no matter how it is configured, it is inseparable from its algorithm. The core principles of the load balancing algorithm will be combined with the actual code to make some comprehensive summaries of commonly used load balancing algorithms.
Polling algorithm
Polling means queuing up and taking turns one after another. From the data structure, there is a ring-shaped node, which is covered with servers. The servers are connected end to end and are sequential. When the request comes, the server of a certain node starts to respond. Then the next time the request comes, the subsequent servers will respond in turn, and continue from there.
According to this description, we can easily imagine that we can use A data structure of a two-way (double-ended) linked list to simulate and implement this algorithm
1. Define a server class to identify the linked list nodes in the server
class Server {
Server prev;
Server next;
String name;
public Server(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}2. Core code
/**
* 轮询
*/
public class RData {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RData.class);
//标识当前服务节点,每次请求过来时,返回的是current节点
private Server current;
public RData(String serverName) {
logger.info("init servers : " + serverName);
String[] names = serverName.split(",");
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
Server server = new Server(names[i]);
//当前为空,说明首次创建
if (current == null) {
//current就指向新创建server
this.current = server;
//同时,server的前后均指向自己
current.prev = current;
current.next = current;
} else {
//说明已经存在机器了,则按照双向链表的功能,进行节点添加
addServer(names[i]);
}
}
}
//添加机器节点
private void addServer(String serverName) {
logger.info("add new server : " + serverName);
Server server = new Server(serverName);
Server next = this.current.next;
//在当前节点后插入新节点
this.current.next = server;
server.prev = this.current;
//由于是双向链表,修改下一节点的prev指针
server.next = next;
next.prev = server;
}
//机器节点移除,修改节点的指向即可
private void removeServer() {
logger.info("remove current = " + current.name);
this.current.prev.next = this.current.next;
this.current.next.prev = this.current.prev;
this.current = current.next;
}
//请求。由当前节点处理
private void request() {
logger.info("handle server is : " + this.current.name);
this.current = current.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//初始化两台机器
RData rr = new RData("192.168.10.0,192.168.10.1");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
rr.request();
}
}
}).start();
//3s后,3号机器加入清单
Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000);
rr.addServer("192.168.10.3");
//3s后,当前服务节点被移除
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
rr.removeServer();
}
}Combined the comments to understand the code. The explanation of this code is to examine the underlying capabilities of double-ended linked lists. When operating the linked list structure, the most important thing is to When adding and removing nodes, clarify the forward and backward directions of the nodes, and then it will be no more difficult to understand this code. Run the program below

Summary of the advantages and disadvantages of polling algorithm
The implementation is simple, the machine list can be added or subtracted freely, and the node search time complexity is o(1)
It is not possible to perform biased customization for nodes. Node processing capabilities cannot be differentiated. For example, some servers with strong processing capabilities and high configurations want to bear more requests. This cannot be done
Random algorithm
Randomly select one from the list of available servers to provide a response.
