 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI July's most popular AI research list is released, with Ma Yi's latest 'Standard Model” ranked ninth
July's most popular AI research list is released, with Ma Yi's latest 'Standard Model” ranked ninthThe list of the most popular AI research in July is out!
This list compiled by Reddit netizen @bycloudai is ranked among the top ten AI research in July 2022 based on Twitter likes, retweets and Github stars, including DeepMind, Google, Well-known institutions such as MIT CSAIL.
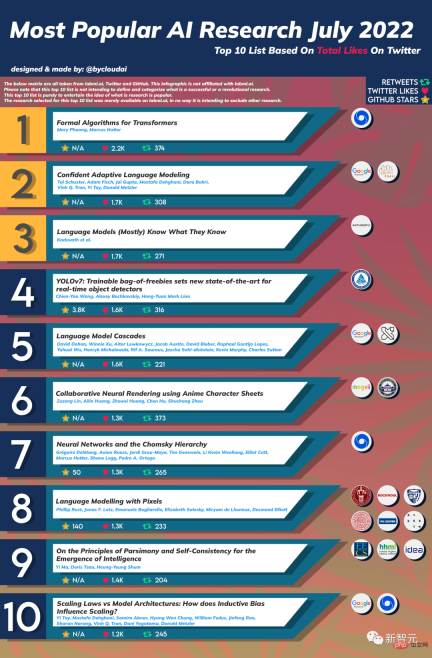
Let’s take a look at who is on the list~
TOP1: Formal Algorithms for Transformers
Author: Mary Phuong, Marcus Hutter
Institution: DeepMind

Abstract: This paper is intended to be a stand-alone, mathematically accurate overview of the Transformer architecture and algorithm. It covers what Transformers are, how they are trained, their uses, their key architectural components and a preview of the most prominent models.
Top2: Confident Adaptive Language Modeling
Authors: Tal Schuster, Adam Fisch, Jai Gupta, Mostafa Dehghani, Dara Bahri, Vinh Q Tran, Yi Tay, Donald Metzler
Institutions: Google, MIT CSAIL

Abstract: Recent advances in Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) have driven significant performance improvements on many tasks. However, while performance improves, model size also increases dramatically, which may lead to complex inference processes and increased costs. In practice, however, large language models produce a series of iterations consisting of varying degrees of difficulty.
In this work, we introduce Confident Adaptive Language Model-ing (CALM), a framework for dynamically allocating varying amounts of computer input and generation duration.
Early exit decoding involves several issues we address here, such as: (1) what confidence measure to use; (2) linking sequence-level constraints to exit decisions for local tokens; (3) backtracking Hidden representation lost due to early exit of the previous token. Through theoretical analysis and experiments on three different text generation tasks, we demonstrate the efficacy of our framework in reducing computation – potentially speeding up up to 3x while maintaining high performance.
Top3:Language Models (Mostly) Know What They Know
Author: Saurav Kadavath, Tom Conerly, Amanda Askell, Tom Henighan, etc.
Organization: Anthropic

Abstract: This paper investigates whether language models can assess the validity of their own claims and predict which questions they will be able to answer correctly. We first show that when larger models are provided in the correct format, they calibrate well to a variety of multiple choice and true/false questions. Therefore, we can self-evaluate the open sampling task by asking the model to first propose an answer and then evaluate the probability P(True) that its answer is correct.
We find P(True) exciting in its performance, calibration, and scaling across a variety of tasks. The performance of the self-assessment improves further when we allow the model to consider many of its own samples before predicting the validity of a particular possibility. Next, we investigate whether we can train a model to predict P(IK), the probability of "I know the answer to the question", without reference to any specific suggested answer.
Top4:YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time objectdetectors
Authors: Chien-Yao Wang, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Hong-Yuan Mark Liao
Institution: Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica

Top5: Language Model Cascades
Author: David Dohan, Winnie Xu, Aitor Lewkowycz et al
Institution: Google

Top6: Collaborative Neural Rendering using AnimeCharacter Sheets
Author: Zuzeng Lin, Ailin Huang, Zhewei Huang et al
Institution: Wuhan University, Megvii Technology

Top7: Neural Networks and the Chomsky Hierarchy
Author: Grégoire Delétang, Anian Ruoss, Jordi Grau-Moya, Tim Genewein, etc.
Institution: DeepMind

 Top8: Language modeling with Pixels
Top8: Language modeling with Pixels
Author: Phillip Rust, Jonas F. Lotz, Emanuele Bugliarello, etc.
Institution: University of Copenhagen, Johns Hopkins University, Uppsala University




