Home >Java >javaTutorial >Java blocking queue BlockingQueue instance analysis
Java blocking queue BlockingQueue instance analysis
- 王林forward
- 2023-04-25 15:13:151309browse
Queue type
Unbounded queue No capacity limit, only changes with storage
Bounded queue Defines the maximum capacity
All operations that add elements to the infinite queue will never block (also thread-safe), so It can grow to very large capacities. Using an infinite blocking queue BlockingQueue The most important thing when designing a producer-consumer model is that the consumer should be able to consume messages as fast as the producer adds messages to the queue. Otherwise, there may be insufficient memory and an OutOfMemory exception may be thrown.
Data structure
1. Usually implemented using linked lists or arrays
2. Generally with FIFO (first in, first out) Feature, it can also be designed as a double-ended queue
3. The main operations of the queue:Entering and dequeuing
Blocking QueueBlockingQueue
Definition: In thread communication, at any time, no matter how high the concurrency is, on a single JVM, only one thread can always queue or enqueue the queue at the same time. Dequeue operation. BlockingQueue can be shared between threads without any explicit synchronization
Types of blocking queues:
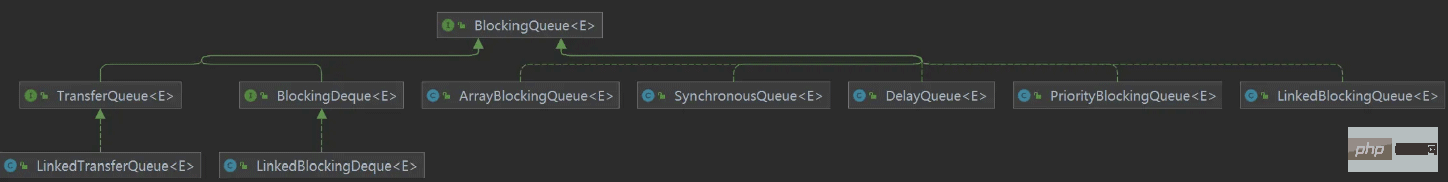
In JAVA Application scenarios: Thread pool, SpringCloud-Eureka three-level cache, Nacos, MQ, Netty, etc.
Common blocking queues
ArrayBlockingQueue: Bounded queue supported by array
Application scenario: There are many applications and producer-consumer models in the thread pool
Working principle: Based on ReentrantLock to ensure thread safety, and based on Condition to achieve blocking when the queue is full
LinkedBlockingQueue: Unbounded queue based on linked list (theoretically bounded)
##PriorityBlockingQueue: By Unbounded priority queue supported by the priority heap
DelayQueue: A time-based scheduling queue supported by the priority heap, internally implemented based on the unbounded queue PriorityQueue, and Array-based expansion implementation of unbounded queue
Instructions for use: The objects added to the queue must implement the Delayed interface, and Delayed is integrated from the Comparable interface
Application scenarios: Selling movie tickets, etc.
- ## Working principle:
The queue will be prioritized according to time Sort. Delay class thread pool cycle execution.
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<> (666);
BlockingQueue API
| add() | |
|---|---|
| put() | |
| offer() | |
| offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | |
| take() | |
|---|---|
| poll (long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | |
The above is the detailed content of Java blocking queue BlockingQueue instance analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- How to set margins for buttons inside a LinearLayout programmatically?
- Why and How Should You Synchronize on String Objects in Java?
- How Can I Customize Input Tokenization in Java Using `Scanner.useDelimiter()`?
- How Can I Dynamically Find All Subclasses of a Base Class in Java at Runtime?
- How Can I Format Java 8's LocalDate with Jackson Without Annotations?