Since it is a random access scenario, it is easy to think that using an array can more efficiently complete random reading through subscripts. The simulation of this algorithm is relatively simple. The code is directly shown below
/**
* 随机
*/
public class RandomMath {
private static List<String> ips;
public RandomMath(String nodeNames) {
System.out.println("init servers : " + nodeNames);
String[] nodes = nodeNames.split(",");
//初始化服务器列表,长度取机器数
ips = new ArrayList<>(nodes.length);
for (String node : nodes) {
ips.add(node);
}
}
//请求处理
public void request() {
Random ra = new Random();
int i = ra.nextInt(ips.size());
System.out.println("the handle server is :" + ips.get(i));
}
//添加节点,注意,添加节点可能会造成内部数组扩容
void addnode(String nodeName) {
System.out.println("add new node : " + nodeName);
ips.add(nodeName);
}
//移除
void remove(String nodeName) {
System.out.println("remove node is: " + nodeName);
ips.remove(nodeName);
}
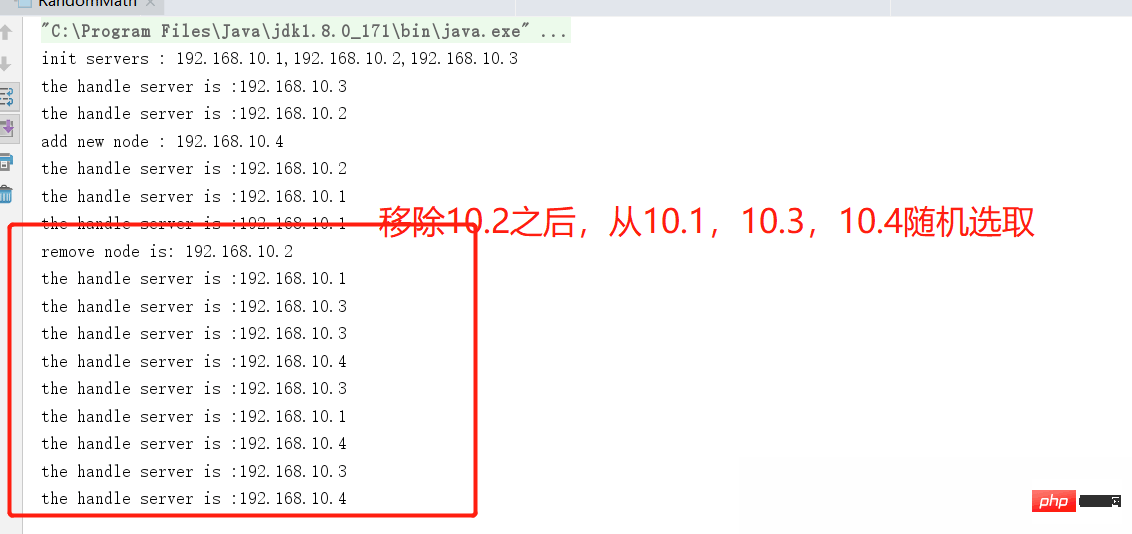
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
RandomMath rd = new RandomMath("192.168.10.1,192.168.10.2,192.168.10.3");
//使用一个线程,模拟不间断的请求
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
rd.request();
}
}
}).start();
//间隔3秒之后,添加一台新的机器
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
rd.addnode("192.168.10.4");
//3s后,当前服务节点被移除
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
rd.remove("192.168.10.2");
}
}Running code observation results:
Summary of random algorithm
The random algorithm is simple and efficient