The above is the detailed content of July's most popular AI research list is released, with Ma Yi's latest 'Standard Model” ranked ninth. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 ai合并图层的快捷键是什么Jan 07, 2021 am 10:59 AM
ai合并图层的快捷键是什么Jan 07, 2021 am 10:59 AMai合并图层的快捷键是“Ctrl+Shift+E”,它的作用是把目前所有处在显示状态的图层合并,在隐藏状态的图层则不作变动。也可以选中要合并的图层,在菜单栏中依次点击“窗口”-“路径查找器”,点击“合并”按钮。
 ai橡皮擦擦不掉东西怎么办Jan 13, 2021 am 10:23 AM
ai橡皮擦擦不掉东西怎么办Jan 13, 2021 am 10:23 AMai橡皮擦擦不掉东西是因为AI是矢量图软件,用橡皮擦不能擦位图的,其解决办法就是用蒙板工具以及钢笔勾好路径再建立蒙板即可实现擦掉东西。
 谷歌超强AI超算碾压英伟达A100!TPU v4性能提升10倍,细节首次公开Apr 07, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
谷歌超强AI超算碾压英伟达A100!TPU v4性能提升10倍,细节首次公开Apr 07, 2023 pm 02:54 PM虽然谷歌早在2020年,就在自家的数据中心上部署了当时最强的AI芯片——TPU v4。但直到今年的4月4日,谷歌才首次公布了这台AI超算的技术细节。论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.01433相比于TPU v3,TPU v4的性能要高出2.1倍,而在整合4096个芯片之后,超算的性能更是提升了10倍。另外,谷歌还声称,自家芯片要比英伟达A100更快、更节能。与A100对打,速度快1.7倍论文中,谷歌表示,对于规模相当的系统,TPU v4可以提供比英伟达A100强1.
 ai可以转成psd格式吗Feb 22, 2023 pm 05:56 PM
ai可以转成psd格式吗Feb 22, 2023 pm 05:56 PMai可以转成psd格式。转换方法:1、打开Adobe Illustrator软件,依次点击顶部菜单栏的“文件”-“打开”,选择所需的ai文件;2、点击右侧功能面板中的“图层”,点击三杠图标,在弹出的选项中选择“释放到图层(顺序)”;3、依次点击顶部菜单栏的“文件”-“导出”-“导出为”;4、在弹出的“导出”对话框中,将“保存类型”设置为“PSD格式”,点击“导出”即可;
 GPT-4的研究路径没有前途?Yann LeCun给自回归判了死刑Apr 04, 2023 am 11:55 AM
GPT-4的研究路径没有前途?Yann LeCun给自回归判了死刑Apr 04, 2023 am 11:55 AMYann LeCun 这个观点的确有些大胆。 「从现在起 5 年内,没有哪个头脑正常的人会使用自回归模型。」最近,图灵奖得主 Yann LeCun 给一场辩论做了个特别的开场。而他口中的自回归,正是当前爆红的 GPT 家族模型所依赖的学习范式。当然,被 Yann LeCun 指出问题的不只是自回归模型。在他看来,当前整个的机器学习领域都面临巨大挑战。这场辩论的主题为「Do large language models need sensory grounding for meaning and u
 ai顶部属性栏不见了怎么办Feb 22, 2023 pm 05:27 PM
ai顶部属性栏不见了怎么办Feb 22, 2023 pm 05:27 PMai顶部属性栏不见了的解决办法:1、开启Ai新建画布,进入绘图页面;2、在Ai顶部菜单栏中点击“窗口”;3、在系统弹出的窗口菜单页面中点击“控制”,然后开启“控制”窗口即可显示出属性栏。
 ai移动不了东西了怎么办Mar 07, 2023 am 10:03 AM
ai移动不了东西了怎么办Mar 07, 2023 am 10:03 AMai移动不了东西的解决办法:1、打开ai软件,打开空白文档;2、选择矩形工具,在文档中绘制矩形;3、点击选择工具,移动文档中的矩形;4、点击图层按钮,弹出图层面板对话框,解锁图层;5、点击选择工具,移动矩形即可。
 强化学习再登Nature封面,自动驾驶安全验证新范式大幅减少测试里程Mar 31, 2023 pm 10:38 PM
强化学习再登Nature封面,自动驾驶安全验证新范式大幅减少测试里程Mar 31, 2023 pm 10:38 PM引入密集强化学习,用 AI 验证 AI。 自动驾驶汽车 (AV) 技术的快速发展,使得我们正处于交通革命的风口浪尖,其规模是自一个世纪前汽车问世以来从未见过的。自动驾驶技术具有显着提高交通安全性、机动性和可持续性的潜力,因此引起了工业界、政府机构、专业组织和学术机构的共同关注。过去 20 年里,自动驾驶汽车的发展取得了长足的进步,尤其是随着深度学习的出现更是如此。到 2015 年,开始有公司宣布他们将在 2020 之前量产 AV。不过到目前为止,并且没有 level 4 级别的 AV 可以在市场


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.




 Top8: Language modeling with Pixels
Top8: Language modeling with Pixels

