Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to use Java multi-threading tool CompletableFuture
How to use Java multi-threading tool CompletableFuture
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-04-29 08:34:152074browse
Preface
Problems with Future
When writing a multi-threaded program, you can use Future to get the result from an asynchronous thread. However, you will find some problems during use:
If you want to perform further operations on the results of Future, you need to block the current thread
Multiple Futures cannot be executed in a chain. The result of each Future is independent. It is expected to do another asynchronous thing to the result of a Future;
There is no exception handling strategy , if Future execution fails, you need to manually capture
CompletableFuture came into being
In order to solve the Future problem, JDK provided us with a useful one in 1.8 Tool class CompletableFuture;
It implements the Future and CompletionStage interfaces and provides corresponding processing methods for the shortcomings of Future.
After the asynchronous thread execution ends, our new processing logic can be automatically called back without blocking.
Can orchestrate multiple asynchronous tasks. Combination or sorting
Exception handling
The core idea of CompletableFuture is that each asynchronous task can be regarded as a step (CompletionStage), and then Other asynchronous tasks can do what they want to do based on this step.
CompletionStage defines many step processing methods, which are very powerful. Here are only some methods commonly used in daily life for your reference.
Usage
Basic usage-submit asynchronous task
Simple usage
Asynchronous execution, no result required:
// 可以执行Executors异步执行,如果不指定,默认使用ForkJoinPool
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> System.out.println("Hello CompletableFuture!"));Asynchronous Execute and return the result at the same time:
// 同样可以指定线程池 CompletableFuture<String> stringCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello CompletableFuture!"); System.out.println(stringCompletableFuture.get());
Process the result of the previous asynchronous task
thenRun: No need for the result of the previous step, directly perform the new operation
thenAccept: Get the content of the previous asynchronous processing and perform new operations
thenApply: Get the content of the previous step and then generate new content
Anything with the Async suffix means that the new processing operation is still asynchronous. Async operations can specify Executors for processing
// Demo
CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello CompletableFuture!")
// 针对上一步的结果做处理,产生新的结果
.thenApplyAsync(s -> s.toUpperCase())
// 针对上一步的结果做处理,不返回结果
.thenAcceptAsync(s -> System.out.println(s))
// 不需要上一步返回的结果,直接进行操作
.thenRunAsync(() -> System.out.println("end"));
;Select the two results-acceptEither
When we have two callbacks processing When , any completion can be used, and there is no relationship between the two results, then use acceptEither.
Whoever completes the execution of the two asynchronous threads first will use whose result, the same is true for other types of methods.
 ##
##
// 返回abc
CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
SleepUtils.sleep(100);
return "Hello CompletableFuture!";
})
.acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "abc"), new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
// 返回Hello CompletableFuture!
CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello CompletableFuture!")
.acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
SleepUtils.sleep(100);
return "abc";
}), new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
});Combine the two results-thenCombine, thenAcceptBoth
thenCombine
When we have two CompletionStages, we need to integrate the results of the two and then calculate a new result.- thenCompose processes the result of the previous CompletionStage and returns the result, and the return type must be CompletionStage.
- thenCombine gets the result of the first CompletionStage, then gets the current CompletionStage, and processes the results of the two.
CompletableFuture<Integer> heightAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 172);
CompletableFuture<Double> weightAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 65)
.thenCombine(heightAsync, new BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Double>() {
@Override
public Double apply(Integer wight, Integer height) {
return wight * 10000.0 / (height * height);
}
})
;
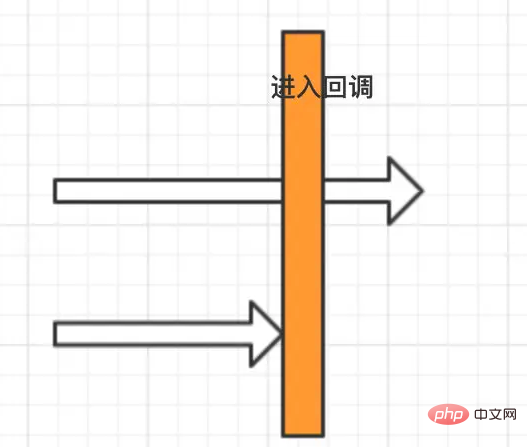
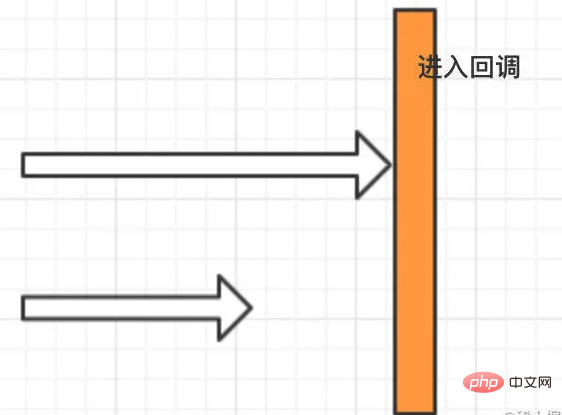
thenAcceptBoth
Requires the results of two asynchronous CompletableFutures. Only when both are completed will the thenAcceptBoth callback be entered.
