
Bubble sorting principle
Compare two adjacent elements. If the first is larger than the second, swap their positions (in ascending order, vice versa in descending order).
Compare each pair of adjacent elements in sequence from the beginning to the end of the list. In this way, the element with the largest value "bubbles" to the end of the list through exchange, completing the first round of "bubbling".
Repeat the previous step and continue to compare adjacent elements in sequence from the beginning of the list. Elements that have "bubbled" out do not need to be compared (you can compare them all the way to the end. Elements that have "bubbled" to the back do not need to be exchanged even if they are compared. Not comparing can reduce steps).
Continue to compare starting from the list, and one element will "bubble" successfully in each round of comparison. The number of elements that need to be compared in each round will decrease until there is only one element left that does not "bubble" (no pair of elements needs to be compared), then the list sorting is completed.
Bubble sorting process
Take this one-dimensional array as an example:
int[] array = new int[]{55,33,22,66,11};First round of bubbles
Figure ① is a column chart of the starting order of the data in the first round of "bubble". As long as the condition is met: "The previous element is larger than the following element, the position order will be exchanged, otherwise no exchange will be made."
array[0]=55 > array[1]=33, if the conditions are met, exchange the position order of the elements, as shown in Figure ②;
array[1]=55 > array[2]=22, if the conditions are met, exchange the position order of the elements, as shown in Figure ③;
- ##array[2] =55
- array[3]=66 > array[ 4]=11, if the condition is met, the position order of the elements is exchanged, as shown in Figure ④;
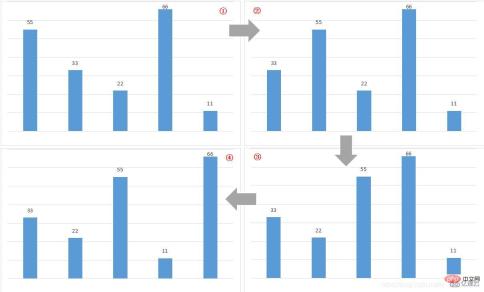
- Figure ④ is a bar chart of the starting order of the data in the second round of "bubble";
- array[0]33 > array[1]=22, if the conditions are met, exchange the position order of the elements, as shown in Figure ⑤; ##array[1 ]33 array[2]55 > array[3 ]=11, the condition is met, and the position order of the elements is exchanged, as shown in Figure ⑥;
- The second round of "bubble" demonstration is as shown in the figure:
 The third round of bubbling
The third round of bubbling
- Figure ⑥ shows the starting sequence column chart of the data in the third round of "bubble";
- array[0]=22 ##array [1]=33 > array[2]=11, if the conditions are met, exchange the position order of the elements, as shown in Figure ⑦;
- The third round of "bubble" demonstration is as follows As shown in the figure:
The fourth round of bubbling
- array[0]=22 > array[1]=11, if the condition is met, exchange the position order of "22" and "11", as shown in Figure ⑧ ;
- The fourth round of "bubble" demonstration is shown in the figure:
At this point, the process of bubble sorting of the array is completed La! 
Specific code implementation
public class BubbleSort {
public static void sort(int array[]) {
//i表示第几轮“冒泡”,j 表示“走访”到的元素索引。
// 每一轮“冒泡”中,j 需要从列表开头“走访”到 array.length - 1 的位置。
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}}
TestMain classimport java.util.Arrays;public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[]{55, 33, 22, 66, 11};
//输出排序前的array数组
System.out.print("排序前:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
//调用BubbleSort类中的sort方法对array数组进行排序
BubbleSort.sort(array);
//输出冒泡排序后的array数组
System.out.print("排序后:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}}The running results are as follows: 排序前:[55, 33, 22, 66, 11]排序后:[11, 22, 33, 55, 66]
The above is the detailed content of How to write code to implement bubble sort in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PMThe article discusses using Maven and Gradle for Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution, comparing their approaches and optimization strategies.
 How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PMThe article discusses creating and using custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management, using tools like Maven and Gradle.
 How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PMThe article discusses implementing multi-level caching in Java using Caffeine and Guava Cache to enhance application performance. It covers setup, integration, and performance benefits, along with configuration and eviction policy management best pra
 How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PMThe article discusses using JPA for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading. It covers setup, entity mapping, and best practices for optimizing performance while highlighting potential pitfalls.[159 characters]
 How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PMJava's classloading involves loading, linking, and initializing classes using a hierarchical system with Bootstrap, Extension, and Application classloaders. The parent delegation model ensures core classes are loaded first, affecting custom class loa
 How can I use Java's RMI (Remote Method Invocation) for distributed computing?Mar 11, 2025 pm 05:53 PM
How can I use Java's RMI (Remote Method Invocation) for distributed computing?Mar 11, 2025 pm 05:53 PMThis article explains Java's Remote Method Invocation (RMI) for building distributed applications. It details interface definition, implementation, registry setup, and client-side invocation, addressing challenges like network issues and security.
 How do I use Java's sockets API for network communication?Mar 11, 2025 pm 05:53 PM
How do I use Java's sockets API for network communication?Mar 11, 2025 pm 05:53 PMThis article details Java's socket API for network communication, covering client-server setup, data handling, and crucial considerations like resource management, error handling, and security. It also explores performance optimization techniques, i
 How can I create custom networking protocols in Java?Mar 11, 2025 pm 05:52 PM
How can I create custom networking protocols in Java?Mar 11, 2025 pm 05:52 PMThis article details creating custom Java networking protocols. It covers protocol definition (data structure, framing, error handling, versioning), implementation (using sockets), data serialization, and best practices (efficiency, security, mainta


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