It is suitable for a server cluster where the configuration of each machine is similar. Like polling, it is not possible to make some directional differentiated treatment based on the configuration of each server itself
Weighted Random Algorithm
On the basis of random selection, machines are still randomly selected, but a set of weighted values is made. According to different weights, each machine in the machine list is selected The probabilities are different. From this perspective, randomness can be considered to be a special case of equal weights.
The design idea is still the same, except that each machine needs to generate a different number of nodes according to the size of the weights. After the nodes are queued, , obtained randomly. The data structure here mainly involves random reading, so the preferred array is
/**
* 加权随机
*/
public class WeightRandom {
ArrayList<String> list;
public WeightRandom(String nodes) {
String[] ns = nodes.split(",");
list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String n : ns) {
String[] n1 = n.split(":");
int weight = Integer.valueOf(n1[1]);
for (int i = 0; i < weight; i++) {
list.add(n1[0]);
}
}
}
public void request() {
//下标,随机数,注意因子
int i = new Random().nextInt(list.size());
System.out.println("the handle server is : " + list.get(i));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
WeightRandom wr = new WeightRandom("192.168.10.1:2,192.168.10.2:1");
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
Thread.sleep(2000);
wr.request();
}
}
}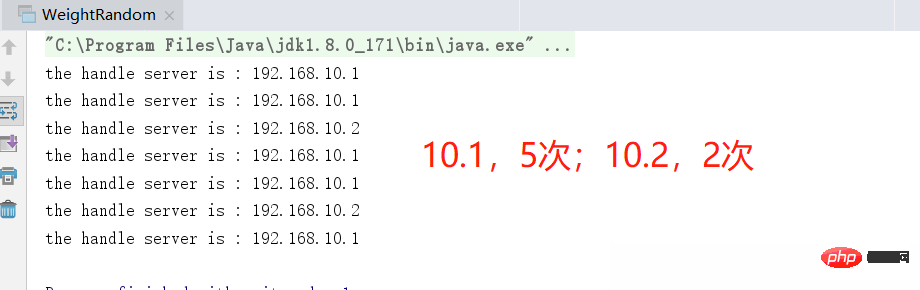
