Last week I sent you an introduction to GPT-4 teaching mathematics. Many people were shocked and felt that it might trigger a revolution in the education industry.
How does it perform in the programming field? Let’s not talk about whether it can replace programmers. This still needs more testing and feedback. I want to try first whether it can teach programming like mathematics.
I found a concept that is difficult to understand in Java programming: dynamic proxy and tested it.
The following is the complete conversation I had with it, where I pretended to be a newbie learning Java programming and didn’t know the proxy pattern to see how it taught me.
The content is a bit long. It is recommended to read it patiently and feel the capabilities of AI.
If you really can’t stand it, you can skip to the end and watch the highlights directly.
[Liu Xin]: Suppose you are a tutor who always answers questions in a Socratic style. You won't give me the answer directly, but will guide me to think, okay?
[GPT]: Of course. If you have any questions, let me guide you to think and discuss.
[Liu Xin]: I am learning Java, and there is a concept of dynamic proxy, which I can’t understand
[GPT]: Very good, let’s use the Socratic method together Explore Java dynamic proxies. First, we need to understand the proxy pattern. What do you know about the agency model? What is the purpose of proxy pattern?
[Liu Xin]: Does it mean that one person does things for another person?
[GPT]: Yes, in a sense, the proxy pattern is to implement similar concepts in software design. In this case, one object (the agent) performs a specific task on behalf of another object (the target object). Now, think about it, why might we need to use the proxy pattern in programming? In what situations would using proxy mode be helpful?
[Liu Xin]: I don’t know
[GPT]: It doesn’t matter, let’s explore some possible reasons together. The proxy pattern is useful in many scenarios, such as when we need to perform some additional operations before or after accessing an object. For example, we can use the proxy pattern in the following situations:
Control access to the target object (access control)
Add additional functionality before and after the target object performs operations (such as logging, caching, etc. )
Lazy loading, creating target objects only when really needed
These are just some application scenarios of the proxy pattern. So, in your opinion, how do dynamic proxies come into play in these scenarios? What is the difference between dynamic proxies and static proxies?
[Liu Xin] What does this mean, I don’t understand it
[GPT] It doesn’t matter, we can help you understand the proxy mode through a simple example.
Suppose you have an application that needs to connect to a remote server to get data. In this case, you can create a class called RemoteServerConnection, which is responsible for establishing a connection with the remote server and getting data.
Now, your application needs to perform some additional actions, such as checking the network status before connecting to the remote server and logging after fetching the data. At this time, you can use proxy mode.
You can create a class called RemoteServerConnectionProxy, which has the same interface as RemoteServerConnection, but adds the functionality of checking network status and logging. The application will use RemoteServerConnectionProxy to get data instead of using RemoteServerConnection directly. The RemoteServerConnectionProxy will handle additional operations and then communicate with the RemoteServerConnection on behalf of the application when needed.
In this example, RemoteServerConnectionProxy is a proxy that represents RemoteServerConnection (target object) to perform specific tasks.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the proxy model, let's look at dynamic proxy. In the above example, we created a separate proxy class (static proxy). Unlike static proxies, dynamic proxies are dynamically generated at runtime rather than written in advance. Dynamic agents can respond to different scenarios more flexibly.
In Java, dynamic proxies are usually implemented by implementing the InvocationHandler interface and using the Proxy class. So, think about it, why dynamic proxies might have advantages over static proxies in some situations?
[Liu Xin]: Wait a minute, let’s finish talking about the static proxy first. In your example
RemoteServerConnectionProxy adds some functions for checking network status and logging to the previous class, but why does it have the same interface as RemoteServerConnection?
[GPT]: Sorry I didn’t explain it clearly before. Let's review the purpose of the proxy pattern: one object (the proxy) performs a specific task on behalf of another object (the target object). In order for the proxy object to successfully perform tasks on behalf of the target object, they need to have the same interface. This way, the client code doesn't care whether it's interacting with the proxy object or the target object, because they have the same interface.
In our example, RemoteServerConnectionProxy (proxy object) and RemoteServerConnection (target object) have the same interface, because this way the application can use these two classes transparently. When we decide to use a proxy in our application, we don't need to change the client code because both the proxy object and the target object implement the same interface. This is why the proxy object and the target object need to have the same interface.