// thenAcceptBoth案例:
CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello CompletableFuture!")
.thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "abc"), new BiConsumer<String, String>() {
// 参数一为我们刚开始运行时的CompletableStage,新传入的作为第二个参数
@Override
public void accept(String s, String s2) {
System.out.println("param1=" + s + ", param2=" + s2);
}
});
// 结果:param1=Hello CompletableFuture!, param2=abcException handlingWhen we use CompleteFuture to make chain calls, in multiple asynchronous callbacks, If there is a problem with one execution, all subsequent callbacks will stop, so an exception handling strategy is needed.
exceptionally
exceptionally means that when an error occurs, it gives us the opportunity to recover and customize the return content. CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
throw new RuntimeException("发生错误");
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
log.error("调用错误 {}", throwable.getMessage(), throwable);
return "异常处理内容";
});
handle
exceptionally is executed only when an exception occurs, while handle is executed regardless of whether an error occurs.CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "abc";
})
.handle((r,err) -> {
log.error("调用错误 {}", err.getMessage(), err);
// 对结果做额外的处理
return r;
})
;CaseA large number of users send text messages|MessagesThe requirement is to notify users with specific conditions in a table via text messages, but there are millions of text message users , if single-threaded reading is used, the reading efficiency will be very slow. At this time, you can consider using multi-threading to read; 1. Split the reading task into multiple different subtasks and specify the offset and number of reads // 假设有500万条记录
long recordCount = 500 * 10000;
int subTaskRecordCount = 10000;
// 对记录进行分片
List<Map> subTaskList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < recordCount / 500; i++) {
// 如果子任务结构复杂,建议使用对象
HashMap<String, Integer> subTask = new HashMap<>();
subTask.put("index", i);
subTask.put("offset", i * subTaskRecordCount);
subTask.put("count", subTaskRecordCount);
subTaskList.add(subTask);
}2. Use multi-threading for batch reading // 进行subTask批量处理,拆分为不同的任务
subTaskList.stream()
.map(subTask -> CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
// 读取数据,然后处理
// dataTunel.read(subTask);
},excuturs)) // 使用应用的通用任务线程池
.map(c -> ((CompletableFuture<?>) c).join());3. Perform business logic processing, or directly perform business logic processing after reading;
并发获取商品不同信息
在系统拆分比较细的时候,价格,优惠券,库存,商品详情等信息分散在不同的系统中,有时候需要同时获取商品的所有信息, 有时候可能只需要获取商品的部分信息。
当然问题点在于要调用多个不同的系统,需要将RT降低下来,那么需要进行并发调用;
List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Object> result = taskList.stream()
.map(task -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
// handlerMap.get(task).query();
return "";
}, executorService))
.map(c -> c.join())
.collect(Collectors.toList());问题
thenRun和thenRunAsync有什么区别
如果不使用传入的线程池,大家用默认的线程池ForkJoinPool
thenRun用的默认和上一个任务使用相同的线程池
thenRunAsync在执行新的任务的时候可以接受传入一个新的线程池,使用新的线程池执行任务;
handle和exceptional有什么区别
exceptionally是只有发生异常时才会执行,而handle则是不管是否发生错误都会执行。
The above is the detailed content of How to use Java multi-threading tool CompletableFuture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