. We might as well adjust the weight value of 10.1 to a larger value, for example, to 3. Run it again and the effect will be even more obvious

Summary of weighted random algorithm
is a random algorithm The upgrade and optimization
solves the problem of server node bias to a certain extent. The bias of a certain machine can be improved by specifying the weight
The algorithm idea of weighted polling is not very easy to understand. I will illustrate it with a diagram below:
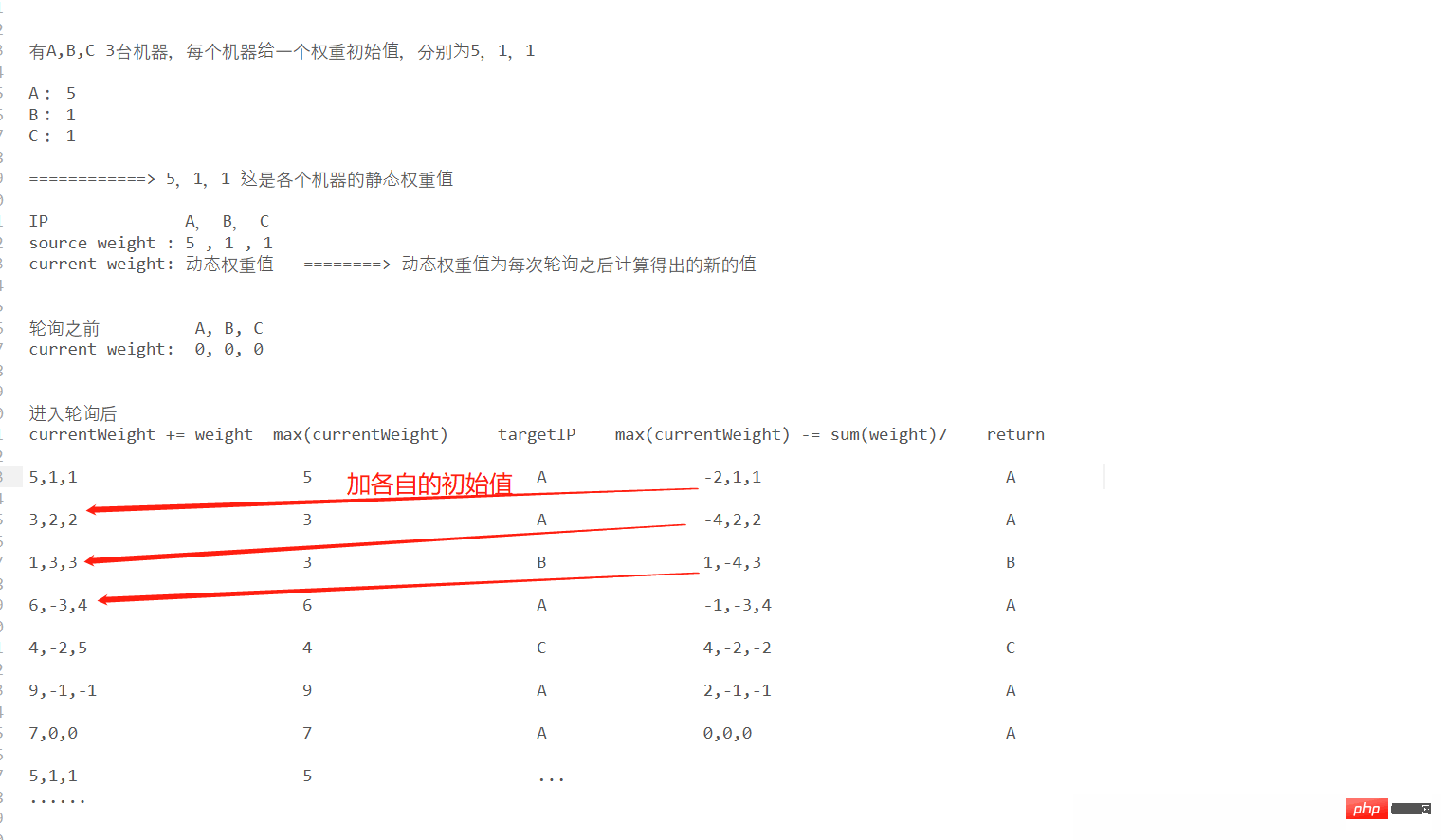

实现思路和轮询差不多,整体仍然是链表结构,不同的是,每个具体的节点需加上权重值属性
1、节点属性类
class NodeServer {
int weight;
int currentWeight;
String ip;
public NodeServer(String ip, int weight) {
this.ip = ip;
this.weight = weight;
this.currentWeight = 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(currentWeight);
}
}2、核心代码
/**
* 加权轮询
*/
public class WeightRDD {
//所有机器节点列表
ArrayList<NodeServer> list;
//总权重
int total;
//机器节点初始化 , 格式:a#4,b#2,c#1,实际操作时可根据自己业务定制
public WeightRDD(String nodes) {
String[] ns = nodes.split(",");
list = new ArrayList<>(ns.length);
for (String n : ns) {
String[] n1 = n.split("#");
int weight = Integer.valueOf(n1[1]);
list.add(new NodeServer(n1[0], weight));
total += weight;
}
}
public NodeServer getCurrent() {
for (NodeServer node : list) {
node.currentWeight += node.weight;
}
NodeServer current = list.get(0);
int i = 0;
//从列表中获取当前的currentWeight最大的那个作为待响应的节点
for (NodeServer node : list) {
if (node.currentWeight > i) {
i = node.currentWeight;
current = node;
}
}
return current;
}
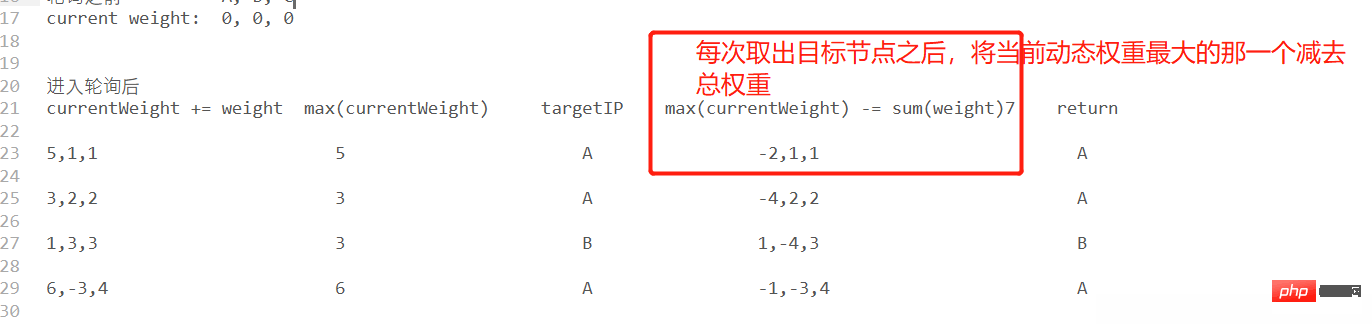
//请求,每次得到请求的节点之后,需要对当前的节点的currentWeight值减去 sumWeight