In addition, having the same interface means that the proxy object can call the target object's methods when performing tasks. This is important for implementing additional functionality like access control, logging, etc., as the proxy object needs to pass control to the target object at the appropriate time.
[Liu Xin]: I understand, this is the proxy mode. So what is a dynamic proxy?
[GPT]: Very good, now that you have understood the proxy mode, let's continue to discuss dynamic proxy.
The main difference between dynamic and static proxies is how they are created. Static proxies are pre-written proxy classes, which means that for each target class, you need to create a separate proxy class for it. However, dynamic proxies are dynamically generated at runtime, which allows you to create generic proxies for multiple classes without changing the source code. This way, you reduce code duplication and improve maintainability.
In Java, dynamic proxy is mainly implemented through the java.lang.reflect.Proxy class and the java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler interface. The following are the basic steps of a dynamic proxy:
Define an InvocationHandler implementation class, which is responsible for processing method calls on the proxy object. In this class, you can add additional operations as needed, such as logging, access control, etc.
Use the Proxy.newProxyInstance() method to create a dynamic proxy. This method receives three parameters: class loader, interface array (the interface that the proxy class needs to implement) and InvocationHandler instance. This method returns a proxy object that implements the specified interface.
In client code, use the created dynamic proxy object to call methods. When you call a method on the proxy object, it forwards the call to the invoke() method of the InvocationHandler instance.
This way, you can create dynamic proxies for one or more classes at runtime without having to write a separate proxy class for each class.
Now that you understand the concept of dynamic proxies, please think about the advantages and limitations of dynamic proxies compared to static proxies.
[Liu Xin] looked confused
[GPT] It doesn’t matter, let us try to help you understand dynamic proxy through a simple example.
Suppose we have a Bank interface, which has a method transfer() to perform transfer operations. We want to add logging functionality to this interface, but we don't want to modify the implementation of the Bank interface. At this time, we can use dynamic proxy.
First, we need to implement an InvocationHandler. This class will be responsible for handling the method invocation of the proxy object and adding logging functionality:
public class LoggingHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
public LoggingHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("日志记录:开始执行 " + method.getName() + " 方法");
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("日志记录:执行 " + method.getName() + " 方法完成");
return result;
}
}
Now, we can use Proxy. The newProxyInstance() method creates a dynamic proxy for the Bank interface. Note that we need to pass the implementation class instance of the Bank interface to LoggingHandler:
Bank realBank = new RealBank(); // 假设RealBank是Bank接口的一个实现 InvocationHandler handler = new LoggingHandler(realBank); Bank proxyBank = (Bank) Proxy.newProxyInstance( realBank.getClass().getClassLoader(), realBank.getClass().getInterfaces(), handler );
Now, when we call the transfer() method using proxyBank, the logging function will be automatically added:
proxyBank.transfer();
Pass With this example, we can see the main advantage of dynamic proxies: instead of writing a separate proxy class for each class, a generic proxy can be created for one or more classes at runtime. At the same time, it also makes the code more flexible and easier to maintain.
However, dynamic proxies also have some limitations. For example, in Java, dynamic proxies can only create proxies for classes that implement interfaces. If the class does not implement any interface, dynamic proxies cannot be used.
Hope this example can help you understand the concept of dynamic proxy. If you still have any questions, please feel free to ask.
[Liu Xin]: In your example, we hope to add logging function to the Bank interface. Then I can just write a BankProxy and add the logging code? Why go to all the trouble to use InvocationHandler?
[GPT]: You raised a very good question. In some cases, using a static proxy (such as the BankProxy you mentioned) can indeed achieve the functionality we want. However, in more complex scenarios, dynamic proxies may bring some significant advantages:
Versatility: Dynamic proxies can create proxies for multiple classes and interfaces without having to write separate Agent class. If you need to add the same functionality to many interfaces, such as logging, access control, etc., dynamic proxies can help you reduce duplicate code and improve code reusability.