public void request() {
NodeServer node = this.getCurrent();
System.out.print(list.toString() + "‐‐‐");
System.out.print(node.ip + "‐‐‐");
node.currentWeight -= total;
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
WeightRDD wrr = new WeightRDD("192.168.10.1#4,192.168.10.2#2,192.168.10.3#1");
//7次执行请求,观察结果
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000);
wrr.request();
}
}
}从打印输出结果来看,也是符合预期效果的,具有更大权重的机器,在轮询中被请求到的可能性更大

源地址hash算法
即对当前访问的ip地址做一个hash值,相同的key将会被路由到同一台机器去。常见于分布式集群环境下,用户登录 时的请求路由和会话保持
源地址hash算法可以有效解决在跨地域机器部署情况下请求响应的问题,这一特点使得源地址hash算法具有某些特殊的应用场景
该算法的核心逻辑是需要自定义一个能结合实际业务场景的hash算法,从而确保请求能够尽可能达到源IP机器进行处理
源地址hash算法的实现比较简单,下面直接上代码
/**
* 源地址请求hash
*/
public class SourceHash {
private static List<String> ips;
//节点初始化
public SourceHash(String nodeNames) {
System.out.println("init list : " + nodeNames);
String[] nodes = nodeNames.split(",");
ips = new ArrayList<>(nodes.length);
for (String node : nodes) {
ips.add(node);
}
}
//添加节点
void addnode(String nodeName) {
System.out.println("add new node : " + nodeName);
ips.add(nodeName);
}
//移除节点
void remove(String nodeName) {
System.out.println("remove one node : " + nodeName);
ips.remove(nodeName);
}
//ip进行hash
private int hash(String ip) {
int last = Integer.valueOf(ip.substring(ip.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, ip.length()));
return last % ips.size();
}
//请求模拟
void request(String ip) {
int i = hash(ip);
System.out.println("req ip : " + ip + "‐‐>" + ips.get(i));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SourceHash hash = new SourceHash("192.168.10.1,192.168.10.2");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