Easy to maintain: If you need to modify or add the functionality of the proxy in the future, it will be easier to use a dynamic proxy. For static proxies, you need to modify each proxy class one by one; for dynamic proxies, you only need to modify the InvocationHandler implementation. This way you can easily modify the agent's behavior without changing the original classes and interfaces.
Decoupling: Dynamic proxies help separate proxy logic from business logic. When you need to modify the proxy logic, there is no need to change the original class and interface. This makes the code easier to understand and maintain.
Still, dynamic proxies are not always the best solution. In some cases, a static proxy may suit your needs better. When choosing between using a dynamic proxy or a static proxy, you need to weigh the pros and cons based on specific scenarios and needs.
Hope this answer can help you better understand the difference between dynamic proxy and static proxy. If you have any further questions, please feel free to ask.
[Liu Xin]: I understand, but why do we need to create a new class through Proxy.newProxyInstance? Isn’t it good to modify the original RealBank class directly?
[GPT]: Your question involves the concepts of code design and decoupling. It is of course feasible to directly modify the RealBank class to add logging functionality, but this may lead to the following problems:
Single responsibility principle: According to the single responsibility principle, a class should only be responsible for one clear function. The main responsibility of the RealBank class is to implement the Bank interface and handle bank-related business logic. If we add logging functionality in the RealBank class, it will be responsible for both business logic and logging, which may violate the single responsibility principle. By using proxies, we can separate these two responsibilities so that each class focuses on a well-defined function.
Decoupling: If we add logging functionality directly to the RealBank class, we will need to change the implementation of the RealBank class when we need to modify or remove the logging functionality in the future. This may result in the RealBank class being tightly coupled with the logging functionality, reducing the maintainability of the code. By using a proxy, we can separate the logging functionality from the RealBank class so that if we need to modify or remove the logging functionality, we do not need to change the RealBank class.
Reusability: Suppose we want to add logging functionality to multiple classes. If we directly modify the implementation of each class, this will lead to a lot of duplication of code. By using proxies (especially dynamic proxies), we can provide common logging functions for multiple classes, thereby reducing code duplication and improving code reusability.
In short, by using proxies, we can follow the single responsibility principle, achieve decoupling, and improve code reusability. While directly modifying the original class is feasible in some cases, there are many scenarios where using a proxy can lead to better code design and maintainability.
Hope this answer is helpful to you. If you have any further questions, please feel free to ask.
[Liu Xin]: The parameters of Proxy.newProxyInstance are so complicated. I understand passing
InvocationHandler in. Why do we need to pass the other two parameters?
[GPT]: The Proxy.newProxyInstance method does require three parameters. Let me explain their functions in detail:
ClassLoader: The class loader is responsible for loading byte code into the Java virtual machine. The purpose of passing the class loader is to let the Proxy.newProxyInstance method know where to look for the class definition and how to load the proxy class into memory. Usually, we use the class loader of the target class because we want the proxy class to be loaded in the same class loader as the target class. This ensures that the proxy class has access to the target class's interface. In most cases, the class loader of the target class can be obtained through target.getClass().getClassLoader().
Interface array (Interface[]): The interface array defines the interface that the proxy class needs to implement. These interfaces are usually the same as those implemented by the target class so that the proxy class can transparently substitute for the target class. When the methods of the proxy object are called, the InvocationHandler will handle the methods defined in these interfaces. In most cases, the interfaces implemented by the target class can be obtained through target.getClass().getInterfaces().
InvocationHandler instance: This parameter is an instance of InvocationHandler implementation, which is responsible for processing method calls of proxy objects. When the proxy object's method is called, the InvocationHandler's invoke() method will be executed. We can customize the behavior of the proxy object by passing an InvocationHandler instance to the Proxy.newProxyInstance method.
Although the Proxy.newProxyInstance method requires three parameters, they are all to ensure that the proxy class can be loaded correctly, implement the interface of the target class, and customize the behavior of the proxy object. Hopefully this explanation helps you understand what these parameters do. If you have any further questions, please feel free to ask.
[Liu Xin]: Although your answer is a bit long-winded, I still understand it
[GPT]: I’m glad you understand. The reason why I explain it in detail is to ensure that you fully understand the parameters of this method and what it does. If you encounter other questions while studying, or need a more concise explanation, please feel free to ask. I will try my best to help you. I wish you good luck with your studies!
Highlights
In terms of teaching methods:
1. It starts from a simple concept (static proxy), very good!
2. When I don’t understand a concept, I will explain it with examples, which is very good!
3. When I deliberately express my incomprehension about what it says, it can explain further every time.
4. It is a bit eager to introduce dynamic agents, and it can go back to the basic concepts during my repeated questions.
Technically, it explains accurately:
1. Why there is a dynamic proxy and the difference between it and a dynamic proxy.
2. Why does Proxy need to be the same as the original class interface?
3. Why three parameters are needed to create a dynamic proxy.
4. Introduced some design principles (single responsibility), decoupling, reuse and other functions.
Whether it is the teaching method or the teaching of knowledge, GPT-4 is very good. I think even if there is an excellent lecturer, this is probably the case.
It just feels like it's a bit verbose. It would be better if it supports voice effects.
No matter how GPT-4 is done internally, it behaves like a programming master externally. Not only has it mastered the concept of dynamic proxy, it has a large number of examples to support it, and it can also explain it from simple to deep. , very powerful. I will try its design capabilities later and share it with you.