String ip = "192.168.1." + i;
hash.request(ip);
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println();
hash.addnode("192.168.10.3");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
String ip = "192.168.1." + i;
hash.request(ip);
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println();
hash.remove("192.168.10.1");
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
String ip = "192.168.1." + i;
hash.request(ip);
}
}
}请关注核心的方法 hash(),我们模拟9个随机请求的IP,下面运行下这段程序,观察输出结果
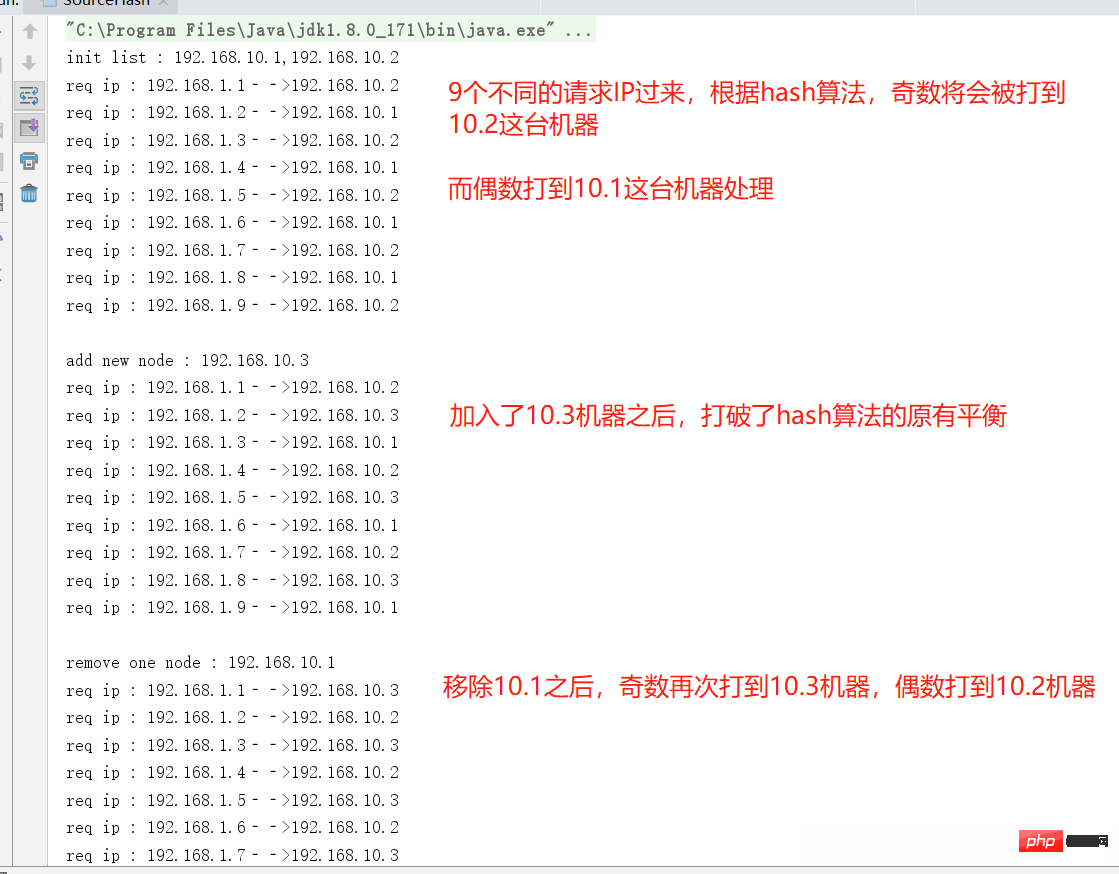
源地址hash算法小结
可以有效匹配同一个源IP从而定向到特定的机器处理
如果hash算法不够合理,可能造成集群中某些机器压力非常大
未能很好的解决新节点加入之后打破原来的请求平衡(一致性hash可解决)
最小请求数算法
即通过统计当前机器的请求连接数,选择当前连接数最少的机器去响应新请求。前面的各种算法是基于请求的维度,而最小 连接数则是站在机器的连接数量维度
从描述来看,实现这种算法需要定义一个链接表记录机器的节点IP,和机器连接数量的计数器
而为了比较并选择出最小的连接数的机器,内部采用最小堆做排序处理,请求响应时取堆顶节点即是 最小连接数(可以参考最小顶堆算法)
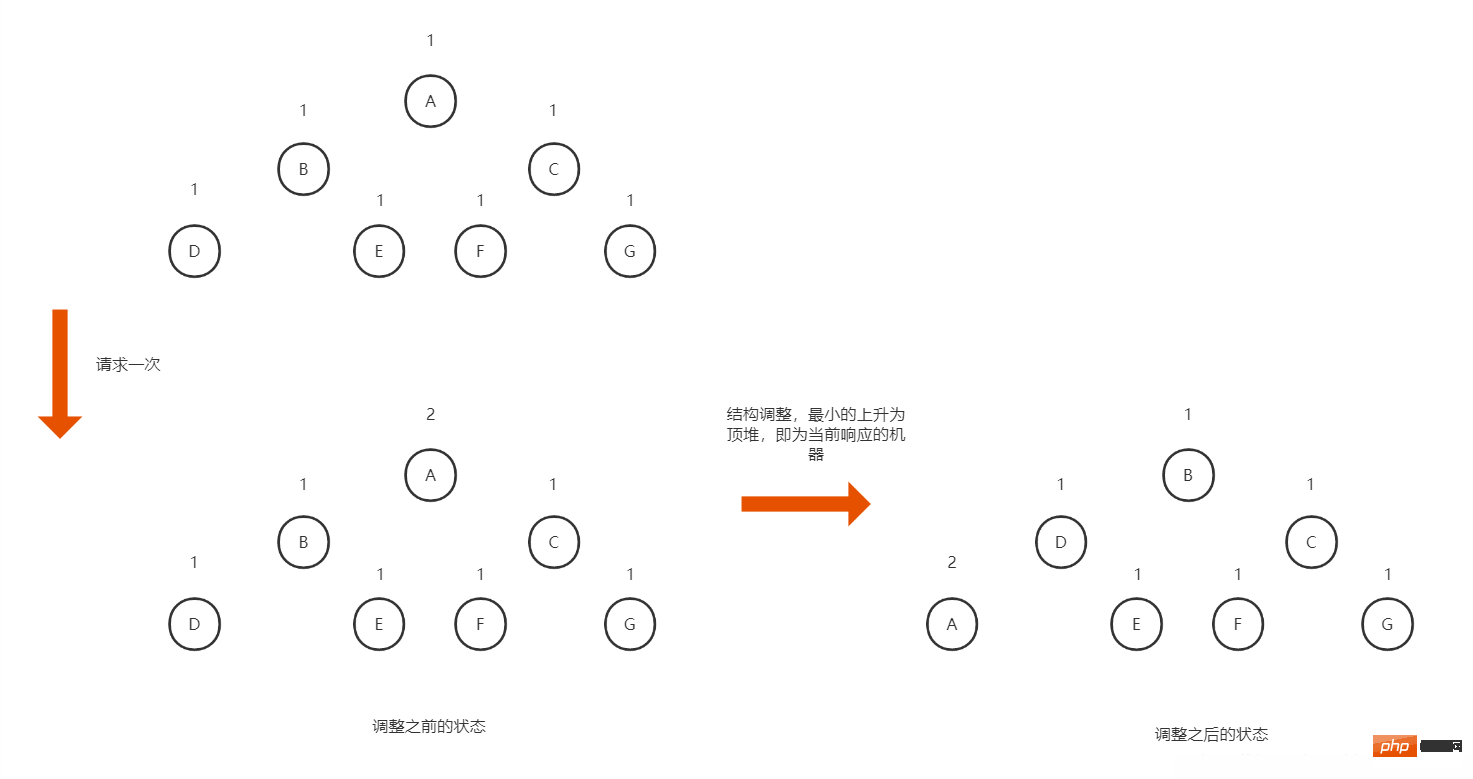
如图所示,所有机器列表按照类二叉树的结构进行组装,组装的依据按照不同节点的访问次数,某次请求过来时,选择堆顶的元素(待响应的机器)返回,然后堆顶机器的请求数量加1,然后通过算法将这个堆顶的元素下沉,把请求数量最小的元素上升为堆顶,以便下次响应最新的请求
1、机器节点
该类记录了节点的IP以及连接数
class Node {
String name;
AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
public Node(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void inc() {
count.getAndIncrement();
}
public int get() {
return count.get();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + "=" + count;
}
}2、核心代码
/**
* 最小连接数算法
*/
public class LeastRequest {
Node[] nodes;
//节点初始化
public LeastRequest(String ns) {
String[] ns1 = ns.split(",");