The above is the detailed content of GPT-4 is a master of programming, I'm really convinced!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
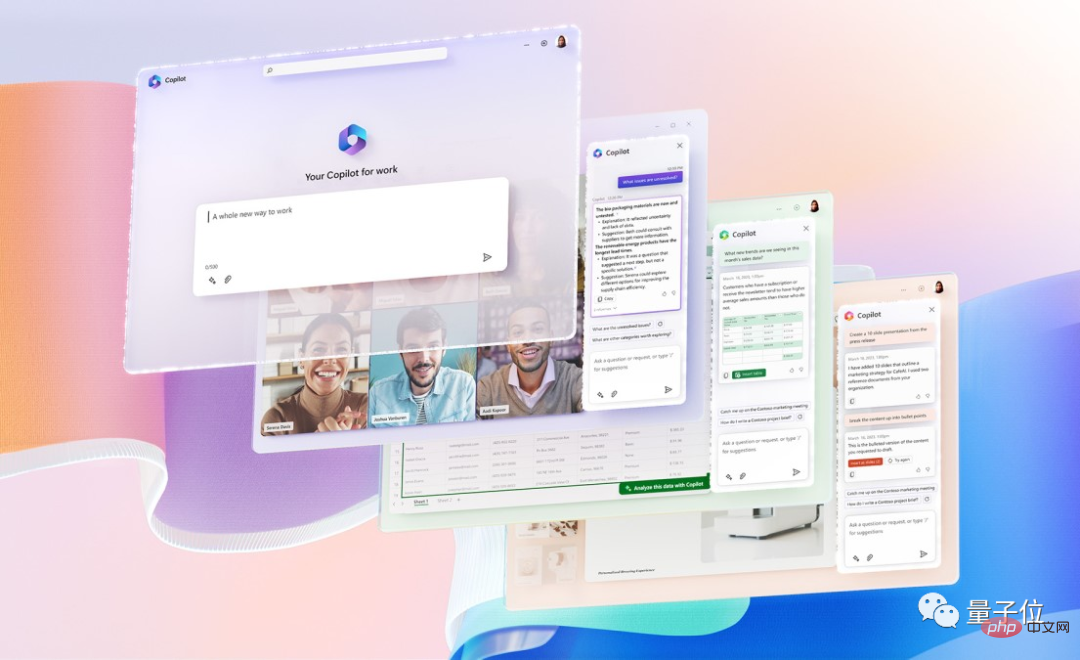 GPT-4接入Office全家桶!Excel到PPT动嘴就能做,微软:重新发明生产力Apr 12, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
GPT-4接入Office全家桶!Excel到PPT动嘴就能做,微软:重新发明生产力Apr 12, 2023 pm 02:40 PM一觉醒来,工作的方式被彻底改变。微软把AI神器GPT-4全面接入Office,这下ChatPPT、ChatWord、ChatExcel一家整整齐齐。CEO纳德拉在发布会上直接放话:今天,进入人机交互的新时代,重新发明生产力。新功能名叫Microsoft 365 Copilot(副驾驶),与改变了程序员的代码助手GitHub Copilot成为一个系列,继续改变更多人。现在AI不光能自动做PPT,而且能根据Word文档的内容一键做出精美排版。甚至连上台时对着每一页PPT应该讲什么话,都给一起安排
 集成GPT-4的Cursor让编写代码和聊天一样简单,用自然语言编写代码的新时代已来Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:15 PM
集成GPT-4的Cursor让编写代码和聊天一样简单,用自然语言编写代码的新时代已来Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:15 PM集成GPT-4的Github Copilot X还在小范围内测中,而集成GPT-4的Cursor已公开发行。Cursor是一个集成GPT-4的IDE,可以用自然语言编写代码,让编写代码和聊天一样简单。 GPT-4和GPT-3.5在处理和编写代码的能力上差别还是很大的。官网的一份测试报告。前两个是GPT-4,一个采用文本输入,一个采用图像输入;第三个是GPT3.5,可以看出GPT-4的代码能力相较于GPT-3.5有较大能力的提升。集成GPT-4的Github Copilot X还在小范围内测中,而
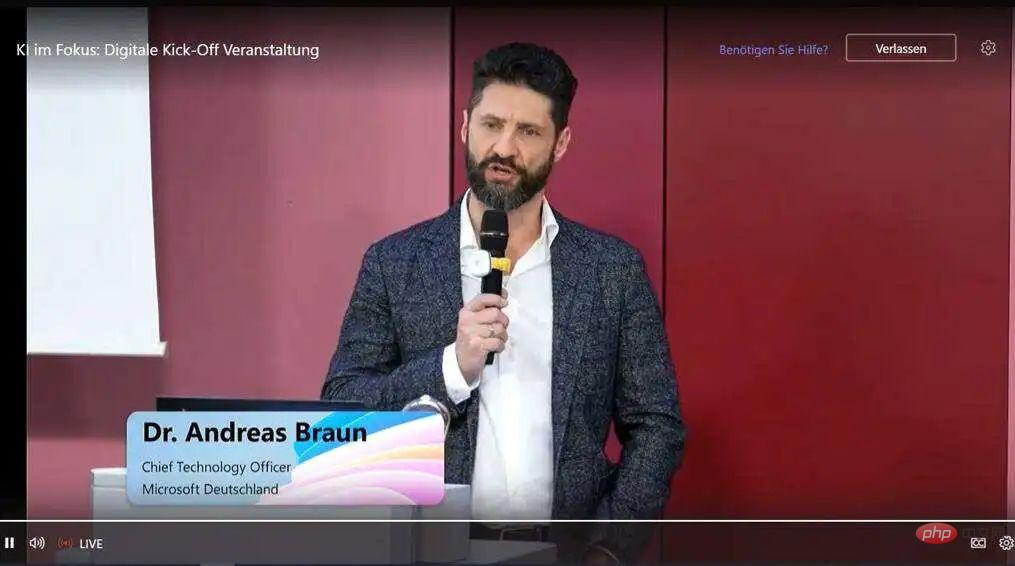 GPT-4的两个谣言和最新预测!Apr 11, 2023 pm 06:07 PM
GPT-4的两个谣言和最新预测!Apr 11, 2023 pm 06:07 PM作者 | 云昭3月9日,微软德国CTO Andreas Braun在AI kickoff会议上带来了一个期待已久的消息:“我们将于下周推出GPT-4,届时我们将推出多模式模式,提供完全不同的可能性——例如视频。”言语之中,他将大型语言模型(LLM)比作“游戏改变者”,因为他们教机器理解自然语言,然后机器以统计的方式理解以前只能由人类阅读和理解的东西。与此同时,这项技术已经发展到“适用于所有语言”:你可以用德语提问,也可以用意大利语回答。借助多模态,微软(-OpenAI)将“使模型变得全面”。那
 再一次改变“AI”世界 GPT-4千呼万唤始出来Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:40 PM
再一次改变“AI”世界 GPT-4千呼万唤始出来Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:40 PM近段时间,人工智能聊天机器人ChatGPT刷爆网络,网友们争先恐后去领略它的超高情商和巨大威力。参加高考、修改代码、构思小说……它在广大网友的“鞭策”下不断突破自我,甚至可以用一整段程序,为你拼接出一只小狗。而这些技能只是基于GPT-3.5开发而来,在3月15日,AI世界再次更新,最新版本的GPT-4也被OpenAI发布了出来。与之前相比,GPT-4不仅展现了更加强大的语言理解能力,还能够处理图像内容,在考试中的得分甚至能超越90%的人类。那么,如此“逆天”的GPT-4还具有哪些能力?它又是如何
 当GPT-4反思自己错了:性能提升近30%,编程能力提升21%Apr 04, 2023 am 11:55 AM
当GPT-4反思自己错了:性能提升近30%,编程能力提升21%Apr 04, 2023 am 11:55 AMGPT-4 的思考方式,越来越像人了。 人类在做错事时,会反思自己的行为,避免再次出错,如果让 GPT-4 这类大型语言模型也具备反思能力,性能不知道要提高多少了。众所周知,大型语言模型 (LLM) 在各种任务上已经表现出前所未有的性能。然而,这些 SOTA 方法通常需要对已定义的状态空间进行模型微调、策略优化等操作。由于缺乏高质量的训练数据、定义良好的状态空间,优化模型实现起来还是比较难的。此外,模型还不具备人类决策过程所固有的某些品质,特别是从错误中学习的能力。不过现在好了,在最近的一篇论文
 「数学天才」陶哲轩:GPT-4无法攻克一个未解决的数学问题,但对工作有帮助Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:21 PM
「数学天才」陶哲轩:GPT-4无法攻克一个未解决的数学问题,但对工作有帮助Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:21 PM当红炸子鸡ChatGPT,也成为数学天才陶哲轩的研究工具了。近日,他在网上称自己发现了一些ChatGPT的小用例。首先,它很擅长解析代码格式的文档(在这种情况下是#arXiv搜索的API),然后返回一个正确格式的代码查询(后来它还提供了一些工作的python代码,以我要求的方式调用这个API,尽管我不得不手动安装一个包来使它运行)。其次,我让它想出一些,聪明的学生在本科线性代数课上可能会问的问题(为此我提供了一些样本题目),它给出了一些很好的例子,让我对课程可能方向,以及潜在的作业问题有所启发。
 微软 Bing Chat 聊天机器人已升级使用最新 OpenAI GPT-4 技术Apr 12, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
微软 Bing Chat 聊天机器人已升级使用最新 OpenAI GPT-4 技术Apr 12, 2023 pm 10:58 PM3 月 15 日消息,今天 OpenAI 发布了全新的 GPT-4 大型语言模型,随后微软官方宣布,Bing Chat 此前已经升级使用 OpenAI 的 GPT-4 技术。微软公司副总裁兼消费者首席营销官 Yusuf Mehdi 确认 Bing Chat 聊天机器人 AI 已经在 GPT-4 上运行,ChatGPT 基于最新版本 GPT-4,由 OpenAI 开发 。微软 Bing 博客网站上的一篇帖子进一步证实了这一消息。微软表示,如果用户在过去五周内的任何时间使用过新的 Bing 预览版,
 GPT-4的早期实验,通用人工智能的火花Apr 07, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
GPT-4的早期实验,通用人工智能的火花Apr 07, 2023 pm 08:01 PM最近,微软发布了一个长达154页的论文名称为《通用人工智能的火花,GPT-4的早期实验》。文章的主要观点是虽然GPT-4还不完整,但是已经可以被视为,一个通用人工智能的早期版本。由于全文将近7万字,本篇将论文的内容做了一下精炼和解读,有兴趣可阅读原文 https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.12712.pdf来自微软的科学家们认为,GPT-4的智能水平已经非常接近于人类的水平,而且远超之前的诸如先前ChatGPT用的GPT-3.5这样的模型,可以将GPT-4视为通用人工智能系统,也


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version