nodes = new Node[ns1.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < ns1.length; i++) {
nodes[i + 1] = new Node(ns1[i]);
}
}
///节点下沉,与左右子节点比对,选里面最小的交换
//目的是始终保持最小堆的顶点元素值最小【结合图理解】
//ipNum:要下沉的顶点序号
public void down(int ipNum) {
//顶点序号遍历,只要到1半即可,时间复杂度为O(log2n)
while (ipNum << 1 < nodes.length) {
int left = ipNum << 1;
//右子,左+1即可
int right = left + 1;
int flag = ipNum;
//标记,指向 本节点,左、右子节点里最小的,一开始取自己
if (nodes[left].get() < nodes[ipNum].get()) {
flag = left;
}
//判断右子
if (right < nodes.length && nodes[flag].get() > nodes[right].get()) {
flag = right;
}
//两者中最小的与本节点不相等,则交换
if (flag != ipNum) {
Node temp = nodes[ipNum];
nodes[ipNum] = nodes[flag];
nodes[flag] = temp;
ipNum = flag;
} else {
//否则相等,堆排序完成,退出循环即可
break;
}
}
}
//请求,直接取最小堆的堆顶元素就是连接数最少的机器
public void request() {
System.out.println("‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐‐");
//取堆顶元素响应请求
Node node = nodes[1];
System.out.println(node.name + " accept");
//连接数加1
node.inc();
//排序前的堆
System.out.println("ip list before:" + Arrays.toString(nodes));
//堆顶下沉,通过算法将堆顶下层到合适的位置
down(1);
//排序后的堆
System.out.println("ip list after:" + Arrays.toString(nodes));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//假设有7台机器
LeastRequest lc = new LeastRequest("10.1,10.2,10.3,10.4,10.5,10.6,10.7");
//模拟10个请求连接
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
lc.request();
}
}
}请关注 down 方法,该方法是实现每次请求之后,将堆顶元素进行移动的关键实现,运行这段代码,结合输出结果进行理解


The above is the detailed content of What is the role of Java load balancing algorithm?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

